Summary
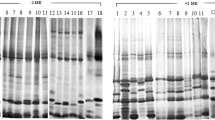
Types representing three subspecies of Oryza sativa, namely, indica, japonica and javanica, and a group of intermediate types collected from North East India, were studied for variation in soluble proteins using acrylamide gel electrophoresis. The study revealed that there was a marked variation within and between varietal groups. Variability for number and intensity of protein bands in indica was wider than in japonica and javanica. Protein pattern in the group comprising N.E. Indian types transgressed that of all three established groups by displaying a wide spectrum. Relative homology, as measured from percentage similarities of N.E. Indian types to the three subspecies, suggested the existence of six different groups. Comparison of varietal groups for the protein mobility pattern showed that japonica and javanica varieties tended to show higher percentages of slow mobility proteins than indica. It appears, from the narrow variability and relatively low percentage of slow mobility proteins, that the japonica and javanica races are of later origin compared to indica. However, the study with a limited number of types suggested the monophyletic origin of varietal groups from an indica-like base predominantly found in the secondary centres of origin of O. sativa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Chatterjee, D.: A modified key and enumeration of the species of Oryza sativa L. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 18, 185–192 (1948).
Chu, Y. E.: Variation on peroxidase isozymes of Oryza perennis and O. sativa. Japan. J. Genetics 42, 233–244 (1967).
Chu, Y. E., Oka, H. I.: Comparison of variation in peroxidase isozymes between perennis-sativa and breviligulata-glaberrima series of Oryza. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sinica 8 (SpecialNo.), 261–270 (1967).
Davis, R. J.: Disc electrophoresis II. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 121, 404–427 (1964).
Desborough, S. L., Peloquin, S. J.: Disc electrophoresis of tuber proteins from Solanum species and interspecific hybrids. Phytochemistry 5, 727–733 (1966).
Duke, E. J., Glassman, E.: Evolution of Xanthine dehydrogenase in Drosophila. Genetics 58, 101–112 (1968).
Fox, D. J., Thurman, D. A., Butler, O.: Studies of the proteins of seeds of the Leguminosae I. Albumins. Phytochemistry 3, 417–419 (1964).
Garber, E. D.: The genus Collinsia XXVIII: A paper chromatographic and disc electrophoresis study of leaf extracts from 14 species and progeny from 5 interspecific hybrids. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 7, 551–558 (1965).
Govindaswamy, S., Krishnamurty, A.: On the occurrence of japonica type of grains in Jeypore tract. Rice News Teller 6 (4) 22–24 (1958).
Hart, G. E., Bhatia, C. R.: Acrylamide gel electrophoresis of soluble leaf proteins and enzymes from Nicotiana species. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 9, 367–374 (1967).
Jawahar Ram, Panwar, D. V. S.: Inter-specific divergence in rice. Indian J. Genet. 30 (1), 1–10 (1970).
Jennings, P. R.: Evaluation of partial sterility in indica X japonica rice hybrids. Technical Bull. 5, IRRI, Los Baños, Philippines, 63 (1964).
Johnson, B. L., Hall, O.: Analysis of phylogenetic affinities in the Triticinae by protein electrophoresis. Am. J. Bot. 52, 506–513 (1965).
Kato, S. C.: On the affinity of the cultivated varieties of rice plants, Oryza sativa, L. Kyushu Imp. Univ. Dept. Agr. J. 2 (9), 241–276 (1930).
Kato, S., Kosaka, H., Kara, S.: On the affinity of rice varieties as shown by the fertility of hybrid plants. Kyusu Imp. Univ. Fakult. Terkult, Bull. Sci. Report 3, 132 (1928).
Kihara, H., Katayama, C.: Occurrence of indica and japonica types among Sikkemese rice varieties. National Inst. Genet. Annual Report No. 14, 67 (1963).
Loeschcke, V., Stegemann, H.: Proteine der Kartoffelknollen in Abhängigkeit von Sorte und Virosen (Polyacrylamid-Elektrophorese). Phytochemistry 5, 985–991 (1966).
Lowry, O. M., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Mizushima, U.: Studies on sexual affinity among rice varieties, Oryza sativa L. I. Analysis of affinity of Japanese, American and Javanese varieties. Biology (Asakura-Shoten, Tokyo) 3 (2), 41–52 (1948).
Mizushima, U. C.: Studies on sexual affinity among rice varieties, Oryza sativa L. II. Analysis of affinity of other Asiatic and Hawaiian varieties. Tohoku J. Agr. Res., Japan 1 (2), 151–160 (1950).
Morishima, H., Oka, H. I., Chang, W. T.: Directions of differentiations in populations of wild rice, Oryza perennis and O. sativa fatua spontanea. Evolution XV (3), 326–339 (1961).
Nakao, S.: Rice — In: Peoples of Nepal, Himalaya Scientific results of the Japanese expedition to Nepal Himalaya. Fauna Flora Res. Soc. Kyoto Univ. 3, 398–400 (1957).
Oka, H. I.: Intervarietal variation and classification of cultivated rice. Indian J. Genet. 18 (2), 80–89 (1958).
Oka, H. I.: Pattern of interspecific relationships and evolutionary dynamics in Oryza. In: Rice Genetics and Cytogenetics, ed. R. F. Chandler, pp. 71–90. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1964a.
Oka, H. I.: Considerations on the genetic basis of intervarietal sterility in Oryza sativa. In: pp. 158–174 (1964b).
Oka, H. I., Chang, W. T., Nanse, T.: A preliminary note on investigations of wild and cultivated rice strains collected from the mountain region of Orissa state, India. Ann. Rept. Natl. Inst. Genet. (Japan) 1958, 18, 34–42 (1959).
Ornstein, L.: Disc Electrophoresis. I. Background and theory. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 121, 321–349 (1964).
Richharia, R. H., Misro, B., Rao, R. K.: Sterility in the rice hybrids and its significance. Euphytica 11, 137–142 (1962).
Sampath, S., Govindaswami, S.: Wild rices of Orissa and their relationship to cultivated rices. Rice News Teller, July, 1958 (1958).
Shahi, B. B., Chu, Y. E., Oka, H. I.: Analysis of genes controlling peroxidase isozymes in Oryza sativa and O. perennis. Japan. J. Genet. 44 (5), 321–328 (1969b).
Shahi, B. B., Morishima, H., Oka, H. I.: A survey of variations in peroxidase, acid phosphatase and esterase isozymes of wild and cultivated Oryza species. Japan. J. Genet. 44 (5), 303–319 (1969a).
Sharma, S. D., Vellanki, J. M. R., Hakim, K. L., Singh, R. K.: Primitive and current cultivars of rice in Assam — A rich source of valuable genes. Curr. Sci. 15 (6), 126–128 (1971).
Terao, H., Mizushima, V.: On the affinity of rice varieties cultivated in East Asia and America. B. Agr. Expt. Sta. Ministry Agr. and Commerce (Japan) 55, 1–7 (1944).
Vairavan, S.: Studies on the nature of genetic divergence in some rice strains from Assam and North East Himalayas. M. Sc. Thesis, P. G. School, I.A.R.I., India (1971).
Vaughan, J. G., Waite, A., Boulter, D., Waiters, S.: Comparative studies of the seed proteins of Brassica campestris, B. oleracea and B. nigra. J. Exptl. Bot. 17, 332–349 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. S. Swaminathan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiq, E.A., Nerkar, Y.S. & Mehta, S.L. Intra and inter subspecific variation in soluble proteins of Oryza sativa L.. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 42, 351–356 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00275360
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00275360