Abstract
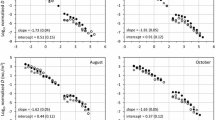
We characterized the size structure of virtually the entire metazoan community in a fourth order, sandybottomed Piedmont stream during late summer. Our study, the first to sample across all habitat types and sizes of metazoans in an aquatic ecosystem, indicates that at the community level, stream size spectra may be bimodal for the benthos or trimodal when fish are included. Animals spanning 10 orders of magnitude in dry mass (from gastrotrichs to fish) were quantitatively collected from nine habitat types. The bimodal benthic size spectrum was characterized by a meiofaunal component (mostly oligochaetes and micro-crustacea) and a macrobenthic component (mostly the introduced asiatic clam, Corbicula fluminea). Insects contributed little to overall standing crop. Size-specific contribution to whole-community metabolism was assessed using allometric equations for respiration, and we found a distinctly bimodal distribution across the entire metazoan size range, with peaks in the meiofaunal and benthic macrofaunal size ranges. Our bimodal benthic size spectrum is similar to that observed for marine benthos but not to other freshwater benthic systems, possibly because the entire range of habitat types and/or animal sizes were not sampled in the latter. Numerous factors may influence size spectra in stream ecosystems, including local geomorphic (habitat) conditions, water level fluctuations, species introductions, and predation processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan JD, Flecker AS (1993) Biodiversity conservation in running waters. BioScience 43: 32–43
Ahrens MA, Peters RH (1991a) Patterns and limitations in limnoplankton size spectra. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48: 1967–1978
Ahrens MA, Peters RH (1991b) Plankton community respiration: relationships with size distribution and lake trophy. Hydrobiol 224: 77–87
Angermeier PL, Smoger RA, Steele SD (1991) An electric seine for collecting fish in streams. N Am J Fish Manage 11: 352–357
Banse K (1982) Mass-scaled rates of respiration and intrinsic growth in very small invertebrates. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 9: 281–297
Banse K, Mosher S (1980) Adult body mass and annual production biomass relationships of field populations. Ecol Monogr 50: 355–379
Benke AC, Van Arsdall TC, Gillespie DM, Parrish FK (1984) Invetebrate productivity in a subtropical blackwater river: the importance of habitat and life history. Ecol Monogr 54: 25–63
Borgmann U (1982) Particle-size-conversion efficiency and total animal production in pelagic ecosystems. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 39: 668–674
Borgmann U (1987) Models of the slope of, and biomass flow up, the biomass size spectrum. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44: 136–140
Boudreau PR, Dickie LM (1992) Biomass spectra of aquatic ecosystems in relation to fisheries yield. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49: 1528–1538
Carlander KD (1977) Handbook of freshwater fishery biology: volume two. Iowa State Univ. Press, Ames, 431 pp
Cattaneo A (1993) Size spectra of benthic communities in Laurentian streams. Can J Fish Aquat Sci (in press)
Cohen RRH, Dresler PV, Phillips EJP, Cory RL (1984) The effect of the Asiatic clam, Corbicula fluminea, on phytoplankton of the Potomac River, Maryland. Limnol Oceanogr 29: 170–180
Cole J, Jovett G, Findlay S (1991) Comparative analyses of ecosystems: patterns, mechanisms, and theories. Springer, New York, 375 pp
Coull BC (1990) Are members of the meiofauna food for higher trophic levels? Trans Am Microsc Soc 109: 233–246
Diamond J, Case TJ (1986) Community ecology. Harper & Row, New York, 665 pp
Duarte CM, Agusti S, Peters RH (1987) An upper limit to the abundance of aquatic organisms. Oecologia 74: 272–276
Fisher SG, Grimm NB (1991) Streams and disturbance: Are crossecosystem comparisons useful? In: Cole J, Lovett G, Findlay S (eds) Comparative analyses of ecosystems: patterns, mechanisms, and theories, Springer, New York, NY. pp 196–221
Gee JM (1989) An ecological and economic review of meiofauna as food for fish. Zool J Linn Soc 96: 243–261
Gerlach SA, Hahn AE, Schrage M (1985) Size spectra of benthic biomass and metabolism. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 26: 161–173
Hanson JM (1990) Macroinvertebrate size-distributions of two contrasting freshwater macrophyte communities. Freshwater Biol 24: 481–491
Hanson JM, Prepas EE, Mackay WC (1989) Size distribution of the macroinvertebrate community in a freshwater lake. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46: 1510–1519
Hornbach DJ (1992) Life history traits of a riverine population of the Asiatic clam Corbicula fluminea. Am Midl Nat 127: 248–257
Kerr SR (1974) Theory of size distribution in ecological communities. J Fish Res Bd Can 31: 1859–1862
Lauritsen DD (1986) Filter-feeding in Corbicula fluminea and its effect on seston removal. J N Am Benthol Soc 5: 165–172
Mattice JS (1979) Interactions of Corbicula sp. with power plants. In: Britton J (ed) Proc. 1st Internat. Corbicula Symposium, Texas Christian Univ., Ft. Worth, pp 119–138
McMahon RF (1982) The occurrence and spread of the introduced Asiatic freshwater clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller), in North America: 1924–1982. The Nautilus 96: 134–141
McMahon RF (1983) Ecology of an invasive pest bivalve, Corbicula. In: Russell-Hunter WD (ed) The mollusca, vol. 6: ecology. Academic Press, NY, pp 505–561
