Summary
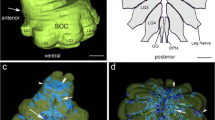
We used physiological recordings, intracellular dye injections and immunocytochemistry to further identify and characterize neurons in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia calif ornica expressing Small Cardioactive Peptide-like immunoreactivity (SCP-LI). Neurons were identified based upon soma size and position, input from premotor cells B4 and B5, axonal projections, muscle innervation patterns, and neuromuscular synaptic properties. SCP-LI was observed in several large ventral neurons including B6, B7, B9, B10, and B11, groups of s1 and s2 cluster cells, at least one cell located at a branch point of buccal nerve n2, and the previously characterized neurons B1, B2 and B15.
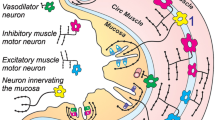
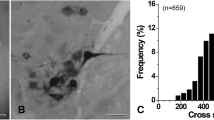
B6, B7, B9, B10 and B11 are motoneurons to intrinsic muscles of the buccal mass, each displaying a unique innervation pattern and neuromuscular plasticity. Combined, these motoneurons innervate all major intrinsic buccal muscles (I1/I3, I2, I4, I5, I6). Correspondingly, SCP-LI processes were observed on all of these muscles. Innervation of multiple nonhomologous buccal muscles by individual motoneurons having extremely plastic neuromuscular synapses, represents a unique form of neuromuscular organization which is prevalent in this system. Our results show numerous SCPergic buccal motoneurons with widespread ganglionic processes and buccal muscle innervation, and support extensive use of SCPs in the control of feeding musculature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SCP-LI :
-
small cardioactive peptide-like immunoreactivity
- PSC :
-
postsynaptic current
- EPSP :
-
excitatory postsynaptic potential
- IPSP :
-
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
- FI :
-
facilitation index
- TMR :
-
time to maximal response
References
Abrams TW, Castellucci VF, Camarado JS, Kandel ER, Lloyd PE (1984) Two endogenous neuropeptides modulate the gill and siphon withdrawal reflex in Aplysia by presynaptic facilitation involving cAMP-dependent closure of a serotonin-sensitive potassium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7956–7960
Alevizos A, Weiss KR, Koester J (1989) SCP-containing R20 neurons modulate respiratory pumping in Aplysia. J Neurosci 9(9): 3058–3071
Atwood HL (1973) An attempt to account for the diversity of crustacean muscles. Am Zool 13:357–378
Bishop CA, Wine JJ, O'Shea M (1984) Neuropeptide proctolin in postural motoneurons of the crayfish. J Neurosci 4(8): 2001–2009
Calabrese RL (1989) Modulation of muscle and neuromuscular junctions in invertebrates. Semin The Neurosci 1:25–34
Church PJ, Kirk MD (1988a) Identification and characterization of peptidergic motoneurons in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia californica using intracellular dye injections and immunocyto-chemistry. Biol Bull 175(2):315
Church PJ, Kirk MD (1988b) Further localization of SCPBergic neurons in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia californica. Neurosci Abstr 14(1): 535
Coates CJ, Bulloch AG (1985) Synaptic plasticity in the molluscan peripheral nervous system: physiology and role for peptides. J Neurosci 5(10): 2677–2684
Cohen KP, Kirk MD (1990) Individual buccal motoneurons of Aplysia californica innervate multiple buccal muscles and display unique neuromuscular synaptic plasticities. Soc Neurosci Abstr 16:1227
Cohen JL, Weiss KR, Kupfermann I (1978) Motor control of buccal muscles in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 41:157–180
Cropper EC, Lloyd PE, Reed W, Tenenbaum W, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1987a) Multiple neuropeptides in cholinergic motoneurons of Aplysia: Evidence for modulation intrinsic to the motor circuit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3486–3490
Cropper EC, Tenenbaum R, Kolks MAG, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1987b) Myomodulin: a bioactive neuropeptide present in an identified cholinergic buccal motor neuron of Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5483–5486
Cropper EC, Miller MW, Tenenbaum R, Kolks MAG, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1988) Structure and action of buccalin: a modulatory neuropeptide localized to an identified small cardioactive peptide-containing cholinergic motor neuron of Aplysia californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6177–6181
