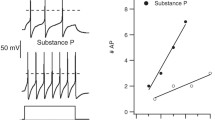
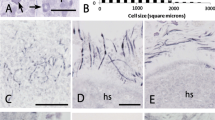
Abstract
In anaesthetized rats, intracellular recordings were made from the somata of lumbar (L4 and L5) dorsal root ganglion cells. The impaled afferent units were first functionally classified by testing the peripheral receptive endings with mechanical stimuli and then iontophoretically injected with a fluorescent dye. Serial sections of the dorsal root ganglion containing the injected soma were incubated with an antibody solution against calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). Somata displaying calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactivity (CGRP-IR) possessed receptive endings in the skin and deep somatic tissues (muscle, fascia, tendon, joint). The majority of calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive (CGRP-ir) neurones had conduction velocities below 2.5 m/s; only a few neurones conducted faster than 10 m/s. The immunostained somata were small to mediumsized (cross-sectional area < 1200 μm2). With one exeption, CGRP-IR was found in all types of ending studied, but the proportion of CGRP-ir neurones differed. Immunostained somata were rare among cutaneous and deep low-threshold mechanosensitive units (e.g. hair follicle and muscle spindle units). CGRP-ir somata were most frequent among high-threshold mechanosensitive (presumably nociceptive) afferent neurones (four out of six cells). The data suggest that CGRP can be expressed not only in nociceptive but also in many other types of primary afferent neurone, the condition being that the conduction velocity is slow and/or the cell soma small.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carr PA, Yamamoto T, Nagy JI (1990) Calcitonin gene-related peptide in primary afferent neurons of rat: co-existence with fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase and depletion by neonatal capsaicin. Neuroscience 36:751–760
Chung K, Lee WT, Carlton SM (1988) The effects of dorsal cord isolation on calcitonin gene-related peptide-labeled terminals in the rat lumbar dorsal horn. Neurosci Lett 90:27–32
Forssmann W-G, Pickel V, Reinecke M, Hock D, Metz J (1981) Immunochemistry and immunocytochemistry of nervous tissue. In: Heym CH, Forssman W-G (eds) Techniques in neuroanatomical research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 171–205
Gibson SJ, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Sabate IM, Mulderry PM, Ghatei MA, McGregor GP, Morrison JFB, Kelly JS, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of man and of eight other species. J Neurosci 4:3101–3111
Hanesch U, Heppelmann B, Schmidt RF (1991) Substance P- and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in primary afferent neurons of the cat's knee joint. Neuroscience 45:185–193
Harper AA, Lawson SN (1985a) Conduction velocity is related to morphological cell type in rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol 359:31–46
Harper AA, Lawson SN (1985b) Electrical properties of rat dorsal root ganglion neurones with different peripheral nerve conduction velocities. J Physiol 359:47–63
Hayes CE, Goldstein IJ (1974) A α-d-galactosyl-binding lectin from Bandeiraea simplicifolia seeds. J Biol Chem 249:1904–1914
Hoheisel U, Mense S (1987) Observations on the morphology of axons and somata of slowly conducting dorsal root ganglion cells in the cat. Brain Res 423:269–278
Hoheisel U, Lehmann-Willenbrock E, Mense S (1989) Termination patterns of identified group II and III afferent fibres from deep tissues in the spinal cord of the cat. Neuroscience 28:495–507
Hunt CC (1990) Mammalian muscle spindle: peripheral mechanisms. Physiol Rev 70:643–663
Hunt SP, Rossi J (1985) Peptide- and non-peptide-containing unmyelinated primary afferents: the parallel processing of nociceptive information. Philos Trans R Soc Lond [Biol] 308:283–289
Ishida-Yamamoto A, Tohyama M (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the nervous tissue. Prog Neurobiol 33:335–386
Ju G, Hökfelt T, Brodin E, Fahrenkrug J, Fischer AJ, Frey P, Elde RP, Brown JC (1987) Primary sensory neurons of the rat showing calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity and their relation to substance P-, somatostatin-, galanin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and cholecystokinin-immunoreactive ganglion cells. Cell Tissue Res 247:417–431
