Abstract
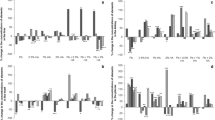
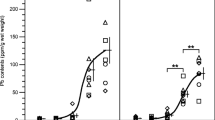
Because there were tendencies for normalization of lead-sensitive parameters in animals with low lead burdens, these phenomena were examined in vivo and in vitro. Lead inhibited the enzyme delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALA-D) dose-dependently and not competitively or irreversibly competitively in vitro. The lead-blocked portion of ALA-D could be reactivated at least partially by glutathione. This part was higher in lead-contaminated animals than in the control group, though there were no significant differences in the free part of the enzyme. The free part of the enzyme was normalized by a resynthesis of the molecule. Therefore the determination of the lead-blocked part and the part reactivated by glutathione, seemed more suitable for determining the chronic lead burden than the measurement of a possible adapted total activity of ALA-D.
Zusammenfassung
Weil sich in Tierversuchen bei niedriger Bleibelastung Tendenzen zur Normalisierung der bleiempfindlichen Parameter zeigten, wurde dieser als Adaptation interpretierte Vorgang in vivo und in vitro geprüft. Blei hemmte in vitro die Delta-Aminolävulinsäure-Dehydratase (ALA-D) dosisabhängig und nicht kompetitiv oder irreversibel kompetitiv. Der durch Blei blockierte Anteil der ALA-D war bei vermehrt bleikontaminierten Versuchstieren höher als bei Kontrolltieren. Dagegen bestanden im freien Anteil keine signifikanten Unterschiede zwischen den beiden Gruppen. Die Normalisierung des freien Anteils erfolgte über eine Neusynthese des Enzyms. Somit erscheint die Messung des durch Blei inaktivierten, durch Glutathion reaktivierten Anteils dieses Fermentes eher geeignet, eine chronische Bleieinwirkung festzustellen, als die Messung der möglicherweise wieder normalisierten ALA-D-Aktivität.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonsignore, D.: Biochemical approach to the physiopathology of porphyrin metabolism in lead poisoning. Lav. umano 13, 606–617 (1961)
Fassbender, C. P.: Versuche zur Enzymdiagnostik der subklinischen Bleivergiftung bei Schafen. Inaug.-Diss., Hannover 1973
Haas, T., Mache, W., Schaller, K.-H., Mache, K., Klavis, G., Stumpf, R.: Zur Bestimmung der Delta-Aminolävulinsäure-Dehydratase und ihrer diagnostischen Wertigkeit. Int. Arch. Arbeitsmed. 30, 87–104 (1972)
Hapke, H.-J.: Subklinische Bleivergiftung bei Schafen. International Symposium “Health Aspects of Environmental Pollution with Lead”. Amsterdam 1972
Hernberg, S., Nikkanen, J.: Enzyme inhibition by lead under normal urban conditions. Lancet 1970 I, 63 (1970a)
Hernberg, S., Nikkanen, J., Tola, S., Valkonen, S., Nordman, C. H.: Erythrocyte ALA-dehydratase as a test of lead exposure. Int. Conf. Chem. Poll. Hum. Ecol., Prague 1970 b
Lehnert, H.: Biokybernetische Probleme der Bleibelastung. Referat VDI-Kommission Reinhaltung der Luft, 19. April 1971, Düsseldorf (1971)
Lichtmann, H. C., Feldmann, F.: In vitro pyrrole and porphyrin synthesis in lead poisoning and iron deficiency. J. clin. Invest. 42, 830 (1963)
Prigge, E.: Versuche zur Frühdiagnose der Bleivergiftung bei Schafen. Inaug.-Diss., Hannover 1971
Prigge, E., Hapke, H.-J.: Die Feststellung einer experimentellen subklinischen Bleivergiftung bei Schafen. Dtsch. tierärztl. Wschr. 79, 475–482 (1971)
Sterner, W.: Die Haaranalyse — eine besonders für epidemiologische Untersuchungen geeignete Methode zur Feststellung von Schwermetallbelastungen bei Mensch und Tier. Arch. Lebensmitt.-Hyg. 10, 209–213 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hapke, H.J., Prigge, E. Interactions of lead and glutathione with delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase. Arch Toxicol 31, 153–161 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310393
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310393