Abstract
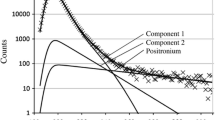
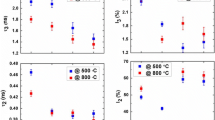
Positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS) has been used to study the vacancy-type defects in fine-particle goethites (α-FeOOH). The PALS spectra reveal three components. The intermediate lifetime component (τ2, I2) is attributed to positrons trapped at vacancy defects. The relative intensity of the intermediate lifetime component, I2, increases significantly with decreasing Néel temperature, and this increase is attributed to increasing concentration of vacancy defects. These results support a model of magnetic ordering of clusters arising from a high concentration of iron vacancies which reduces the Néel temperature in these fine-particle goethites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bocquet S, Kennedy SJ (1992) The Néel temperature of fine particle goethite. J Magn Magn Mat 109:260–264
Bocquet S, Pollard RJ, Cashion JD (1992) Dynamic magnetic phenomena in fine-particle goethite. Phys Rev B 46:11657–11664
Brandt W (1967) Positron annihilation in molecular substances and ionic crystals. In: Stewart AT, Roellig LO (eds) Positron Annihilation, Academic, New York, pp 155–182
Brož D, Straková J, Šubrt J, Vinš J, Sedlák B, Reiman SI (1990) Mössbauer spectroscopy of goethite of small particle size. Hyperfine Interact 54:479–482
Chambaere D, De Grave E (1984) On the Néel temperature of β-FeOOH structural dependence and its implications. J Magn Magn Mater 42:263–268
Coey JMD, Barry A, Brotto J-M, Rakoto H, Brennan S, Mussel WN, Collomb A, Fruchart D (1995) Spin flop in goethite. J Phys Condens Matter 7:759–768
De Grave E, Persoons RM, Chambaere DG, Vandenberghe RE, Bowen LH (1986) An 57Fe Mössbauer effect study of poorly crystalline γ-FeOOH. Phys Chem Minerals 13:61–67
Forsyth JB, Hedley IG, Johnson CE (1968) The magnetic structure and hyperfine field of goethite (α-FeOOH). J Phys C 1:179–188
Gidley DW, Marko KA, Rich A (1976) Precision measurement of the decay rate of orthopositronium in SiO2 powders. Phys Rev Lett 36:395–398
Hall TM, Goland AN, Snead CL (1974) Applications of positron-lifetime measurements to the study of defects in metals. Phys Rev B 10:3062–3074
Harris AB, Kirkpatrick S (1977) Low-frequency response functions of random magnetic systems. Phys Rev B 16:542–576
Hautöjarvi P (ed) (1979) Positrons in solids, Springer, Heidelberg
Hill AJ, Katz IM, Jones PL, Pagano RP (1991) The study of the high temperature superconductor Y-Ba-Cu-O by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy. Physica C 176:64–74
MacKenzie IK, Khoo TL, McDonald AB, McKee BTA (1967) Temperature dependence of positron mean lives in metals. Phys Rev Lett 19:946–948
Mascher P, Dannefaer S, Kerr D (1989) Positron trapping rates and their temperature dependencies in electron-irradiated silicon. Phys Rev B 40:11764–11771
Mørup S, Madsen MB, Franck J, Villadsen J, Koch CJW (1983) A new interpretation of Mössbauer spectra of micro-crystalline goethite: “superferromagnetism” or “super-spin-glass” behaviour? J Magn Magn Mater 40:163–174
Murad E, Johnston JH (1987) Iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. In: Long GJ (ed) Mössbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Inorganic Chemistry, Vol. 2, Plenum, New York, pp 507–582
Pollard RJ, Pankhurst QA, Zientek P (1991) Magnetism in aluminous goethite. Phys Chem Minerals 18:259–264
Puff W (1983) PFPOSFIT: A new version of a program for analyzing positron lifetime spectra with non-gaussian prompt curve. Comput Phys Commun 30:359–368
Puska MJ, Nieminen RM (1994) Theory of positrons in solids and on solid surfaces. Rev Mod Phys 66:841–897
Rochette P, Fillion G (1989) Field and temperature behaviour of remanence in synthetic goethites: paleomagnetic implications. Geophys Res Lett 16:851–854
St. Pierre TG, Sipos P, Chan P, Chua-Anusorn A, Bauchspiess KR, Webb J (1993) Synthesis of nanoscale iron oxide structures using protein cages and polysaccharide networks. In: Hadjipanayis GC, Siegel RW (eds) Nanophase Materials: Synthesis — Properties — Applications (NATO ASI series), Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 49–56
Schwertmann U, Cambier P, Murad E (1985) Properties of goethites of varying crystallinity. Clays Clay Min 33:369–378
Schwertmann U, Taylor RM (1977) Iron oxides. In: Dixon JB, Weed SB (eds) Minerals in Soil Environments, Soil Sci Soc America, Madison, p 159
Sedov VE (1990) Diffusion Model of Superparamagnetic Relaxation. Hyperfine Interact 56:1491–1494
Seeger A (1973) Investigation of point defects in equilibrium concentrations with particular reference to positron annihilation techniques. J Phys F: Metal Phys. 3:248–294
Seeger A, Banhart E (1987) On the systematics of positron lifetimes in metals. Phys Stat Sol (a) 102:171–179
Shinjo T (1966) Mössbauer Effect in Antiferromagnetic Fine Particles. J Phys Soc Jpn 21:917–922
Siegel RW (1980) Positron annihilation spectroscopy. Ann Rev Mater Sci 10:393–425
Taylor RM (1987) Non-silicate oxides and hydroxides. In: Newman ACD (ed) Chemistry of Clays and Clay Minerals, Longman/Mineralogical Society, London, pp 134–140
van der Kraan AM (1972) Mössbauer effect studies of superparamagnetic α-FeOOH and α-Fe2O3. PhD Thesis, Technische Hogeschoo Delft, Netherlands
van der Woude F, Dekker AJ (1966) Mössbauer effect in α-FeOOH. Phys Stat Sol 13:181–193
van Oosterhout GW (1965) The structure of goethite. Proc Intl Conf on Magnetism, Nottingham 1964, Institute of Physics and Physical Society, London pp 529–532
Yamamoto N (1968) The particle size dependence of the Néel temperature of α-FeOOH fine particles. Bull Inst Chem Res Kyoto Univ 46:283–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bocquet, S., Hill, A.J. Correlation of Néel temperature and vacancy defects in fine-particle goethites. Phys Chem Minerals 22, 524–528 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209379
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209379