Abstract
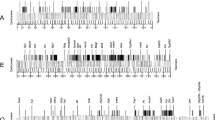
The genomic distribution of elements of the copia, 412, B 104, mdg 1, mdg 4 and 1731 transposon families was compared by the Southern technique in DNA preparations extracted from brains, salivary glands and adult flies of two related Drosophila lines. The copia, 412 and mdg 1 sequences were also probed in DNA from sperm, embryos, and 1st and 2nd instar larvae. The homogeneity of the patterns observed shows that somatic transposition is unlikely to occur frequently. A correlation between mobility and the euchromatic or heterochromatic location of transposable elements is discussed. In addition, an explanation of the variable band intensities of transposable elements in Southern autoradiographs is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananiev EV, Ilyin YV (1981) A comparative study of the location of mobile dispersed genes in salivary gland and midgut polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 82:429–435
Ananiev EV, Gvozdey VA, Ilyin YV, Tchurikov NA, Georgiev GP (1978) Reiterated genes with varing location in intercalary heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma 70:1–17
Ananiev EV, Barsky VE, Ilyin YV, Ryzic MV (1984) The arrangement of transposable elements in the polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 90:366–377
Bayev Jr AA, Lyubomirskaya NV, Dzhumagalier EB, Ananiev EV, Amiantova IG, Ilyin YV (1984) Structural organization of transposable element mdg 4 from Drosophila melanogaster and a nucleotide sequence of its long terminal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res 12:3707–3723
Biémont C, Aouar A (1987) Copy number dependent transpositions and exisions of the mdg 1 mobile element in inbred lines of Drosophila melanogaster. Heredity 58:39–47
Biémont C, Aouar A, Arnault C (1987) Genome reshuffling of the copia element in an inbred line of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 329:742–744
Bonaldo MF, Santelli RV, Lara FJS (1979) The transcript from a DNA puff of Rhynosciara and its migration to the cytoplasm. Cell 17:827–833
Bryan GJ, Jacobson JW, Hartl DL (1987) Heritable somatic excision of a Drosophila transposon. Science 235:1636–1638
Couderec JL, Sobrier ML, Giraud G, Becker JL, Dasitugue B (1983) Actin gene expression is modulated by Ectysterone in a Drosophila cell line. J Mol Biol 164:419–430
Crozatier M, Vaury C, Busseau I, Pelisson A, Bucheton A (1988) Structure and genomic organization of I elements involved in I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 16:9199–9213
Dickson E, Boyd JB, Laird CD (1971) Sequence diversity of polytene chromosome DNA from Drosophila hydei. J Mol Biol 61:615–627
Di Nocera PP, Dawid IB (1983) Interdigitated arrangement of two oligo(A)-terminated DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res 11:5475–5482
Di Nocera PP, Graziani F, Lavorgna G (1986) Genomic and structural organization of Drosophila melanogaster. G elements. Nucleic Acids Res 14:675–691
Dolfini S (1971) Karyotype polymorphism in a cell population of Drosophila melanogaster culture in vitro. Chromosoma 33:196–208
Echalier G, Ohanessian A (1969) Isolementen cultures in vitro, de lignees cellulaires diploides de Drosophila melanogaster. CR Acad Sci Paris 268:1771–1773
Emmons SW, Yesner L (1984) High-frequency excision of transposable element Tc1 in the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is limited to somatic cells. Cell 36:599–609
Finnegan DJ (1985) Transposable elements in eukaryotes. Int Rev Cytol 93:281–326
Finnegan DJ, Fawcett DA (1986) Transposable elements in Drosophila melanogaster. In: Oxford surveys of eukaryotic genes, vol 3, pp 24–62
Finnegan DJ, Rubin GM, Young MW, Hogness DS (1978) Repeated gene families in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 42:1053–1063
Gall JG, Cohen EH, Polan ML (1971) Repetitive DNA sequences in Drosophila. Chromosoma 33:319–344
Green MM (1988) Mobile DNA elements and spontaneous gene mutation. In: Lambert ME, McDonald JF, Weinstein IB (eds) Eucaryotic transposable elements as mutagenic agents. 30th Banbury report, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, pp 41–50
Hennig W (1967) Untersuchungen zur Struktur und Funktion des Lampenbursten-Y-Chromosoms in der Spermatogenese von Drosophila. Chromosoma 22:294–357
Holden JJ, Ashburner M (1978) Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. Chromosoma 68:2051–2055
Ilyin YV, Tchurikov NA, Ananiev EV, Ryskov AP, Yenikopolov GN, Limborska SA, Maleeva NE, Gvozdev VA, Georgiev GP (1978) Studies on the DNA fragments of mammals and Drosophila containing structural genes and adjacent sequences. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 42:959–969
