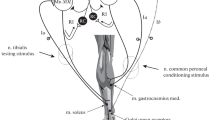
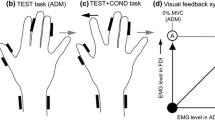
Summary
A magnetic stimulus applied to the human scalp over the motor cortex causes a short latency contraction of contralateral limb muscles. This is presumed to result from the indirect excitation of corticospinal neurons with monosynaptic connections to motoneurons. The excitability of these cortical neurons can be estimated from the magnitude of the postsynaptic potentials produced in spinal motoneurons by a given magnetic stimulus. In man the characteristics of these postsynaptic potentials can be derived from changes in the firing probability of single motor units. When a subject increases the level of a sustained voluntary contraction the excitability of the corticospinal neurons estimated in this way becomes less. We conclude that the additional synaptic input to motoneurons required to maintain a stronger muscle contraction comes from fiber systems other than the population of fast corticospinal neurons activated by magnetic stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amassian VE, Stewart M, Quirk GJ, Rosenthal JL (1987) Physiological basis of motor effects of a transient stimulus to cerebral cortex. J Neurosurg 20: 74–93
Ashby P, Zilm D (1982a) Relationship between EPSP shape and cross-correlation profile explored by computer simulation for studies on human motoneurons. Exp Brain Res 47: 33–40
Ashby P, Zilm D (1982b) Characteristics of postsynaptic potentials produced in single human motoneurons by homonymous group I volleys. Exp Brain Res 47: 41–48
Barker AT, Jalinous R, Freeston IL (1985) Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet i: 1106–1107
Bernhard CG, Bohm E, Petersen I (1953) Investigations of the organization of the corticospinal system in monkeys. Acta Physiol Scand 20 [Suppl]106: 79–105
Cheney PD, Fetz EE (1980) Functional classes of primate corticomotoneuronal cells and their relation to active force. J Neurophysiol 44: 773–791
Conrad B, Weisendanger M, Matsunami K, Brooks VB (1977) Precentral unit activity related to control of arm movements. Exp Brain Res 29: 85–95
Cope TC, Fetz EE, Matsumura M (1987) Cross-correlation assessment of synaptic strength of single Ia fibre connections with triceps surae motoneurons in cats. J Physiol (Lond) 390: 161–188
Cowan J, Day BK, Marsden CD, Rothwell JC (1986) The effects of percutaneous motor cortex stimulation on H reflexes in muscles of the arm and leg in intact man. J Physiol (Lond) 377: 333–347
Day BL, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD, Dick JPR, Cowan JMA, Berardelli A, Marsden CD (1987) Motor cortex stimulation in intact man. Brain 110: 1191–1209
Evarts EV (1969) Activity of pyramidal tract neurons during postural fixation. J Neurophysiol 32: 375–385
Evarts EV, Fromm C (1978) The pyramidal tract neuron as a summing point in a closed-loop control system in the monkey. In: Desmedt JE (ed) Cerebral motor control in man: long loop mechanisms. Karger, Basel, pp 55–69
Gualtierotti T, Paterson AS (1954) Electrical stimulation of the unexposed cerebral cortex. J Physiol (Lond) 125: 278–291
Hepp-Reymond M-C, Wyss VR, Anner R (1978) Neuronal coding of static force in the primate motor cortex. J Physiol (Paris) 74: 287–291
Hess CW, Mills KR, Murray NMF (1987) Responses in small hand muscles from magnetic stimulation, the human brain. J Physiol (Lond) 388: 397–419
Hoffman DS, Luschei ES (1980) Responses of monkey precentral cortical cells during a controlled jaw bite task. J Neurophysiol 44: 333–348
Landgren S, Phillips CG, Porter R (1962) Minimal synaptic actions of pyramidal impulses of some alpha motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol (Lond) 161: 91–111
Mao CC, Ashby P, Wang M, McCrea D (1984) Synaptic connections from large muscle afferents to the motoneurons of various leg muscles in man. Exp Brain Res 56: 341–350
Merton PA, Morton HB (1980) Stimulation of the cerebral cortex in the intact human subject. Nature 285: 227
Muir RB, Lemon RN (1983) Corticospinal neurons with a special role in precision grip. Brain Res 261: 312–316
Preston JB, Whitlock DG (1961) Intracellular potentials recorded from motoneurons following pre-central gyrus stimulation in primate. J Neurophysiol 24: 91–100
Stephens JA, Usherwood TP, Garnet R (1976) Techniques for studying synaptic connections of single motoneurones in man. Nature 263: 343–394
Thatch WT (1978) Correlation of neural discharge with pattern and force of muscular activity, joint position, and direction of intended next movement in motor cortex and cerebellum. J Neurophysiol 41: 654–676
Williams IR, Hayward M (1981) The effect of afferent stimuli on steadily discharging single motor units in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 44: 1040–1045
Zidar J, Trontelj JV, Mihelin M (1987) Percutaneous stimulation of human corticospinal tract: a single fibre EMG study of individual motor unit responses. Brain Res 422: 196–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brouwer, B., Ashby, P. & Midroni, G. Excitability of corticospinal neurons during tonic muscle contractions in man. Exp Brain Res 74, 649–652 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00247369
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00247369