Summary
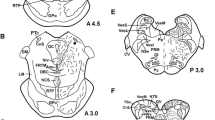
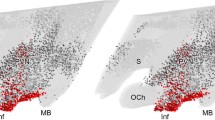
Immunocytological tests reveal the presence of a somatostatin-like substance in perikarya and axons in the brain of the giant slug Limax maximus L. Controls carried out on adjacent sections with absorbed antiserum or different antibodies raised against several biologically active peptides of vertebrates (ACTH-17-39, α- and β endorphin, α- and β MSH, methionin-enkephalin, TRH) demonstrate the specificity of the “staining”. However, some cells are both somatostatin- and FMRF-amide-positive. In the cerebral ganglia, the right Z-area cells, responsible for the synthesis of the maturation hormone (MH) are strongly somatostatin-positive. These results suggest a similarity between the MH and the somatostatin-like material contained in the Z-area cells. The simultaneous presence of two peptides in one and the same cell, the nature (elementary granules or soluble product) of the material, and its site of release are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geraerts WPM (1976) Control of growth by the neurosecretory hormone of the light green cells in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 29:61–71
Grimm-Jørgensen Y (1979) Effect of thyrotropin releasing factor on body weight of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Exp Zool 208:169–176
Grimm-Jørgensen Y (1983) Immunoreactive somatostatin in two pulmonate gastropods. Gen Comp Endocrinol 49:108–114
Grimm-Jørgensen Y, McKelvy JF, Jackson IMD (1975) Immunoreactive thyrotropin releasing factor in gastropod circumoesophageal ganglia. Nature 254:620
Larsson LI (1980) On the possible existence of multiple endocrine, paracrine and neurocrine messengers in secretory cells systems. Invest Cell Pathol 3:73–85
Marchand CR, Dubois MP (1981) Preliminary cytoimmunological observations in the brain of Helix aspersa Müller (Mollusc Gastropod). XIth Conf The Europ Soc Comp Endocrinol Jerusalem. Gen Comp Endocrinol 46:71
Marchand CR, Dubois MP (1982) Détection immunocytologique de matériel apparenté à différents peptides de Vertébrés dans le collier nerveux de l'Escargot (Helix aspersa Müller) J Physiol Paris 78:595–598
Marchand CR, Wijdenes J, Schot LPC (1982) Localisation par la technique cytoimmuno-enzymologique d'un neuropeptide cardio-excitateur (le FMRF-amide) dans le collier nerveux périoesophagien d'Helix aspersa Müller (Gastéropode, Pulmoné, Stylommatophore). CR Acad Sc Paris 294:39–44
McCrone EJ, Sokolove PG (1979) Brain-gonad axis and photoperiodically-stimulated sexual maturation in the slug, Limax maximus. J Comp Physiol 133:117–123
McCrone EJ, Minnen J Van, Sokolove PG (1981) Slug reproductive maturation hormone: In vivo evidence for long-day stimulation of secretion from brains and cerebral ganglia. J Comp Physiol 143:311–315
Minnen J Van, Sokolove PG (1981) Neurosecretory cells in the central nervous system of the giant garden slug, Limax maximus. J Neurobiol 12:297–301
Osborne NN, Cuello AC, Dockray GJ (1982) Substance P and cholecystokinin-like peptides in Helix neurons and cholecystokinin and serotonin in a giant neuron. Science 216:409–411
Scharrer B (1937) Über sekretorisch tätige Nervenzellen bei wirbellosen Tieren. Naturwissenschaften 25:131–138
Scharrer E (1928) Die Lichtempfindlichkeit blinder Elritzen. 1. Untersuchungen über das Zwischenhirn der Fische. Z vergl Physiol 7:1–38
Schot LPC, Boer HH, Swaab DF, Noorden S Van (1981) Immunocytochemical demonstration of peptidergic neurons in the central nervous system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis with antisera raised to biologically active peptides of vertebrates. Cell Tissue Res 216:273–291
Sokolove PG, McCrone EJ (1978) Reproductive maturation in the slug, Limax maximus, and the effects of artificial photoperiod. J Comp Physiol 125:317–325
Sokolove PG, Minnen J Van (1983) Control of reproductive development in the giant garden slug, Limax maximus. In: Lever J and Boer HH (eds) Molluscan neuroendocrinology, IMME 1982, 101–105
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1970) Ultrastructure and histochemistry of neurosecretory cells and neurohemal areas in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis L. Z Zellforsch 108:190–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchand, CR., Sokolove, P.G. & Dubois, M.P. Immimocytological localization of a somatostatin-like substance in the brain of the giant slug, Limax maximus L.. Cell Tissue Res. 238, 349–353 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217307
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217307