Abstract
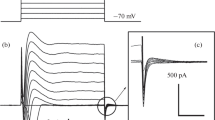
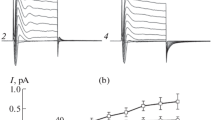
Large conductance channels were observed in the membrane of cultured cardiac cells of newborn rats studied with the patch-clamp technique in cell-attached and inside-out configurations. These channels were observed in ≃4% of the patches. In the cell-attached configuration they exhibited outward rectification and partial inactivation. In the inside-out configuration no rectification occurred but inactivation was present, mainly during hyperpolarizations. Two channels with large single unit conductances (400–450 pS) and one with a smaller conductance (200–250 pS) were frequently observed in the same patch. The two large channels generally had different kinetics. Under steady-state conditions the opening probability of the faster channel appeared to be voltage-independent. The slower channel was activated by depolarization. In asymmetrical solutions the permeability ratios P Na/P Cl were 0.03 and 0.24 for the larger and smaller channels, respectively; corresponding values for P Ba/P Cl were 0.04 and 0.09. It is proposed that in cardiac membranes the chloride permeability system is composed of widely dispersed microclusters forming grouped channels of different types and sizes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bechem M, Glitsch HG, Pott L (1983) Properties of an inward rectifying K channel in the membrane of guinea-pig atrial cardioballs. Pfluegers Arch 399:186–193
Blatz AL, Magleby KL (1983) Single voltage-dependent chloride-selective channels of large conductance in cultured rat muscle. Biophys J 43:237–241
Blatz AL, Magleby KL (1985) Single chloride-selective channels active at resting membrane potentials in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Biophys J 47:119–123
Cachelin AB, de Peyer JE, Kokubun S, Reuter H (1983) Ca2+ channel modulation by 8-bromocyclic AMP in cultured heart cells. Nature 304:462–464
Carmeliet E (1961a) Chloride and potassium permeability in cardiac Purkinje fibres. Arscia S.A. & Presses Acad Europ, Bruxelles, 146 p
Carmeliet E (1961b) Chloride ions and the membrane potential of Purkinje fibres. J Physiol (London) 156:375–388
Carmeliet E, Verdonck F (1977) Reduction of potassium permeability by chloride substitution in cardiac cells. J Physiol (London) 265:193–206
Clapham DE, DeFelice LJ (1984) Voltage-activated K channels in embryonic chick heart. Biophys J 45:40–42
Corey DP, Stevens CF (1983) Science and technology of patch-recording electrodes. In: Sakmann B, Neher E (eds) Single-channel recording. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 53–68
Coulombe A, Duclohier H (1984) A large unit conductance channel permeable to chloride ions in cultured rat heart cells. J Physiol (London) 350:52P
Deck KA, Trautwein W (1964) Ionic currents in cardiac excitation. Pfluegers Arch 280:63–80
Fozzard HA, Lee CO (1976) Influence of changes in external potassium and chloride ions on membrane potential and intracellular potassium ion activity in rabbit ventricular muscle. J Physiol (London) 256:663–689
Goldman Y, Morad M (1977) Ionic membrane conductance during the time course of the cardiac action potential. J Physiol (London) 268:655–695
Gorman ALF, Hermann A (1979) Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones. J Physiol (London) 296:393–410
Gray PTA, Bevan S, Ritchie JM (1984) High conductance anion-selective channels in rat cultured Schwann cells. Proc R Soc London B 221:395–409
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Horackova M, Vassort G (1982) Effects of chloride replacement in cardiac muscle: mechanisms of positive inotropy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 14:123–130
Hutter OF, Noble D (1961) Anion conductance of cardiac muscle. J Physiol (London) 157:335–350
Kolb HA, Brown CDA, Murer H (1985) Identification of a voltage dependent anion channel in the apical membrane of a Cl--secretory epithelium (MDCK). Pfluegers Arch 403:262–265
Lenfant J, Goupil N (1977) Effects of the replacement of chloride by methylsulphate on the membrane currents in frog atrial trabeculae. Pfluegers Arch 372:121–129
Macchia DD, Bankston PW (1983) Effects of temperature on anion distribution in perfused rat, guinea-pig and hamster ventricle. Experientia 39:1291–1293
Martin BJ, Thorn P (1984) A high conductance anion channel in somatic muscle cells of Ascaris suum. J Physiol (London) 354:46P
Miller C (1982) Open-state substructure of single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Philos Trans R Soc London B 299:401–411
Nelson DJ, Tang JM, Palmer LG (1984) Single-channel recordings of apical membrane chloride conductance in A6 epithelial cells. J Membr Biol 80:81–89
Nosek TM (1979) Effects of chloride on the electrical and mechanical properties of guinea pig ventricle. Pfluegers Arch 381:171–177
Nosek TM, Lieberman EM (1981) Contribution of chloride to the membrane input conductance of the ventricle: the effect of ouabain. Life Sci 28:2659–2669
Piwnica-Worms D, Jacob R, Horres RC, Lieberman M (1983) Transmembrane chloride flux in tissue-cultured chick heart cells. J Gen Physiol 81:731–748
Robinson RB, Legato MJ (1980) Maintained differentiation in rat cardiac monolayer cultures: tetrodotoxin sensitivity and ultrastructure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 12:493–498
Schwarze W, Kolb H-A (1984) Voltage-dependent kinetics of an anionic channel of large unit conductance in macrophages and myotube membranes. Pfluegers Arch 402: 281–291
Trube G, Hescheler J (1984) Inward-rectifying potassium channels in isolated patches of the heart cell membrane: ATP-dependence and comparison with cell-attached patches. Pfluegers Arch 401:178–184
Vaughan-Jones RD (1979) Regulation of chloride in quiescent sheep-heart Purkinje fibres studied using intracellular chloride and pH-sensitive micro-electrodes. J Physiol (London) 295:111–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coulombe, A., Duclohier, H., Coraboeuf, E. et al. Single chloride-permeable channels of large conductance in cultured cardiac cells of new-born rats. Eur Biophys J 14, 155–162 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253840
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253840