Abstract
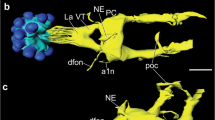
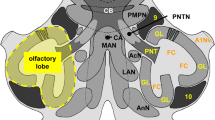
Several lines of evidence suggest that pigment-dispersing hormone-immunoreactive neurons with ramifications in the accessory medulla are involved in the circadian system of insects. The present study provides a detailed analysis of the anatomical and neurochemical organization of the accessory medulla in the brain of the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. We show that the accessory medulla is compartmentalized into central dense nodular neuropil surrounded by a shell of coarse fibers. It is innervated by neurons immunoreactive to antisera against serotonin and the neuropeptides allatostatin 7, allatotropin, corazonin, gastrin/cholecystokinin, FMRFamide, leucokinin I, and pigment-dispersing hormone. Some of the immunostained neurons appear to be local neurons of the accessory medulla, whereas others connect this neuropil to various brain areas, including the lamina, the contralateral optic lobe, the posterior optic tubercles, and the superior protocerebrum. Double-label experiments show the colocalization of immunoreactivity against pigment-dispersing hormone with compounds related to FMRFamide, serotonin, and leucokinin I. The neuronal and neurochemical organization of the accessory medulla is consistent with the current hypothesis for a role of this brain area as a circadian pacemaking center in the insect brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers HE, Liou S-Y, Stopa EG, Zoeller RT (1991) Interaction of colocalized neuropeptides: functional significance in the circadian timing system. J Neurosci 11:846–851
Bellés X, Maestro J-L, Piulachs M-D, Johnson AH, Duve H, Thorpe A (1994) Allatostatic neuropeptides from the cockroach Blattella germanica (L.) (Dictyoptera, Blattellidae). Identification, immunolocalization and activity. Regul Pept 53:237–247
Chiba Y, Tomioka K (1987) Insect circadian activity with special reference to the localization of the pacemaker. Zool Sci 4:945–954
Colwell CS, Page TL (1989) The electroretinogram of the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 92:117–123
Colwell CS, Page TL (1990) A circadian rhythm in neural activity can be recorded from the central nervous system of the cockroach. J Comp Physiol [A] 166:643–649
Dircksen H, Zahnow CA, Gaus G, Keller R, Rao KR, Riehm JP (1987) The ultrastructure of nerve endings containing pigment-dispersing hormone (PDH) in crustacean sinus glands: identification by an antiserum against synthetic PDH. Cell Tissue Res 250:377–387
Fleissner G, Fleissner G, Frisch B (1993) A new type of putative non-visual photoreceptors in the optic lobe of beetles. Cell Tissue Res 273:435–445
Füller H, Eckert M, Blechschmidt K (1989) Distribution of GABA-like immunoreactive neurons in the optic lobes of Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 255:225–233
Hagberg M (1986) Ultrastructure and central projections of extraocular photoreceptors in caddisflies (Insecta: Trichoptera). Cell Tissue Res 245:643–648
Helfrich-Förster C, Homberg U (1993) Pigment-dispersing hormone-immunoreactive neurons in the nervous system of wild-type Drosophila melanogaster and of several mutants with altered circadian rhythmicity. J Comp Neurol 337:177–190
Hofbauer A, Buchner E (1989) Does Drosophila have seven eyes? Naturwissenschaften 76:335–336
Holman GM, Cook BJ, Nachman RJ (1986) Isolation, primary structure and synthesis of leucomyosuppressin, and insect neuropeptide that inhibits the spontaneous contractions of the cockroach hindgut. Comp Biochem Physiol [C] 85:329–333
Holman GM, Nachman RJ, Wright MS (1990) Insect neuropeptides. Annu Rev Entomol 35:201–217
Homberg U (1994) Distribution of neurotransmitters in the insect brain. Progress in Zoology 40. Fischer, Stuttgart
Homberg U, Würden S, Dircksen H, Rao KR (1991) Comparative anatomy of pigment-dispersing hormone-immunoreactive neurons in the brain of orthopteroid insects. Cell Tissue Res 266:343–357
Katoaka H, Toschi A, Li JP, Carney AL, Schooley DA, Kramer SJ (1989) Identification of an allatotropin from adult Manduca sexta. Science 243:1481–1483
Labhart T, Petzold J (1993) Processing of polarized light information in the visual system of crickets. In: Wiese K, Gribakin FG, Popov AV, Renninger G (eds) Sensory systems in arthropods. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 158–169
