Summary
-
1.
Unit spikes of burst neurons were extracellularly recorded in the pontomedullary reticular formation of the cat. These neurons were identified by their burst activity coincident with the quick inhibitory phase of the contralateral abducens nerve during vestibular nystagmus and their antidromic activation from the contralateral abducens nucleus.
-
2.
When the extracellular field potentials in and near the abducens nucleus were triggered by spikes of a contralateral burst neuron, the averaged potential consisted of an early di- or triphasic spike and a late slow positive wave. The early spike was an action current caused by impulses conducting along the axon of the burst neuron.
-
3.
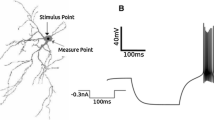
The action potentials of a contralateral burst neuron were employed to trigger a post-spike average of the membrane potential of abducens motoneurons. Then unitary IPSPs with monosynaptic latencies were revealed. This provided direct evidence that the burst neurons are inhibitory in nature. The amplitudes of unitary IPSPs ranged from 18 to 220 μV. Each inhibitory burst neuron branched widely in the abducens nucleus and was estimated to make inhibitory connections with approximately 60% of the motoneuron pool.
-
4.
The post-spike average of compound potentials of the abducens nerve triggered by action potentials of contralateral single inhibitory burst neurons revealed inhibition of spike activity with latencies and time courses compatible with those of unitary IPSPs in motoneurons. The inhibition was observed with all inhibitory burst neurons tested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asanuma, H., Rosén, I.: Spread of mono- and polysynaptic connections within cat's motor cortex. Exp Brain Res 16, 507–520 (1973)
Baker, R., Berthoz, A.: Organization of vestibular nystagmus in oblique oculomotor system. J Neurophysiol 37, 195–217 (1974)
Baker, R.G., Mano, N., Shimazu, H.: Intracellular recording of antidromic responses from abducens. motoneurons in the cat. Brain Res 15, 573–576 (1969a)
Baker, R.G., Mano, N., Shimazu, H.: Postsynaptic potentials in abducens motoneurons induced by vestibular stimulation. Brain Res 15, 577–580 (1969b)
Büttner-Ennever, J.A., Henn, V.: An autoradiographic study of the pathways from the pontine reticular formation involved in horizontal eye movements. Brain Res 108, 155–164 (1976)
Clamann, H.P., Henneman, E.: Electrical measurement of axon diameter and its use in relating motoneuron size to critical firing level. J Neurophysiol 39, 844–851 (1976)
Cohen, B., Henn, V.: The origin of quick phases of nystagmus in the horizontal plane. Bibl Ophthalmol 82, 36–55 (1972a)
Cohen, B., Henn, V.: Unit activity in the pontine reticular formation associated with eye movements. Brain Res 46, 403–410 (1972b)
Duensing, F., Schaefer, K.P.: Die Neuronenaktivität in der Formatio reticularis des Rhombencephalons beim vestibulären Nystagmus. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 196, 265–290 (1957)
Eccles, J.C.: The Physiology of Synapses. Berlin: Springer 1964
Fetz, E.E., Cheney, P.D., German, D.C.: Corticomotoneuronal connections of precentral cells detected by post-spike averages of EMG activity in behaving monkeys. Brain Res 114, 505–510 (1976)
Fuchs, A.F., Luschei, E.S.: Firing patterns of abducens neurons of alert monkeys in relationship to horizontal eye movement. J Neurophysiol 33, 382–392 (1970)
Grantyn, A.A., Grantyn, R.: Synaptic actions of tectofugal pathways on abducens motoneurons in the cat. Brain Res 105, 269–285 (1976)
Graybiel, A.M.: Direct and indirect preoculomotor pathways of the brainstem: an autoradiographic study of the pontine reticular formation in the cat. J Comp Neurol 175, 37–78 (1977)
Highstein, S.M., Cohen, B., Matsunami, K.: Monosynaptic projections from the pontine reticular formation to the Illrd nucleus in the cat. Brain Res 75, 340–344 (1974)
Highstein, S.M., Maekawa, K., Steinacker, A., Cohen, B.: Synaptic input from the pontine reticular nuclei to abducens motoneurons and internuclear neurons in the cat. Brain Res 112, 162–167 (1976)
Hikosaka, O., Kawakami, T.: Inhibitory interneurons in the reticular formation and their relation to vestibular nystagmus. Brain Res 117, 513–518 (1976)
Hikosaka, O., Kawakami, T.: Inhibitory reticular neurons related to the quick phase of vestibular nystagmus — their location and projection. Exp Brain Res 27, 377–396 (1977)
