Abstract
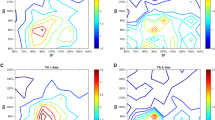
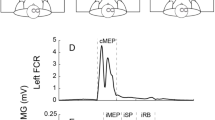
The present study examined whether the excitability of the corticospinal pathway and the GABA-mediated inhibitory circuits of the primary motor cortex that project onto the corticospinal neurons in the tonically contracting hand muscle are changed by tonic contraction of the adjacent hand muscle. The motor evoked potential (MEP) and cortical silent period (CSP) in the tonically contracting hand muscle were obtained while the adjacent hand muscle was either tonically contracting or at rest. The MEP and CSP of the first dorsal interosseous (FDI) muscle elicited across the scalp sites where the MEP is predominantly elicited in the FDI muscle were decreased by tonic contraction of the abductor digiti minimi (ADM) muscle. The centers of the area of the MEP and the duration of the CSP in the FDI muscle elicited across the sites where the MEP is predominantly elicited in the FDI muscle were lateral to those in the FDI muscle elicited across the sites where the MEP is elicited in both the FDI and ADM muscles. They were also lateral to those in the ADM muscle elicited either across the sites where the MEP is predominantly elicited in the ADM muscle, or across the sites where the MEP is elicited in both the FDI and ADM muscles. The decrease in the corticospinal excitability and the excitability of the GABA-mediated inhibitory circuits of the primary motor cortex that project onto the corticospinal neurons in the FDI muscle may be due either to (1) the interaction between the activity of the lateral area of the FDI representation and the descending drive to the ADM muscle, or (2) the decreased susceptibility of the primary motor area that predominantly projects onto the corticospinal neurons in the FDI muscle, which also plays a role in independent finger movement when both the FDI and ADM muscles act together as synergists.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aimonetti JM, Nielsen JB (2002) Cortical excitability and motor task in man: an investigation of the wrist extensor motor area. Exp Brain Res 143(4):431–439. doi:10.1007/s00221-002-1010-3
Aoki T, Furuya S, Kinoshita H (2005) Finger-tapping ability in male and female pianists and nonmusician controls. Mot Control 9(1):23–39
Beck S, Richardson SP, Shamim EA, Dang N, Schubert M, Hallett M (2008) Short intracortical and surround inhibition are selectively reduced during movement initiation in focal hand dystonia. J Neurosci 28(41):10363–10369. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3564-08.2008
Beisteiner R, Windischberger C, Lanzenberger R, Edward V, Cunnington R, Erdler M, Gartus A, Streibl B, Moser E, Deecke L (2001) Finger somatotopy in human motor cortex. Neuroimage 13(6 Pt 1):1016–1026. doi:10.1006/nimg.2000.0737
Carroll TJ, Riek S, Carson RG (2001) Reliability of the input-output properties of the cortico-spinal pathway obtained from transcranial magnetic and electrical stimulation. J Neurosci Methods 112(2):193–202. doi:10.1016/S0165-02700100468-X
Chen R, Lozano AM, Ashby P (1999) Mechanism of the silent period following transcranial magnetic stimulation evidence from epidural recordings. Exp Brain Res 128(4):539–542. doi:10.1007/s002210050878
Chen R, Cros D, Curra A, Di Lazzaro V, Lefaucheur JP, Magistris MR, Mills K, Rösler KM, Triggs WJ, Ugawa Y, Ziemann U (2008) The clinical diagnostic utility of transcranial magnetic stimulation: report of an IFCN committee. Clin Neurophysiol 119(3):504–532. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2007.10.014
Classen J, Knorr U, Werhahn KJ, Schlaug G, Kunesch E, Cohen LG, Seitz RJ, Benecke R (1998) Multimodal output mapping of human central motor representation on different spatial scales. J Physiol 512(Pt 1):163–179. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.163bf.x
Cunningham DA, Machado A, Yue GH, Carey JR, Plow EB (2013) Functional somatotopy revealed across multiple cortical regions using a model of complex motor task. Brain Res 1531:25–36. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2013.07.050
Daskalakis ZJ, Molnar GF, Christensen BK, Sailer A, Fitzgerald PB, Chen R (2003) An automated method to determine the transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced contralateral silent period. Clin Neurophysiol 114(5):938–944. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(03)00038-5
