Summary
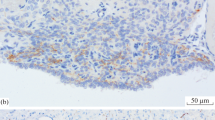
Immuno-enzyme cytochemical investigations showed that the whole amphibian pars intermedia of the hypophysis is innervated by an intercellular network of peptidergic varicose nerve fibres which contain mesotocin or (and) parts of the mesotocin molecule. The pars intermedia does not contain vasotocinergic fibres. The mesotocinergic fibres are branches of axons leaving the pituitary stalk and the neural lobe. In animals of which the hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory preoptic nuclei had been completely removed, the immuno-reactive mesotocinergic fibres of the pars intermedia had totally disappeared. From this result, it is concluded that the mesotocinergic fibres of the pars intermedia of the amphibian hypophysis are axons of neurosecretory perikarya located in the hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory preoptic nuclei.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acher, R.: Chemistry of the neurohypophysial hormones: an example of molecular evolution. In: Handbook of Physiology. Section 7: Endocrinology. Vol. IV. The pituitary gland and its neuroendocrine control, Part 1, p. 119–130 (R.O. Greep and E.B. Astwood, eds.). Washington: American Physiological Society 1974
Bargmann, W., Lindner, E., Andres, K.H.: Über Synapsen an endokrinen Epithelzellen und die Definition sekretorischer Neurone. Untersuchungen am Zwischenlappen der Katzenhypophyse. Z. Zellforsch. 77, 282–298 (1967)
Dierickx, K.: The extirpation of the neurosecretory preoptic nucleus and the reproduction of Rana temporaria. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 145, 580–589 (1963)
Dierickx, K.: The function of the hypophysis without preoptic neurosecretory control. Z. Zellforsch. 78, 114–130 (1967)
Dodd, J.M., Follett, B.K., Sharp, P.J.: Hypothalamic control of pituitary function in submammalian vertebrates. In: Advances in Comparative Physiology and Biochemistry, Vol. 4, pp. 113–223 (O. Lowenstein, ed.). New York-London: Academic Press 1971
Doerr-Schott, J., Dubois, M.P.: Identification par immunofluorescence des cellules corticotropes et mélanotropes de l'hypophyse des Amphibiens. Z. Zellforsch. 132, 323–331 (1972)
Doerr-Schott, J., Dubois, M.P.: Détection par immunofluorescence des cellules corticotropes et mélanotropes dans l'hypophyse de la grenouille, Rana temporaria L., au cours du développement. Z. Zellforsch. 142, 571–580 (1973)
Doerr-Schott, J., Follenius, E.: Innervation de l'hypophyse intermédiaire de Rana esculenta, et identification des fibres aminergiques par autoradiographie au microscope électronique. Z. Zellforsch. 106, 99–118 (1970)
Etkin, W.: Relation of the pars intermedia to the hypothalamus. In: Neuroendocrinology, Vol. II, pp. 261–282 (L. Martini and W.F. Ganong, eds.). New York-London: Academic Press 1967
Hadley Mac, E., Hruby, V.J., Bower, S.R.A.: Cellular mechanisms controlling melanophore stimulating hormone (MSH) release. Gen. comp. Endocr. 26, 24–35 (1975)
Holmes, R.L., Ball, J.N.: The pituitary gland. A comparative account. Cambridge: University Press 1974
Iturriza, F.C.: Monoamines and control of the pars intermedia of the toad pituitary. Gen. comp. Endocr. 6, 19–25 (1966)
Iturriza, F.C.: The secretion of intermedin in autotransplants of pars intermedia growing in the anterior chamber of intact and sympathectomized eyes of the toad. Neuroendocrinology 2, 11–18 (1967)
Iturriza, F.C.: Further evidences for the blocking effect of catecholamines on the secretion of melanocyte-stimulating hormone in toads. Gen. comp. Endocr. 12, 417–426 (1969)
Iturriza, F.C., Kasal-Iturriza, M.: Noradrenalin inhibition of MSH release in incubates of toad pars intermedia. Gen. comp. Endocr. Suppl. 3, 108–113 (1972)
Jørgensen, C.B.: Integrative functions of the brain. In: Physiology of the amphibia, Vol. II, pp. 1–51 (B. Lofts, ed.). New York-London: Academic Press 1974