Nachman RJ, Holman GM, Cook BJ, Haddon WF, Ling N (1986) Leucosulfakinin II, a blocked sulphated insect neuropeptide with homology to cholecystokinin and gastrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 140:357–364
Nässel DR (1991) Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the insect visual system. Prog Neurobiol 37:179–254
Nässel DR (1993) Neuropeptides in the insect brain: a review. Cell Tissue Res 273:1–29
Nässel DR, Holmquist MH, Hardie RC, Håkanson R, Sundler F (1988) Histamin-like immunoreactivity in photoreceptors of the compound eyes and ocelli of the flies Calliphora erythrocephala and Musca domestica. Cell Tissue Res 253:639–646
Nässel DR, Shiga S, Wikstrand EM, Rao KR (1991) Pigment-dispersing hormone-immunoreactive neurons and their relation to serotonergic neurons in the blowfly and cockroach visual system. Cell Tissue Res 266:511–523
Nässel DR, Cantera R, Karlsson A (1992) Neurons in the cockroach nervous system reacting with antisera to the neuropeptide leucokinin I. J Comp Neurol 322:45–67
Nässel DR, Shiga S, Mohrherr CJ, Rao KR (1993) Pigment-dispersing hormone like peptide in the nervous system of the flies Phormia and Drosophila: immunocytochemistry and partial characterization. J Comp Neurol 331:183–198
Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J, Pittendrigh CS (1968) Central nervous system control of circadian rhythmicity in the cockroach. II. The pathway of light signals that entrain the rhythm. Z Vgl Physiol 58:1–13
O'Donahue T, Bishop JF, Chronwall BM, Groome J, Watson WH III (1984) Characterization and distribution of FMRFamide immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Peptides 5:563–568
Paemen L, Tips A, Schoofs L, Proost P, Van Damme J, De Loof A (1991) Lom-AG-myotropin: A novel myotropic peptide from male accessory glands of Locusta migratoria. Peptides 12:7–10
Paemen L, Schoofs L, De Loof A (1992) Localization of Lom-AG-myotropin I-like substances in the male reproductive and nervous tissue of the locust, Locusta migratoria. Cell Tissue Res 286:91–97
Page TL (1978) Interaction between bilaterally paired components of the cockroach circadian system. J Comp Physiol 124:225–236
Page TL (1983a) Regeneration of the optic tracts and circadian pacemaker activity in the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. J Comp Physiol 152:231–240
Page TL (1983b) Effects of optic-tract regeneration on internal coupling in the circadian system of the cockroach. J Comp Physiol 153:353–363
Page TL (1984) Neural organization of a circadian clock in the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. In: Porter R, Collins GM (eds) Photoperiodic regulation of insect and molluscan hormones. Pitman, London, pp 115–135
Page TL (1987) Serotonin phase-shifts the circadian rhythm of locomotor activity in the cockroach. J Biol Rhythms 2:23–34
Page TL, Caldarola PC, Pittendrigh CS (1977) Mutual entrainment of bilaterally distributed circadian pacemakers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 58:14–46
Petri B, Stengl M (1994) The role of neuropeptides in the generation of circadian rhythms in the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. In: Elsner N, Breer H (eds) Göttingen neurobiology report 1994. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 314
Predel R, Agricola H, Linde D, Wollweber L, Veenstra JA, Penzlin H (1994) The insect neuropeptide corazonin: physiological and immunocytochemical studies in Blattariae. Zoology 98:35–49
Rao RK, Riehm JP (1993) Pigment-dispersing hormones. Ann NY Acad Sci 680:78–88
Reischig T, Stengl M (1995) Light- and electron microscopic analysis of the accessory medulla of the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. In: Elsner N, Menzel R (eds) Göttingen neurobiology report 1995. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 252
Richardson KC, Jarett I, Finke EH (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35:313–323
Roberts SK (1965) Photoperception and entrainment of cockroach activity rhythms. Science 148:958–959
Roberts SK (1974) Circadian rhythm in cockroaches. Effects of optic lobe lesions. J Comp Physiol 88:21–30
Schildberger K, Agricola H (1992) Immunocytochemical distribution of allatostatin in the nervous system of the cockroach Periplaneta americana. In: Elsner N, Richter DW (eds) Rhythmogenesis in neurons and networks. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 494
