Summary
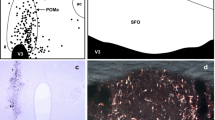
Restricted numbers of substance P-like-immuno-reactive (SPL-IR) neurons were demonstrated in the photosensory pineal organ of the rainbow trout. The small parapineal organ of this teleost species receives a distinct SPL-IR innervation via the habenular nuclei, but displays no intrinsic SPL-IR neurons. Intrapineal SPL-IR neurons were located in the rostral portion of the pineal end-vesicle. Neuronal somata were found in a lateral position with smooth axonal processes extending mediad. Immunoreactive somata and axonal processes were observed intraparenchymally as well as in the pineal lumen. The pattern of immunoreactivity was not changed in excised pineal organs that had been incubated in tissue culture medium in the dark for 18 h. The possibility that the intrapineal SPL-IR neurons are not part of the neural circuitry involved in the transduction of photic information, but may have other functions, is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolz J, Thier P (1985) Photopic action of thyrotropin-releasing hormone in the cat retina. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 224:463–473
Borg B, Ekström P, van Veen Th (1983) The parapineal organ of teleosts. Acta Zool (Stockh) 64:211–218
Brecha N (1983) A review of retinal neurotransmitters: Histochemical and biochemical studies. In: Emson PC (ed) Neurochemical anatomy. Raven press, New York, pp 85–129
Dick E, Miller RF (1981) Peptides influence retinal ganglion cells. Neurosci Lett 26:131–135
Dodt E (1963) Photosensitivity of the pineal organ in the teleost, Salmo irideus (Gibbons). Experientia 19:642–643
Dodt E, Scherer E (1968) Photic responses from the parietal eye of the lizard, Lacerta sicula campestris (de Betta). Vision Res 8:61–72
Dowling JE, Dubin MW (1984) The vertebrate retina. In: Brookhart JM, Mountcastle VB (eds) Handbook of physiology — the nervous system III, part 1. Am Physiol Soc, Bethesda, pp 317–339
Ekström P (1985) Anterograde and retrograde filling of central neuronal systems with horseradish peroxidase under in vitro conditions. J Neurosci Methods 15:21–35
Ekström P (1986) Photoreceptors and CSF-contacting neurons in the pineal organ of a teleost fish have direct axonal connections with the brain: an HRP-electron microscopic study. (Submitted for publication (J Neurosci))
Ekström P, Korf H-W (1985) Pineal neurons projecting to the brain of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri (Richardson) (Teleostei). In vitro retrograde filling with horseradish peroxidase. Cell Tissue Res 240:693–700
Ekström P, Korf H-W (1986) Putative cholinergic elements in the photosensory pineal organ and retina of a teleost, Phoxinus phoxinus L (Cyprinidae). Distribution of ChAT immunoreactivity, AChE-positive elements, and pinealofugally projecting neurons. Cell Tissue Res. Please fill in the correct page numbers for MS No. 565
Ekström P, Meissl H (1986) Physiological and morphological characterization of pineal photoreceptors: intracellular recordings combined with HRP and Lucifer yellow staining. Pflügers Arch [Suppl] (in press)
Ekström P, van Veen Th (1984) Pineal neural connections with the brain in two teleosts, the crucian carp and the European eel. J Pineal Res 1:245–261
Eldred WD, Nolte J (1981) Multiple classes of photoreceptors and neurons in the frontal organ of Rana pipiens. J Comp Neurol 203:269–295
Engbretson GA, Reiner A, Brecha N (1981) Habenular assymmetry and the central connections of the parietal eye of the lizard. J Comp Neurol 198:155–165
Engbretson GA, Brecha N, Reiner A (1982) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in the parietal eye visual system of the lizard Uta stansburiana. Cell Tissue Res 227:543–554
Glickman RD, Adolph AR, Dowling JE (1982) Inner plexiform circuits in the carp retina: Effects of cholinergic agonists, GABA, and substance P on the ganglion cells. Brain Res 234:81–99
Gurusinghe CJ, Ehrlich D (1985) Sex-dependent asymmetry of the medial habenular nucleus of the chicken brain. Cell Tissue Res 240:149–152
Kappers JA (1965) Survey of the innervation of the epiphysis cerebri and the accessory pineal organs of vertebrates. Prog Brain Res 10:87–153
Korf H-W (1974) Acetylcholinesterase-positive neurons in the pineal and parapineal organs of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri (with special reference to the pineal tract). Cell Tissue Res 155:475–489
