Summary
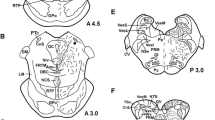
The presence of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the pedal ganglion of the bivalve mollusc Mytilus edulis has been demonstrated. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity is highly localized in those intraganglionic regions rich in dopamine-containing structures. In addition, FMRF-NH2-like (Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2) immunoreactivity was found to occur in intraganglionic regions that are devoid of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity. The differential topographic distribution of these peptidergic immunoreactivities suggests involvement in separate functions. By contrast, the closeness of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity to dopamine histofluorescence supports previous data demonstrating biochemical and physiological links between these two systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alumets J, Håkanson R, Sundler F, Thorell J (1979) Neuronal localization of immunoreactive enkephalin and β-endorphin in the earthworm. Nature 279:805–806
Bloom F, Fattenberg E, Rossier J, Ling N, Guillemin R (1978) Neurons containing β-endorphin in rat brain exist separately from those containing enkephalin: immunocytochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wash) 75:1591–1595
Dockray GJ, Vaillant C, Williams RG (1981) New vertebrate brain-gut peptide related to a molluscan neuropeptide and an opioid peptide. Nature 293:656–657
Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl A, Terenius L, Elde R, Wilson G (1977) Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substanceP. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wash) 74:3081–3085
Hong JS, Jang HY, Eratta W, Costa E (1977) Determination of met enkephalin in discrete regions of rat brain. Brain Res 134:383–386
Kobayashi R, Palkovits M, Miller RJ, Chang KJ, Cuatrecasas P (1978) Hypophysectomy does not alter rat brain enkephalin distribution. Life Sci 22:379–389
Kream RM, Zukin RS, Stefano GB (1980) Demonstration of two classes of opiate binding sites in the nervous tissue of the marine mollusc Mytilus edulis: Positive homotropic cooperativity of lower affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem 225(19):9218–9224
Martin R, Frosch D, Kiehling C, Voigt KH (1981) Molluscan neuropeptide-like and enkephalin-like material coexists in octopus nerves. Neuropeptides 2:141–150
Martin R, Frosch D, Weber E, Voigt KH (1979) Met-enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in a cephalopod neurohemal organ. Neurosci Lett 15:253–257
Martin R, Geis R, Holl R, Schafer M, Voigt KH Co-existence of unrelated peptides in oxytocin and vasopressin terminals of rat neurohypophyses: immunoreactive methionine leucine5enkephalin and cholecystokinin-like substances. Neurosciences, (in press)
Miller RJ, Pickel VM (1980) Immunohistochemical distribution of enkephalins: Interactions with catecholamine containing systems. In: Eränkö O (ed) Histochemistry of cell biology of autonomic neurons, SIF cells and paraneurons. Raven Press, New York 349–359, 1980
Moore RY, Bloom FE (1978) Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of dopamine systems. Ann Rev Neurosci 1:129–169
Osborne NN, Neuhoff V (1979) Are there opiate receptors in the invertebrates? J Pharm Pharmacol 31:481
Rémy Ch, Dubois MP (1979) Localization par immunofluorescence de peptides analogues à α-endorphine dans les ganglions infraoesophagiens du lombricide Dendrobaena subrubicunda Eisen. Experientia 35:137–138
Rémy CH, Dubois MP (1981) Immunohistological evidence of methionine enkephalin-like material in the brain of the migratory locust. Cell Tissue Res 218:271–278
Rémy Ch, Girardie J, Dubois MP (1978) Présence dans le ganglion sous-oesophagien de la Chenille processionnaire du Pin (Thaumetopoea pityocampa Schiff) de cellules revelées en immunofluorescence par un anticorps anti-α-endorphine. CR Acad Sci Paris Ser D 286:651–653
Rémy Ch, Girardie J, Dubois MP (1979) Vertebrate neuropeptide-like substances in the suboesophageal ganglion of two insects: Locusta migratoria R. and F. (Orthoptera) and Bombyx mori L. (Lepidoptera). Immunocytological investigation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 37:93–100
Sar N, Stumpf WERJ, Chang KJ, Cuatrecasas P (1978) Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat brain and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 182:17–38
Scharrer B (1978) Peptidergic neurons: facts and trends. Gen Comp Endocrinol 34:50–62
Simantov R, Kuhar MJ, Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1977) Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wash) 74:2167–2171
Stefano GB (1982) Comparative aspects of opioid-dopamine interaction. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2:167–178
Stefano GB, Aiello E (1975) Histofluorescent localization of serotonin and dopamine in the nervous system and gill of Mytilus edulis (Bivalvia). Biol Bull 148:141–156
Stefano GB, Catapane EJ (1978) Methionine enkephalin increases dopamine levels. Soc Neurosci Abstr 4:283
Stefano GB, Catapane EJ (1979) Enkephalins increase dopamine levels in the CNS of a marine mollusc. Life Sci 24:1617–1622
Stefano GB, Catapane EJ, Aiello E (1976) Dopaminergic agents: Influence in molluscan nervous system, Science, 194:539–541
Stefano GB, Kream RM, Zukin RS (1980) Demonstration of stereospecific opiate binding in the nervous tissue of the marine mollusc Mytilus edulis. Brain Res 181:445–450
Stefano GB, Kream RM, Zukin RS, Catapane EJ (1982) Seasonal variation of stereospecific enkephalin binding and dopamine responsiveness in Mytilus edulis pedal ganglia. In: Rozsa KS (ed) Neurotransmitters in Invertebrates Adv Physiol Sciences, Pergamon Press, London 22: 453–459
Stefano GB, Catapane EJ, Kream RM (1981a) Characterization of the dopamine stimulated adenylate cyclase in the pedal ganglia of Mytilus edulis: Interactions with etorphine, β-endorphin DALA and methionine enkephalin. Cell Mol Neurobiol 1:57–68
Stefano GB, Hall B, Makman MH, Dvorkin B (1981b). Opioids inhibit potassium-stimulated dopamine release in the marine mussel Mytilus edulis and in the cephalopod Octopus bimaculatus. Science, 213:928–930
Sternberger LH, Hardy PH, Cuculis JJ, Meyer HG (1970) The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 18:315–333
Venturini G, Carolei A, Palladini G, Margotta V, Cerbo R (1981) Naloxone enhances cAMP levels in Planaria. Comp Biochem Physiol 69c: 105–108
Weber E, Evans CJ, Samuelson SJ, Barchas JD (1981) A novel peptide neuronal system in rat brain and pituitary. Science 214:1248–1251
Zipser B (1980) Identification of specific leech neurons immunoreactive to enkephalin. Nature 283:857–858
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work supported by NIH-MBRS Grant RR 08180 (GBS) and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 87/B2, RM).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stefano, G.B., Martin, R. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the pedal ganglion of Mytilus edulis (Bivalvia) and its proximity to dopamine-containing structures. Cell Tissue Res. 230, 147–153 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216035
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216035