Dechent P, Frahm J (2003) Functional somatotopy of finger representations in human primary motor cortex. Hum Brain Mapp 18(4):272–283. doi:10.1002/hbm.10084
Devanne H, Lavoie BA, Capaday C (1997) Input–output properties and gain changes in the human corticospinal pathway. Exp Brain Res 114(2):329–338. doi:10.1007/PL00005641
Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Pilato F, Saturno E, Dileone M, Mazzone P, Insola A, Tonali PA, Rothwell JC (2004) The physiological basis of transcranial motor cortex stimulation in conscious humans. Clin Neurophysiol 115(2):255–266. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2003.10.009
Fuhr P, Agostino R, Hallett M (1991) Spinal motor neuron excitability during the silent period after cortical stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 81(4):257–262. doi:10.1016/0168-5597(91)90011-L
Groppa S, Oliviero A, Eisen A, Quartarone A, Cohen LG, Mall V, Kaelin-Lang A, Mima T, Rossi S, Thickbroom GW, Rossini PM, Ziemann U, Valls-Solé J, Siebner HR (2012) A practical guide to diagnostic transcranial magnetic stimulation: report of an IFCN committee. Clin Neurophysiol 123(5):858–882. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2012.01.010
Häger-Ross C, Schieber MH (2000) Quantifying the independence of human finger movements: comparisons of digits, hands, and movement frequencies. J Neurosci 20(22):8542–8550
Hasegawa Y, Kasai T, Tsuji T, Yahagi S (2001) Further insight into the task-dependent excitability of motor evoked potentials in first dorsal interosseous muscle in humans. Exp Brain Res 140(4):387–396. doi:10.1007/s002210100842
Hess CW, Mills KR, Murray NMF (1986) Magnetic stimulation of the human brain: facilitation of motor responses by voluntary contraction of ipsilateral and contralateral muscles with additional observations on an amputee. Neurosci Lett 71(2):235–240. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(86)90565-3
Hetu S, Gagne M, Reilly KT, Mercier C (2011) Short-term reliability of transcranial magnetic stimulation motor maps in upper limb amputees. J Clin Neurosci 18(5):728–730. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2010.09.011
Hlustik P, Solodkin A, Gullapalli RP, Noll DC, Small SL (2001) Somatotopy in human primary motor and somatosensory hand representations revisited. Cereb Cortex 11(4):312–321. doi:10.1093/cercor/11.4.312
Huntley GW, Jones EG (1991) Relationship of intrinsic connections to forelimb movement representations in monkey motor cortex: a correlative anatomic and physiological study. J Neurophysiol 66(2):390–413
Inghilleri M, Berardelli A, Cruccu G, Manfredi M (1993) Silent period evoked by transcranial stimulation of the human cortex and cervicomedullary junction. J Physiol 466:521–534
Jono Y, Chujo Y, Nomura Y, Tani K, Nikaido Y, Hatanaka R, Hiraoka K (2015) The effect of tonic contraction of the hand muscle on the motor cortical representation of the contracting adjacent muscle. Somatosens Mot Res 32(2):114–121. doi:10.3109/08990220.2014.994738
Kleinschmidt A, Nitschke MF, Frahm J (1997) Somatotopy in the human motor cortex hand area. A high-resolution functional MRI study. Eur J Neurosci 9(10):2178–2186. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.1997.tb01384.x
Kojima S, Onishi H, Sugawara K, Kirimoto H, Suzuki M, Tamaki H (2013) Modulation of the cortical silent period elicited by single- and paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation. BMC Neurosci 14:43. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-14-43
Li S, Latash ML, Zatsiorsky VM (2003) Finger interaction during multi-finger tasks involving finger addition and removal. Exp Brain Res 150(2):230–236. doi:10.1007/s00221-003-1449-x
Littmann AE, McHenry CL, Shields RK (2013) Variability of motor cortical excitability using a novel mapping procedure. J Neurosci Methods 214(2):137–143. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.01.013
Malcolm MP, Triggs WJ, Light KE, Shechtman O, Khandekar G, Gonzalez Rothi LJ (2006) Reliability of motor cortex transcranial magnetic stimulation in four muscle representations. Clin Neurophysiol 117(5):1037–1046. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2006.02.005
Nakamura H, Kitagawa H, Kawaguchi Y, Tsuji H (1997) Intracortical facilitation and inhibition after transcranial magnetic stimulation in conscious humans. J Physiol 498(3):817–823. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp021905