Korf H-W (1976) Histological, histochemical and electron microscopical studies on the nervous apparatus of the pineal organ in the tiger salamander, Ambystoma tigrinum. Cell Tissue Res 174:475–497
Korf H-W, Møller M (1985) The central innervation of the mammalian pineal organ. In: Mess B, Ruzsas Cs, Tima L, Pévet P (eds) The pineal gland. Current state of pineal research. Akademiai Kiàdo, Budapest, pp 47–69
Mariani AP, Kolb H, Nelson R (1984) Dopamine-containing amacrine cells of rhesus monkey retina parallel rods in spatial distribution. Brain Res 322:1–7
Meissl H, Dodt E (1981) Comparative physiology of pineal photoreceptor organs. In: Oksche A, Pévet P (eds) The pineal organ: Photobiology — Biochronometry — Endocrinology. Elsevier, North Holland Biomedical Press, pp 61–80
Meissl H, Ekström P (1986) Rod- and cone-like components of pineal photoreceptor responses. Pflügers Arch (in press)
Meissl H, George S (1984) Electrophysiological studies on neuronal transmission in the frog's photosensory pineal organ. The effect of amino acids and biogenic amines. Vision Res 24:1727–1734
Meissl H, George S (1985) Effect of GABA and its antagonists, bicuculline and picrotoxin, on nerve cell discharges of the photosensory pineal organ of the frog, Rana esculenta. Brain Res 332:39–46
Morita Y (1966) Entladungsmuster pinealer Neurone der Regenbogenforelle (Salmo irideus) bei Belichtung des Zwischenhirns. Pflügers Arch 289:155–167
Naka K-I (1980) A class of catfish amacrine cells responds preferentially to objects which more vertically. Vision Res 20:961–965
Neary TJ, Northcutt RG (1983) Nuclear organization of the bull-frog diencephalon. J Comp Neurol 213:262–278
Omura Y (1984) Pattern of synaptic connections in the pineal organ of the ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis (Teleostei). Cell Tissue Res 236:611–617
Pu GA, Dowling JE (1981) Anatomical and physiological characteristics of pineal photoreceptor cell in the larval lamprey, Petromyzon marinus. J Neurophysiol 46:1018–1038
Schnitzlein HN (1962) The habenula and the dorsal thalamus of some teleosts. J Comp Neurol 118:225–267
Tamura T, Hanyu I (1980) Pineal photosensitivity in fishes. In: Ali MA (ed) Environmental physiology of fishes. Nato Advanced Study Institute Series A: Life sciences, vol 35. Plenum Press, New York, pp 477–496
Thier P, Wässle H (1984) Indoleamine-mediated reciprocal modulation of on-centre and off-centre ganglion cell activity in the retina of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 351:613–630
Vaillant C, Bu'Lock A, Dimaline R, Dockray GJ (1982) Distribution and development of peptidergic nerves and gut endocrine cells in mice with congenital aganglionic colon, and their normal littermates. Gastroenterology 82:291–300
Vigh-Teichmann I, Vigh B, Aros B (1973) CSF contacting axons and synapses in the lumen of the pineal organ. Z Zellforsch 144:139–152
Vigh-Teichmann I, Korf H-W, Oksche A, Vigh B (1982) Opsinimmunoreactive outer segments and acetylcholinesterase-positive neurons in the pineal complex of Phoxinus phoxinus (Teleostei, Cyprinidae). Cell Tissue Res 227:351–369
Vigh-Teichmann I, Korf H-W, Nürnberger F, Oksche A, Vigh B, Olsson R (1983) Opsin-immunoreactive outer segments in the pineal and parapineal organs of the lamprey (Lampetra fluviatilis), the eel (Anguilla anguilla), and the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Cell Tissue Res 230:289–307
Wake K (1973) Acetylcholinesterase-containing nerve cells and their distribution in the pineal organ of the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Z Zellforsch 145:287–298
Wake K, Ueck M, Oksche A (1974) Acetylcholinesterase-containing nerve cells in the pineal complex and subcommissural area of the frogs, Rana ridibunda and Rana esculenta. Cell Tissue Res 154:423–442
Wheeler TG (1982) Color vision and retinal chromatic information processing in teleost: a review. Brain Res Rev 4:177–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Fellow of the Alexander von Humboldt-Stiftung, Bonn, Federal Republic of Germany
Supported by research funds from the Deutsche Forschungsge-meinschaft (Ko 758/2-4)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ekström, P., Korf, H.W. Substance P-like-immunoreactive neurons in the photosensory pineal organ of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson (Teleostei). Cell Tissue Res. 246, 359–364 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215898
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215898