Cropper EC, Price D, Tenenbaum R, Kupfermann I (1990) Release of peptide cotransmitters from a cholinergic motor neuron under physiological conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:933–937
Fiore L, Meunier JM (1979) Synaptic connections and functional organization in Aplysia buccal ganglia. J Neurobiol 10(1):13–29
Gardner D (1971) Bilateral symmetry and interneuronal organization in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia. Science 173:550–553
Goldstein R, Kistler HB Jr., Steinbusch HWM, Schwartz JH (1984) Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in juvenile Aplysia. J Neurosa 11:535–547
Goldstein RS, Schwartz JH (1989) Catecholamine neurons in Aplysia: Improved light-microscope resolution and ultrastructural study using paraformaldehyde and glutaraldehyde (FaGlu) cytochemistry. J Neurobiol 20(4): 203–218
Greenberg MJ, Price DA (1983) Invertebrate neuropeptide: native and naturalized. Annu Rev Physiol 45:271–288
Hess SD, Prior DJ (1989) Small cardioactive peptide B modulates Limax feeding motoneurones. J Exp Biol 142:473–478
Howells HH (1942) The structure and function of the alimentary canal of Aplysia punctata. Q J Microsc Sci 83:357–397
Jan LY, Jan YN (1982) Peptidergic transmission in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. J Physiol (Lond) 327:219–246
Kandel ER (1979) Behavioral biology of Aplysia. WH Freeman, San Fransisco CA
Kirk MD (1989) Premotor neurons in the feeding system of Aplysia. J Neurobiol 20(5):497–512
Kow LM, Pfaff DW (1988) Neuromodulatory actions of peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 28:163–188
Krieger DT (1983) Brain peptides: What, Where, Why? Science 222:975–985
Kreiner T, Kirk MD, Scheller RH (1987) Cellular and synaptic morphology of a feeding motor circuit in Aplysia californica. J Comp Neurol 264(3): 311–325
Kupfermann I (1974a) Feeding behavior in Aplysia: a simple system for the study of motivation. Behav Biol 10:1–26
Kupfermann I (1974b) Dissociation of the appetitive and consummatory phases of feeding behavior in Aplysia: a lesion study. Behav Biol 10:89–97
Lehman HK, Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1984) The FMRFamide-like neuropeptide of Aplysia is FMRFamide. Biol Bull 167:460–466
Lloyd PE (1988) Fast axonal transport of modulatory neuropeptides from central ganglia to components of the feeding system in Aplysia. J Neurosci 8(9): 3507–3514
Lloyd PE, Willows AOD (1980) Identified peptidergic neurons activate the feeding motor program of Tritonia. Soc Neurosci Abstr 6:704
Lloyd PE, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1984) Evidence for parallel actions of a molluscan neuropeptide and serotonin in mediating arousal in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:2934–2937
Lloyd PE, Mahon AC, Kupfermann I, Cohen JL, Scheller RH, Weiss KR (1985) Biochemical and immunocytochemical localization of molluscan small cardioactive peptides in the nervous system of Aplysia californica. J Neurosci 5:1851–1861
Lloyd PE, Schacher S, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1986) Release of neuropeptides during intracellular stimulation of single identified Aplysia neurons in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:2934–2937
Lloyd PE, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1987) Sequence of small cardioactive peptide a: a second member of a class of neuropeptides in Aplysia. Peptides 8:179–184
Lloyd PE, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1988) Central peptidergic motoneurons regulate gut motility in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 59(5):1613–1626
Mahon AC, Lloyd PE, Weiss KR, Kupfermann I, Scheller RH (1985) The small cardioactive peptides a and b of Aplysia are derived from a common precursor molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3925–3929
Mayeri E, Rothman BS, Brownell PH, Branton WD, Padgett L (1985) Nonsynaptic characteristics of neurotransmission mediated by egg-laying hormone in the abdominal ganglion of Aplysia. J Neurosci 5:2060–2077
McAllister LB, Scheller RH, Kandel ER, Axel R (1983) In situ hybridization to study the origin and fate of identified neurons. Science 222:800–808
McCaman MW, Weinreich D, McCaman RE (1973) The determination of picomole levels of 5-HT and dopamine in Aplysia, Tritonia, and leech nervous tissues. Brain Res 53:129–137
Miller MW, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1988) Characterization of SCPB immunoreactive cells in the buccal ganglion of Aplysia. Neurosci Abstr 14:536
Morris HR, Panico M, Karplus A, Lloyd PE, Piniker B (1982) Ellucidation by FAB-MS of the structure of a new cardioactive peptide from Aplysia. Nature 300:643–645