Kastin, A.J., Viosca, S., Schally, A.V.: Regulation of melanocyte-stimulating hormone release. In: Handbook of physiology. Section 7: Endocrinology, Vol. IV. The pituitary gland and its neuroendocrine control, Part 2, pp. 551–562 (R.O. Greep and E.B. Astwood, eds.). Washington: American Physiological Society 1974
Kraicer, J., Gosbee, J.L., Bencosme, S.A.: Pars intermedia and pars distalis: two sites of ACTH production in the rat hypophysis. Neuroendocrinology 11, 156–176 (1973)
Lowry, P.J., Scott, A.P.: The evolution of vertebrate corticotrophin and melanocyte stimulating hormone. Gen. comp. Endocr. 26, 16–23 (1975)
Mey, J. de, Vandesande, F., Dierickx, K.: Identification of neurophysin producing cells. II. Identification of the neurophysin I and the neurophysin II producing neurons in the bovine hypothalamus. Cell Tiss. Res. 153, 531–543 (1974)
Moens, L.: Isolation of neurohypophysial hormones of Rana temporaria. Nature, 237, 268–269 (1972)
Moens, L.: Isolation of neurointermediate pituitary proteins of the frog (Rana temporaria) and their tentative identification as neurophysins. Gen. comp. Endocr. 22, 70–76 (1974)
Moriarty, C.M., Moriarty, G.C.: Bioactive and immunoactive ACTH in the rat pituitary: Influence of stress and adrenalectomy. Endocrinology 96, 1419–1425 (1975)
Moriarty. G.C., Halmi, N.S., Moriarty, C.M.: The effect of stress on the cytology and immunocytochemistry of pars intermedia cells in the rat pituitary. Endocrinology 96, 1426–1436 (1975)
Naik, D.V.: Immunohistochemical localization of adrenocorticotropin and melanocyte stimulating hormone in pars intermedia of rat hypophysis. Z. Zellforsch. 142, 289–304 (1973)
Naik, D.V.: Electron microscopic-immunocytochemical localization of adrenocorticotropin and melanocyte stimulating hormone in the pars intermedia cells of rats and mice. Z. Zellforsch. 142, 305–328 (1973)
Nakai, Y., Gorbman, A.: Evidence for a doubly innervated secretory unit in the anuran pars intermedia. II. Electron microscopic studies. Gen. comp. Endocr. 13, 108–116 (1969)
Saffran, M.: Chemistry of hypothalamic hypophysiotropic factors. In: Handbook of physiology. Section 7: Endocrinology, Vol. IV. The pituitary gland and its neuroendocrine control, Part 2, pp. 563–586 (R.O. Greep and E.B. Astwood, eds.). Washington: American Physiological Society 1974
Sternberger, L.A., Hardy, P.H., Jr., Cuculis, J.J., Meyer, H.G.: The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry. Preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 315–333 (1970)
Tilders, F.J.H., Mulder, A.H., Smelik, P.G.: On the presence of a MSH-release inhibiting system in the rat neurointermediate lobe. Neuroendocrinology 18, 125–130 (1975)
Vandesande, F., Dierickx, K.: Identification of the vasopressin producing and of the oxytocin producing neurons in the hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory system of the rat. Cell Tiss. Res. 164, 153–162 (1975)
Vandesande, F., Dierickx, K.: Immuno-cytochemical demonstration of the inability of the homozygous Brattleboro rat to synthesize vasopressin and vasopressin-associated neurophysin. Cell Tiss. Res. 165, 307–316 (1976)
Vandesande, F., Dierickx, K., Mey, J. de: Identification of the vasopressin-neurophysin II and the oxytocin-neurophysin I producing neurons in the bovine hypothalamus. Cell Tiss. Res. 156, 189–200 (1975)
Watkins, W.B.: Immunocytochemical identification of neurophysin-secreting neurons in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system of some non-mammalian vertebrates. Cell Tiss. Res. 162, 511–521 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Berta Scharrer on the accasion of her 70th birthday
This investigation was supported by a grant from the Belgian Nationaal Fonds voor Geneeskundig Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dierickx, K., Vandesande, F. Immuno-enzyme cytochemical demonstration of mesotocinergic nerve fibres in the pars intermedia of the amphibian hypophysis. Cell Tissue Res. 174, 25–33 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222148
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222148