Schulz W-D, Schlüter U, Seifert G (1984) Extraocular photoreceptors in the brain of Epilachna varivestis (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae). Cell Tissue Res 236:317–320
Sokolove PG (1975) Localization of the optic lobe circadian pacemaker with microlesions. Brain Res 87:13–21
Sossin WS, Fisher JM, Scheller RH (1989) Cellular and molecular biology of neuropeptide processing and packaging. Neuron 2:1407–1417
Stay B, Chan KK, Woodhead AP (1992) Allatostatin-immunoreactive neurons projecting to the corpora allata of adult Diploptera punctata. Cell Tissue Res 270:15–23
Stengl M, Homberg U (1993) Pigment-dispersing hormone-immunoreactive neurons as possible candidates for the circadian pacemaker in orthopteroid insects. In: Elsner N, Richter DW (eds) Rhythmogenesis in neurons and networks. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 89
Stengl M, Homberg U (1994) Pigment dispersing hormone-immunoreactive neurons in the cockroach Leucophaea maderae share properties with circadian pacemaker neurons. J Comp Physiol [A] 175:203–213
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry. Wiley, New York
Strausfeld NJ (1976) Atlas of an insect brain. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Tobe SS, Stay B (1985) Structure and regulation of the corpus allatum. Adv Insect Physiol 18:305–432
Veenstra JA (1989) Isolation and structure of corazonin, a cardioactive peptide from the American cockroach. FEBS Lett 250:231–234
Veenstra JA (1991) Presence of corazonin in three insect species, and isolation and identification of [His7]-corazonin from Schistocerca gregaria. Peptides 12:1285–1289
Veenstra JA, Davis NT (1993) Localization of corazonin in the nervous system of the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 274:57–64
Veenstra JA, Hagedorn HH (1993) Sensitive enzyme immunoassay for Manduca allatotropin and the existence of an allatotropin-immunoreactive peptide in Periplaneta americana. Arch Insect Biochem 23:99–109
Wallace JA, Petrusz P, Lauder JM (1982) Serotonin immunocytochemistry in the adult and developing rat brain: methodological and pharmacological considerations. Brain Res Bull 9:117–129
Weaver RJ, Freeman ZA, Pickering MG, Edwards JP (1994) Identification of two allatostatins from the CNS of the cockroach Periplaneta americana: novel members of a family of neuropeptide inhibitors of insect juvenile hormone biosynthesis. Comp Biochem Physiol [C] 107:119–127
Wills SA, Page TL, Colwell CS (1985) Circadian rhythms in the electroretinogram of the cockroach. J Biol Rhythms 15: 25–37
Woodhead AP, Stay B, Seidel SL, Khan MA, Tobe SS (1989) Primary structure of four allatostatins: neuropeptide inhibitors of juvenile hormone synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5997–6001
Woodhead AP, Khan MA, Stay B, Tobe SS (1994) Two new allatostatins from the brains of Diploptera punctata. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 24:257–263
Würden S, Homberg U (1992) Colocalization of peptide immunoreactivities in the lamina and accessory medulla of the locust Schistocerca gregaria. In: Elsner N, Richter D (eds) Rhythmogenesis in neurons and networks. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 307
Würden S, Homberg U (1993) A simple method for immunofluorescent double staining with primary antisera from the same species. J Histochem Cytochem 41:627–630
Würden S, Homberg U (1994) Anatomy and physiology of neurons innervating the accessory medulla in the brain of the locust Schistocerca gregaria. In: Elsner N, Breer H (eds) Göttingen neurobiology report 1994. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 463
Würden S, Homberg U (1995) Immunocytochemical mapping of serotonin and neuropeptides in the accessory medulla of the locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J Comp Neurol (in press)
Žitňan D, Sehnal F, Bryant PJ (1993) Neurons producing specific neuropeptides in the central nervous system of normal and pupariation-delayed Drosophila. Dev Biol 156:117–135
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petri, B., Stengl, M., Würden, S. et al. Immunocytochemical characterization of the accessory medulla in the cockroach Leucophaea maderae . Cell Tissue Res 282, 3–19 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319128
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319128