Ilyin YV, Chmellauskaite VG, Ananlev EV, Lyubomirskaya NV, Kulguskin VV, Bayev Jr AA, Georgiev GP (1980) Mobile dispersed genetic element mdg 1 of Drosophila melanogaster: structural organization. Nucleic Acids Res 8:5333–5346
Junakovic N, Angelucci V (1986) Polymorphisms in the genomic distribution of copia-like elements in related laboratory stocks of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Evol 24:83–88
Junakovic N, Caneva R, Ballario P (1984) Genomic distribution of copia-like elements in laboratory stocks of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 90:378–382
Junakovic N, Di Franco C, Barsanti P, Palumbo G (1986) Transposition of copia-like nomadic elements can be induced by heatshock. J Mol Evol 24:89–92
Junakovic N, Di Franco C, Best-Belpomme M, Echalier G (1988) On the transposition of copia-like nomadic elements in cultured cells of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 98:212–218
Laski FA, Rio DC, Rubin GM (1986) Tissue specificity of Drosophila P element transposition is regulated at the level of mRNA splicing. Cell 44:7–19
Levine M, Garen A, Lepesant JA, Lepesant-Kejzlarova J (1981) Constancy of somatic DNA organization in developmentally regulated regions of the Drosophila genome. Proc Natl Sci USA 78:2417–2421
Loukas M, Kafatos CF (1986) The actin loci in the genus Drosophila: Establishment of chromosomal homologies among distantly related species by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 94:297–308
Miklos GLG, Yamamoto M, Davies J, Pirrotta V (1988) Microcloning reveals a high frequency of repetitive sequences characteristic of chromosome 4 and the beta-heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2051–2055
Peronnet F, Becker LL, Becker J, d'Auriol L, Galibert F, Best-Belpomme M (1986) 1731, a new retrotransposon with hormone modulated expression. Nucleic Acids Res 14:9017–9033
Pierce DA, Luchesi JC (1981) Analysis of a dispersed repetitive DNA sequence in isogenic lines of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 82:471–492
Piñol J, Francino O, Fontdevila A, Cabré O (1988) Rapid isolation of Drosophila high molecular weight DNA to obtain genomic libraries. Nucleic Acids Res 16:2736
Potter SS, Thomas Jr CA (1978) The two-dimensional fractionation of Drosophila DNA. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 42:1023–1031
Potter SS, Brorein Jr WJ, Dunsmuir P, Rubin GM (1979) Transposition of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families in Drosophila. Cell 17:415–427
Richards G (1980) The polytene chromosomes in the fat body nuclei of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 79:241–250
Rubin GM (1983) In: Shapiro JA (ed) Mobile genetic elements. Academic Press, New York, pp 329–361
Scherer G, Tschudi C, Perera J, Delius H, Pirrotta V (1982) B 104, a new dispersed repeated gene family in Drosophila melanogaster and its analogies with retroviruses. J Mol Biol 157:435–451
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Spradling AC, Mahowald AP (1980) Amplification of genes for chorion proteins during oogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1096–1100
Spradling AC, Rubin MG (1981) Drosophila genome organization: conserved and dynamic aspects. Annu Rev Genet 15:219–264
Strobel E, Dunsmuir P, Rubin GM (1979) Polymorphisms in chromosomal location of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families. Cell 17:429–439
Tchurikov NA, Zelentsova ES, Georgiev GP (1980) Clusters containing different mobile dispersed genes in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 8:1243–1258
Tchurikov NA, Ilyin YV, Skryabin KG, Ananiev EV, Bayev Jr AA, Krayev AS, Zelentsova ES, Kulguskin VV, Lyubomirskaya NV, Georgiev GP (1981) General properties of mobile dispersed genetic elements in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 45:655–665
Vaury C, Bucheton A, Pélisson A (1989) The β heterochromatic sequences flanking the I elements are themselves defective transposable elements. Chromosoma 98:215–224
Wensink PC, Tabata D, Pachl C (1979) The clustered and scrambled arrangement of moderately repetitive elements in Drosophila DNA. Cell 18:1231–1246
Young MW, Schwartz HE (1981) Nomadic gene families in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 45:629–640
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Franco, C., Pisano, C., Dimitri, P. et al. Genomic distribution of copia-like transposable elements in somatic tissues and during development of Drosophila melanogaster . Chromosoma 98, 402–410 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292785
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292785