Summary
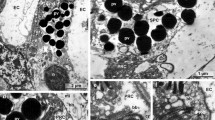
By use of a modified fixation technique, the receptor cells of the compound eye of the blowfly Calliphora erythrocephala were found to contain a regular, paracrystalline array of alternating rows of hexagonally shaped microvilli. The receptor cells R1 to R6 have a cell-specific number of microvilli per row in a cross section. Every microvillus has a filament cluster connecting the axial skeleton with the microvillar membrane. This cluster is preferentially right-left oriented relative to the longitudinal axis of the microvillar array. Three adjacent microvilli are interconnected by an electron-dense substance. A mirroring technique indicated that this intermicrovillar structure consists of three subunits, although these subunits could not be conclusively demonstrated by classical densitometry or image subtraction techniques. The electron-dense substance can be seen in all cross sections of the proximal and distal parts of the microvilli. They are cylindrical structures separating the microvilli along their entire length. It is suggested that these cylindrical aggregates contain an enzymatic complex separating the rhodopsin-containing microvillar membrane into six compartments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blest AD, Stowe S, Eddey W (1982) A labile, Ca2+-dependent cytoskeleton in rhabdomeral microvilli of the blowflies. Cell Tissue Res 223:553–573
Carlson SD, Chi C (1979) The functional morphology of the insect photoreceptor. Annu Rev Entomol 24:379–416
Franceschini N (1972) Pupil and pseudopupil in the compound eye of Drosophila. In: Wehner R (ed) Information processing in the visual systems of arthropods. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 75–82
Franceschini N (1975) Sampling of the visual environment by the compound eye of the fly: Fundamentals and applications. In: Snyder AW; Menzel R (ed) Photoreceptor optics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 98–125
Goldsmith TH, Wehner R (1977) Restrictions on rotational and translational diffusion of pigment in the membranes of a rhabdomeric photoreceptor. J Gen Physiol 70:453–490
Kirschfeld K (1972) The visual system of Musca: Studies on optics, structure and function. In: Wehner R (ed) Information processing in the visual systems of arthropods. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 61–74
Langer H (1966) Grundlagen der Wahrnehmung von Wellenlänge und Schwingungsebene des Lichtes. Verh der Deutschen Zool Gesellschaft, Suppl 30, 195–233
Paulsen R, Bentrop J (1986) Light-modulated biochemical events in fly photoreceptors. In: Lüttgauer (ed) Rheinland-Pfälzische-Akademie der Wissenschaften
Paulsen R, Bentrop J, Peters K (1984) Photochemistry and biochemistry of blowfly photoreceptor membranes. Vision Res 24:1700
Perrelet A (1970) The fine structure of the retina of the honey bee drone. An electron microscopical study. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 108:530–562
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
el-Gammal, S., Hamdorf, K. & Henning, U. The paracrystalline structure of an insect rhabdomere (Calliphora erythrocephala). Cell Tissue Res. 248, 511–518 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216477
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216477