Summary
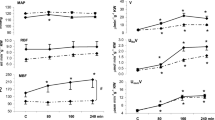
Experiments are described in which the influence of adrenal steroids on Na+ reabsorption in the distal segment of the rat nephron has been investigated, using the modified stop-flow technique of Metaxas.
In brief, this consists of simultaneous occlusion of the ureter and the vessels of the renal pedicle, thus allowing variation and shortening of the period of occlusion, without “smudging” of the eventual tubulogram due to movement of the trapped urine and the replacement of reabsorbate by new filtrate.
Occlusion periods of 5, 10, and 20 seconds were used in normal Sprague-Dawley rats, and in a second series in which the adrenals had been removed 24 hours previously. Reabsorption was calculated as the percentage difference between the ratios of Na+ to inulin clearance in the free flow urine and that in the “best” distal fraction.
Tubular reabsorption of Na+ in the distal segment was shown to increase in both groups of animals with prolongation of the period of occlusion, but the percentage reabsorbed during the occlusions was diminished after adrenalectomy. This difference is statistically significant at 5 seconds, but becomes progressively less so with 10 and 20 seconds occlusion.
It is suggested that the adrenal steroids may increase the rate of sodium reabsorption in the distal segment without affecting the total reabsorptive capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Borgmann, D. H. W.: Über den Mechanismus der renalen Elimination des Chlortetracyclins und seines demethylierten Derivates. Inauguraldissertation, Medizinische Fakultät der Freien Universität Berlin, 1964.
Deuticke, B., u. E. Gerlach: Nucleotid-Stoffwechsel in der Niere während und nach Sauerstoffmangel. Vortrag auf dem 3. Symposium der Gesellschaft für Nephrologie, Berlin 1964 (im Druck).
Führ, J., J. Kaczmarczyk u. C. D. Krüttgen: Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin. Wschr. 33, 729 (1955).
Fujimoto, M., F. D. Nash, and R. H. Kessler: Effects of cyanide, Q0 and DNP on renal sodium reabsorption and oxygen consumption. Amer. J. Physiol. 206, 1327 (1964).
Gerlach, E., B. Deuticke u. R. H. Dreisbach: Zum Verhalten von Nucleotiden und ihren dephosphorylierten Abbauprodukten in der Niere bei Ischämie und kurzzeitiger post-ischämischer Wiederdurchblutung. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 278, 296 (1963).
Heintz, R., W. Hoffmeister, F. Krück, and R. Wolf: Aldactone bei der Behandlung des nephrotischen Syndroms. In: Krück, Koczorek u. Betzien: Klinische Anwendung der Aldosteron-Antagonisten. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1962.
Herken, H., G. Senft u. B. Zemisch: Die Einschränkung des tubulären Natriumund Kaliumtransportes durch Biosynthese 6-Aminonicotinsäureamid enthaltender Nucleotide. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 249, 54 (1964).
Hierholzer, K.: Analyse der Natriumtransport-Störung in der Niere adrenalektomierter Ratten. — Untersuchungen am Einzelnephron. Habilitationsschrift, Medizinische Fakultät der Freien Universität Berlin, 1964.
Malvin, R. L.: The stop flow method and its use in studying renal function. Progr. cardiovasc. Dis. 3, 432 (1961).
— W. S. Wilde, and L. P. Sullivan: Localisation of nephron transport by stop flow analysis. Amer. J. Physiol. 194, 135 (1958).
McEvoy, J.: In Vorbereitung (1965). Unveröffentlichte Untersuchungen aus dem Pharmakologischen Institut der Freien Universität Berlin.
— G. Hollmann u. G. Senft: Zur Lokalisation der Wirkung von Mineralocorticoiden auf den Natriumtransport in der Niere. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 247, 350 (1964).
Metaxas, P.: Stop flow techniques using clamping of the renal pedicle to arrest movement of trapped urine. Clin. Sci. 23, 385 (1962).
Nicholson, T. F.: A comparison of the effects of proximal and distal tubular damage on the action of desoxycorticosterone and aldosterone. Canad. J. Biochem. 35, 641 (1957).
Omachi, A., and R. I. Macey: Intratubular fluid movement in dog kidney during stop flow. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 101, 386 (1959).
Rotter, W., H. Lapp u. H. Zimmermann: Pathogenese und morphologisches Substrat des „akuten Nierenversagens“ und seine Erholungszeit. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 87, 669 (1962).
Senft, G.: Membrantransport und Pharmaka. Vortrag auf dem 3. Symposium der Gesellschaft für Nephrologie, Berlin 1964 (im Druck).
Taylor, M. G., and E. Ullmann: Glomerular filtration after obstruction of the ureter. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 157, 38 (1961).
Vander, A. J., R. L. Malvin, W. S. Wilde, J. Lapides, L. P. Sullivan, and M. V. McMurray: Effects of adrenalectomy and aldosterone on proximal and distal tubular sodium reabsorption. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 99, 323 (1958).
— W. S. Wilde, and R. L. Malvin: Stop flow analysis of aldosterone and steroidal antagonist SC 8109 on renal tubular sodium transport kinetics. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 103, 525 (1960).
Wiederholt, M., K. Hierholzer, G. Rumrich u. H. Holzgreve: Transtubuläre Natriumströme im proximalen und distalen Tubulus adrenalektomierter Ratten. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 281, 96 (1964).
Williamson, H. E., T. W. Skulan, and F. E. Shideman: Effect of adrenalectomy on the pattern in the renal tubule of the rat. Fed. Proc. 18, 459 (1959).
— Effects of adrenalectomy and desoxycorticosterone on stop flow pattern of sodium and potassium in the rat. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 131, 49 (1961).
Zemisch, B.: Störungen des Elektrolyt- und Wasserhaushalts nach Bildung abnorm strukturierter NAD- bzw. NADP-Analoga. Inauguraldissertation, Medizinische Fakultät der Freien Universität Berlin, 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 3 Textabbildungen
Die Ergebnisse wurden auszugsweise auf der 5. Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Pharmakologischen Gesellschaft vorgetragen (McEvoy, Hollmann u. Senft 1964).
Stipendiat der Alexander von Humboldt-Stiftung.
Wir danken der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft für die Unterstützung unserer Untersuchungen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McEvoy, J., Hollmann, G. & Senft, G. Einfluß von Mineralocorticoiden auf die tubuläre Rückgewinnung von Natriumionen. Naunyn - Schmiedebergs Arch 250, 318–324 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258525
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258525