Meyer E (1989) The relationship between body length parameters and dry mass in running water invertebrates. Arch Hydrobiol 117: 191–203
Meyer JL (1990) A blackwater perspective on riverine ecosystems. BioScience 40: 643–650
Morin A, Nadon D (1991) Size distribution of epilithic lotic invertebrates and implications for community metabolism. J N Am Benthol Soc 10: 300–308
Neves RJ, Odum MC (1989) Muskrat predation on endangered freshwater mussels in Virginia. J Wildl Manage 53: 934–941
O'Doherty EC (1988) The ecology of meiofauna in an Appalachian headwater stream. PhD Thesis, University of Georgia, 113 pp
Palmer MA (1990) Temporal and spatial dynamics of meiofauna within the hyporheic zone of Goose Creek, Virginia. J N Am Benthol Soc 9: 17–25
Palmer MA (1992) Incorporating lotic meiofauna into our under-standing of faunal transport processes. Limnol Oceanogr 37: 329–341
Palmer MA, Arensburger P, Martin AP (1992a) The role of patch dynamics in explaining the population persistence of hyporheic biota: a numerical simulation model. In: Stanford JA, Simons JJ (eds) Proceedings of the first international conference on ground water ecology, American Water Resources Association, Bethesda, MD, pp 119–131
Palmer MA, Bely AE, Berg KE (1992b) Response of invertebrates to lotic disturbance: a test of the hyporheic refuge hypothesis. Oecologia 89: 182–194
Peters RH (1983a) Size structure of the plankton community along the trophic gradient of Lake Memphremagog. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 40: 1770–1778
Peters RH (1983b) The ecological implications of body size. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 329 pp
Peters RH, Wassenberg K (1983) The effect of body size on animal abundance. Oecologia 60: 89–96
Poff NL, Ward JV (1989) Implications of streamflow variability and predictability for lotic comimunity structure: A regional analysis of streamflow patterns. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46: 1805–1818
Resh VH, Brown AV, Covich AP, Gurtz ME, Li HW, Minshall GW, Reice SR, Sheldon AL, Wallace JB, Wissmar R (1988) The role of disturbance in stream ecology. J N Am Benthol Soc 7: 433–455
Robinson WR, Peters RH, Zimmerman J (1983) Body size and temperature effects on metabolic rates of organisms. Can J Zool 61: 281–288
Schoener TW (1986) Overview: kinds of ecological communities — ecology becomes pluralistic. In: Diamond J, Case TJ (eds) Community ecology, Harper & Row Publ., NY, pp 467–479
Schwinghammer P (1981) Characteristic size distributions of integral benthic communities. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 38: 1255–1263
Schwinghammer P (1983) Generating ecological hypotheses from biomass spectra using causal analysis: a benthic example. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 13: 151–166
Sheldon RW, Parsons JR (1967) A continuous size spectrum for particulate matter in the sea. J Fish Res Bd Can 24: 909–915
Sheldon RW, Prahash A, Sutcliffe WH (1972) The size distribution of particles in the ocean. Limnol Oceanogr 17: 327–339
Sheldon RW, Sutcliffe WH, Paranjape MA (1977) Structure of pelagic food chains and relationship between plankton and fish production. J Fish Res Bd Canada 34: 2344–2353
Smock LA (1980) Relationships between body size and biomass of aquatic insects. Freshwat Biol 10: 375–383
Sprules WG, Casselman JM, Shuter BJ (1983) Size distribution of pelagic particles in lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 40: 1761–1769
Sprules WG, Munawar M (1986) Plankton size spectra in relation to ecosystem productivity, size, and perturbation. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 43: 1789–1794
Strayer D (1984) The benthic micrometazoans of Mirror Lake, New Hampshire. PhD Thesis, Cornell Univ., Ithaca, NY, 348 pp
Strayer D (1986) The size structure of a lacustrine zoobenthic community. Oecologia 69: 513–516
Strayer D (1991) Perspectives on the size structure of lacustrine zoobenthos, its causes, and its consequences. J N Am Benthol Soc 10: 210–221
Strayer D, Likens GE (1986) An energy budget for the zoobenthos of Mirror Lake, New Hampshire. Ecology 67: 303–313
Tokeshi M (1990) Density-body size allometry does not exist in a chironomid community on Myriophyllum. Freshwat Biol 24: 613–618
Vadas RL Jr (1990) The importance of omnivory and predator regulation of prey in freshwater fish assemblages in North America. Env Biol Fishes 27: 285–302
Vadas RL Jr (1991) Seasonal habitat use, species associations, and assemblage structure of forage fishes in Goose Creek, northern Virginia. II. Macrohabitat patterns. J Freshwat Ecol 6: 403–417
Vadas RL Jr (1992) The ichthyofauna of Goose Creek, Potomac drainage, Virginia. Maryland Natur 36(1–2): 5–20
Ward JV (1992) Aquatic insect ecology. 1. Biology and habitat. John Wiley & Sons, NY, 438 pp
Warwick RM (1984) Species size distributions in marine benthic communities. Oecologia (Berlin) 61: 32–41
Warwick RM, Joint IR (1987) The size distribution of organisms in the Celtic Sea: from bacteria to metazoa. Oecologia 73: 185–191
Wiens JA (1981) Single-sample surveys of communities: are the revealed patterns real? Am Nat 117: 90–98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poff, N.L., Palmer, M.A., Angermeier, P.L. et al. Size structure of the metazoan community in a Piedmont stream. Oecologia 95, 202–209 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323491
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323491