Hikosaka, O., Maeda, M., Nakao, S., Shimazu, H., Shinoda, Y.: Presynaptic impulses in the abducens nucleus and their relation to postsynaptic potentials in motoneurons during vestibular nystagmus. Exp Brain Res 27, 355–376 (1977)
Jankowska, E., Roberts, W.J.: An electrophysiological demonstration of the axonal projections of single spinal interneurones in the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 222, 597–622 (1972a)
Jankowska, E., Roberts, W.J.: Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal la inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 222, 623–642 (1972b)
Keller, E.L.: Participation of medial pontine reticular formation in eye movement generation in monkey. J Neurophysiol 37, 316–332 (1974)
Kirkwood, P.A., Sears, T.A.: Monosynaptic excitation of thoracic expiratory motoneurones from lateral respiratory neurones in the medulla of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 234, 87P-89P (1973)
Kirkwood, P.A., Sears, T.A.: Monosynaptic excitation of motoneurones from secondary endings of muscle spindles. Nature (Lond) 252, 243–244 (1974)
Lorente de Nó, R.: Vestibulo-ocular reflex arc. Arch Neurol Psychiat (Chic) 30, 245–291 (1933)
Luschei, E.S., Fuchs, A.F.: Activity of brain stem neurons during eye movements of alert monkeys. J Neurophysiol 35, 445–461 (1972)
Maciewicz, R.J., Eagen, K., Kaneko, C.R.S., Highstein, S.M.: Vestibular and medullary brain stem afferents to the abducens nucleus in the cat. Brain Res 123, 229–240 (1977)
Maeda, M., Shimazu, H., Shinoda, Y.: Nature of synaptic events in cat abducens motoneurons at slow and quick phase of vestibular nystagmus. J Neurophysiol 35, 279–296 (1972)
Mendell, L.M., Henneman, E.: Terminals of single la fibers: location, density and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 34, 171–187 (1971)
Ramön y Cajal, S.: Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés. Paris: Maloine 1911
Rapoport, S., Susswein, A., Uchino, Y., Wilson, V.J.: Synaptic actions of individual vestibular neurones on cat neck motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 272, 367–382 (1977)
Robinson, D.A.: Oculomotor unit behavior in the monkey. J Neurophysiol 33, 393–404 (1970)
Scheibel, M.E., Scheibel, A.B.: Structural substrates for integrative patterns in the brain stem reticular core. In: Reticular Formation of the Brain (eds. H.H. Jasper, L.D. Proctor, R.S. Knighton, W.C. Noshay, R.T. Costello), pp. 31–55. Boston: Little Brown 1958
Scott, J.G., Mendell, L.M.: Individual EPSPs produced by single triceps surae la afferent fibers in homonymous and heteronymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 39, 679–692 (1976)
Sparks, D.L., Travis, R.P., Jr.: Firing patterns of reticular formation neurons during horizontal eye movements. Brain Res 33, 477–481 (1971)
Stauffer, E.K., Watt, D.G.D., Taylor, A., Reinking, R.M., Stuart, D.G.: Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 2. Spindle group II afferents, J Neurophysiol 39, 1393–1402 (1976)
Stoney, S.D., Jr., Thompson, E.D., Asanuma, H.: Excitation of pyramidal tract cells by intracortical microstimulation: effective extent of stimulating current. J Neurophysiol 31, 659–669 (1968)
Szentágothai, J.: Pathways and synaptic articulation patterns connecting vestibular receptors and oculomotor nuclei. In: The Oculomotor System (ed. M.B. Bender), pp. 205–223. New York: Harper & Row 1964
Tasaki, I.: New measurements of the capacity and the resistance of the myelin sheath and the nodal membrane of the isolated frog nerve fiber. Amer J Physiol 181, 639–650 (1955)
Taylor, A., Stephens, J.A., Somjen, G., Appenteng, K., O'Donovan, M.J.: Extracellular spike triggered averaging for plotting synaptic projections. Brain Res 140, 344–348 (1978)
Thomas, R.C., Wilson, V.J.: Precise localization of Renshaw cells with a new marking technique. Nature (Lond) 206, 211–213 (1965)
Watt, D.G.D., Stauffer, E.K., Taylor, A., Reinking, R.M., Stuart, D.G.: Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 1. Spindle primary and tendon organ afferents. J Neurophysiol 39, 1375–1392 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hikosaka, O., Igusa, Y., Nakao, S. et al. Direct inhibitory synaptic linkage of pontomedullary reticular burst neurons with abducens motoneurons in the cat. Exp. Brain Res. 33, 337–352 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235558
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235558