Murphy AD, Lukowiak K, Stell WK (1985) Peptidergic modulation of patterned motor activity in identified neurons in Helisoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7140–7144
Nagahama T, Takata M (1988) Food-induced firing patterns in motoneurons producing jaw movements in Aplysia kurodai. J Comp Physiol A 162:729–738
Ocorr KA, Byrne JH (1986) Evidence for separate receptors that mediate parallel effects of serotonin and small cardioactive peptide b (SCPb) on adenylate cyclase in Aplysia californica. Neurosci Lett 70:283–288
Ono JK (1989) Synaptic connections in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia mediated by an identified neuron containing a CCK/gastrinlike peptide co-localized with acetylcholine. Brain Res 493:212–224
O'Shea M, Schaefer M (1985) Neuropeptide function: the invertebrate contribution. Annu Rev Neurosci 8:171–198
Plummer MR, Kirk MD (1990) Premotor neurons B51 and B52 in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia californica: synaptic connections, effects on ongoing motor rhythms, and peptide modulation. J Neurophysiol 63(3): 539–558
Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1977) The structure of a molluscan cardioexcitatory neuropeptide. Science 197:670–671
Prior DJ, Watson WH (1988) The molluscan neuropeptide, SCPB, increases the responsiveness of the feeding motor program of Limax maximus. J Neurobiol 19:87–105
Rathouz MM, Kirk MD (1988) Localization of catecholamines in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia californica. Brain Res 458:170–175
Richmond JE, Murphy AD, Bulloch AGM, Lukowiak K (1986) Evidence for an excitatory effect of GABA on feeding patterned motor activity of Helisoma trivolvis. Neurosci Abstr 12:792
Reed W, Weiss KR, Lloyd PE, Kupfermann I, Chen M, Bailey CH (1988) Association of neuroactive peptides with the protein secretory pathway in identified neurons of Aplysia californica: immunolocalization of SCPA and SCPB to the contents of dense-core vesicles and the trans face of the Golgi apparatus. J Comp Neurol 272:358–369
Scott ML, Govind CK, Kirk MD (1991) Neuromuscular organization of the buccal system in Aplysia californica. J Comp Neurol (in press)
Shyamala M, Nambu JR, Scheller RH (1986) Expression of the egg-laying hormone gene family in the head ganglia of Aplysia. Brain Res 371:49–57
Sossin WS, Kirk MD, Scheller RH (1987) Peptidergic modulation of neuronal circuitry controlling feeding in Aplysia. J Neurosci 7(3):671–681
Strumwasser F (1967) Types of information stored in single neurons. In: Wiersma CAG (ed) Invertebrate nervous systems. Univ Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 291–319
Susswein AJ, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1976) The stimulus control of biting in Aplysia. J Comp Physiol 108:75–96
Susswein AJ, Weiss KR, Kupfermann I (1978) The effects of food arousal on the latency of biting in Aplysia. J Comp Physiol 123:31–41
Taussig R, Sweetcordero A, Scheller RH (1989) Modulation of ionic currents in Aplysia motoneuron B15 by serotonin, neuropeptides and second messengers. J Neurosci 9(9): 3218–3229
Weiss KR, Koch UT, Koester J, Rosen SC, Kupfermann I (1982) The role of arousal in modulating feeding behavior of Aplysia: neural and behavioral studies. In: Hoebel BG, Novin D (eds) The neural basis of feeding and reward. Haer Institute, Brunswick, ME, pp 25–57
Weiss KR, Chiel HJ, Koch U, Kupfermann I (1986) Activity of an identified histaminergic neuron, and its possible role in arousal of feeding behavior in semi-intact Aplysia. J Neurosci 6(8): 2403–2415
Whim MD, Lloyd PE (1989) Frequency-dependent release of peptide cotransmitters from identified cholinergic motor neurons in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9034–9038
Willows AOD, Lloyd PE, Masinovsky BP (1988) Multiple transmitter types in Trifonia. III. Modulation of central pattern generator controlling feeding. J Neurobiol 19:69–86
Zoran MJ, Haydon PG, Matthews PJ (1989) Aminergic and peptidergic modulation of motor function at an identified neuromuscular junction in Helisoma. J Exp Biol 142:225–243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Church, P.J., Cohen, K.P., Scott, M.L. et al. Peptidergic motoneurons in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia californica Immunocytochemical, morphological, and physiological characterizations. J Comp Physiol A 168, 323–336 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198352
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198352