Abstract
Mercury distribution in pregnant mice, subcutaneously injected with 1.5 or 15.0 μmol/kg of methylmercury chloride (MeHg) and 0, 1.5 or 15.0 μmol/kg of sodium selenite, was investigated.
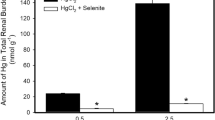
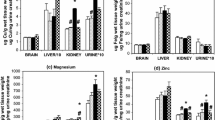
Selenite increased the retention of mercury in maternal brain in every combination of doses. Selenite also increased mercury concentrations in maternal blood except one combination (MeHg 1.5; selenite 1.5 μmol/kg), and the increased mercury was partitioned to red blood cells. The increased mercury retention by selenite was also found in fetal brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, L. W., Reuhl, K. R., Spyker, J. M.: Ultrastructural study of latent effects of methylmercury on nervous system after prenatal exposure. Environ. Res. 13, 171–185 (1977)
Iijima, S., Tohyama, C., Lu, C-v, Matsumoto, N.: Placental transfer and body distribution of methylmercury and selenium in pregnant mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 44, 143–146 (1978)
Magos, L.: Selective atomic-absorption determination of inorganic mercury and methylmercury in undigested biological samples. Analyst 96, 847–853 (1971)
Magos, L., Webb, M.: The effect of selenium on the brain uptake of methylmercury. Arch. Toxicol. 38, 201–207 (1977)
Nobunaga, T., Satoh, H., Suzuki, T.: Effects of sodium selenite on methylmercury embryotoxicity and teratogenicity in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 47, 79–88 (1979)
Ohi, G., Nishigaki, S., Seki, H., Tamura, Y., Maki, T., Konno, H., Ochiai, S., Yamada, H., Shimamura, Y., Mizoguchi, I., Yagu, H.: Efficacy of selenium in tuna and selenite in modifying methylmercury intoxication. Environ. Res. 12, 49–58 (1976)
Satoh, H.: Residual blood volumes in organs of pregnant mice and fetuses. Tohoku. J. Exp. Med. 128 (in press, 1979)
Spyker, J. M., Sparber, S. B., Goldberg, A. M.: Subtle consequences of methylmercury exposure; behavioral deviations in offspring from treated mothers. Science 177, 621–623 (1972)
Su, M-Q., Okita, G. T.: Behavioral effects on the progeny of mice treated with methylmercury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 38, 195–205 (1976)
Wannag, A.: The importance of organ blood mercury when comparing foetal and maternal organ distribution of mercury after methyl mercury exposure. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 38, 289–298 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satoh, H., Suzuki, T. Effects of sodium selenite on methylmercury distribution in mice of late gestational period. Arch Toxicol 42, 275–279 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334841
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334841