Ni Z, Gunraj C, Chen R (2007) Short interval intracortical inhibition and facilitation during the silent period in human. J Physiol 583(Pt 3):971–982. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2007.135749
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113. doi:10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4
Pascual-Leone A, Nguyet D, Cohen LG, Brasil-Neto JP, Cammarota A, Hallett M (1995) Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new fine motor skills. J Neurophysiol 74(3):1037–1045
Poston B, Kukke SN, Paine RW, Francis S, Hallett M (2012) Cortical silent period duration and its implications for surround inhibition of a hand muscle. Eur J Neurosci 36(7):2964–2971. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08212.x
Reilly KT, Hammond GR (2000) Independence of force production by digits of the human hand. Neurosci Lett 290(1):53–56. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01328-8
Reilly KT, Mercier C (2008) Cortical topography of human first dorsal interroseus during individuated and nonindividuated grip tasks. Hum Brain Mapp 29(5):594–602. doi:10.1002/hbm.20421
Sacco P, Thickbroom GW, Thompson ML, Mastaglia FL (1997) Changes in corticomotor excitation and inhibition during prolonged submaximal muscle contractions. Muscle Nerve 20(9):1158–1166. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199709)20:9<1158:AID-MUS11>3.0.CO;2-P
Sakai K, Ugawa Y, Terao Y, Hanajima R, Furubayashi T, Kanazawa I (1997) Preferential activation of different I waves by transcranial magnetic stimulation with a figure-of-eight-shaped coil. Exp Brain Res 113(1):24–32. doi:10.1007/BF02454139
Sanes JN, Donoghue JP, Thangaraj V, Edelman RR, Warach S (1995) Shared neural substrates controlling hand movements in human motor cortex. Science 268(5218):1775–1777. doi:10.1126/science.7792606
Schieber MH, Poliakov AV (1998) Partial inactivation of the primary motor cortex hand area: effects on individuated finger movements. J Neurosci 18(21):9038–9054
Siebner HR, Dressnandt J, Auer C, Conrad B (1998) Continuous intrathecal baclofen infusions induced a marked increase of the transcranially evoked silent period in a patient with generalized dystonia. Muscle Nerve 21(9):1209–1212. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199809)21:9<1209:AID-MUS15>3.0.CO;2-M
Slobounov S, Johnston J, Chiang H, Ray W (2002a) The role of sub-maximal force production in the enslaving phenomenon. Brain Res 954(2):212–219. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03288-2
Slobounov S, Johnston J, Chiang H, Ray WJ (2002b) Motor-related cortical potentials accompanying enslaving effect in single versus combination of fingers force production tasks. Clin Neurophysiol 113(9):1444–1453. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00195-5
Sohn YH, Hallett M (2004a) Surround inhibition in human motor system. Exp Brain Res 158(4):397–404. doi:10.1007/s00221-004-1909-y
Sohn YH, Hallett M (2004b) Disturbed surround inhibition in focal hand dystonia. Ann Neurol 56(4):595–599. doi:10.1002/ana.20270
Tinazzi M, Farina S, Tamburin S, Facchini S, Fiaschi A, Restivo D, Berardelli A (2003) Task-dependent modulation of excitatory and inhibitory functions within the human primary motor cortex. Exp Brain Res 150(2):222–229. doi:10.1007/s00221-003-1448-y
Tyč F, Boyadjian A (2011) Plasticity of motor cortex induced by coordination and training. Clin Neurophysiol 122(1):153–162. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2010.05.022
Wassermann EM, McShane LM, Hallett M, Cohen LG (1992) Noninvasive mapping of muscle representations in human motor cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85(1):1–8. doi:10.1016/0168-5597(92)90094-R
Wilson SA, Thickbroom GW, Mastaglia FL (1995) Comparison of the magnetically mapped corticomotor representation of a muscle at rest and during low-level voluntary contraction. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 97(5):246–250. doi:10.1016/0924-980X(95)80001-8
Zatsiorsky VM, Li ZM, Latash ML (2000) Enslaving effects in multi-finger force production. Exp Brain Res 131(2):187–195. doi:10.1007/s002219900261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jono, Y., Iwata, Y., Mizusawa, H. et al. Change in Excitability of Corticospinal Pathway and GABA-Mediated Inhibitory Circuits of Primary Motor Cortex Induced by Contraction of Adjacent Hand Muscle. Brain Topogr 29, 834–846 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0499-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0499-x