Kakudo K, Hasegawa H, Komatsu N, Nakamura A, Itoh Y, Watanabe K (1988) Immuno-electron microscopic study of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in axis cylinders of the vagus nerve. CGRP is present in both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers. Brain Res 440:153–158
Kow LM, Pfaff DW (1979) Responses of single units in sixth lumbar dorsal root ganglion of female rats to mechanostimulation relevant for lordosis reflex. J Neurophysiol 42:203–213
Kruger L, Silverman JD, Manthy PW, Sternini C, Brecha NC (1989) Peripheral patterns of calcitonin gene-related peptide general somatic sensory innervation: cutaneous and deep terminations. J Comp Neurol 280:291–302
Kuraishi Y, Nanayama T, Ohno H, Minami M, Satoh M (1988) Antinociception induced in rats by intrathecal administration of antiserum against calcitonin gene-related peptide. Neurosci Lett 92:325–329
Leah JD, Cameron AA, Snow PJ (1985) Neuropeptides in physiologically identified mammalian sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett 56:257–263
Lee KH, Chung K, Chung MJ, Coggeshall RE (1986) Correlation of cell body size, axon size, and signal conduction velocity for individually labelled dorsal root ganglion cells in the cat. J Comp Neurol 243:335–346
Lee Y, Takami K, Kawai Y, Girgis S, Hillyard CJ, MacIntyre I, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1985) Distribution of calcitonin generelated peptide in the rat peripheral nervous system with reference to its coexistence with substance P. Neuroscience 15:1227–1237
Light AR, Perl ER (1979) Spinal termination of functionally identified primary afferent neurons with slowly conducting myelinated fibers. J Comp Neurol 186:133–150
Lynn B, Carpenter SE (1982) Primary afferent units from the hairy skin of the rat hind limb. Brain Res 238:29–43
Marx JL (1979) Brain peptides: is substance P a transmitter of pain signals? Science 205:886–889
McCarthy PW, Lawson SN (1989) Cell type and conduction velocity of rat primary sensory neurons with substance P-like immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 28:745–753
McCarthy PW, Lawson SN (1990) Cell type and conduction velocity of rat primary sensory neurons with calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 34:623–632
Molander C, Ygge J, Dalsgaard C-J (1987) Substance P-, somatostatin- and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity and fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase-activity in relation to retrogradely labeled cutaneous, muscular and visceral primary sensory neurons in the rat. Neurosci Lett 74:37–42
Morton CR, Hutchison WD (1989) Release of sensory neuropeptides in the spinal cord: studies with calcitonin gene-related peptide and galanin. Neuroscience 31:807–815
O'Brien C, Woolf CJ, Fitzgerald M, Lindsay RM, Molander C (1989) Differences in the chemical expression of rat primary afferent neurons which innervate skin, muscle or joint. Neuroscience 32:493–502
Otsukai M, Yanagissawa M (1987) Does substance P act as a pain transmitter? Trends Pharmacol Sci 8:501–505
Plenderleith MB, Cameron AA, Key B, Snow PJ (1989) The plant lectin soybean agglutinin binds to the soma, axon and central terminals of a subpopulation of small-diameter primary sensory neurons in the rat and cat. Neuroscience 31:683–695
Ryu PD, Gerber G, Murase K, Randic M (1988) Actions of calcitonin gene-related peptide on rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. Brain Res 441:357–361
Scharfman HE, Kunkel DD, Schwartzkroin PA (1989) Intracellular dyes mask immunoreactivity of hippocampal interneurons. Neurosci Lett 96:23–28
Silverman JD, Kruger L (1988) Lectin and neuropeptide labeling of separate populations of dorsal root ganglion neurons and associated “nociceptor” thin axons in rat testis and cornea whole-mount preparations. Somatosens Res 5:259–267
Stoward PJ, Spicer SS, Miller RL (1980) Histochemical reactivity for peanut lectin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate. J Histochem Cytochem 28:979–990
Streit WJ, Schulte BA, Balentine JD, Spicer SS (1986) Evidence for glycoconjugate in nociceptive primary sensory neurons and its origin from the Golgi complex. Brain Res 377:1–17
Woolf CJ, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (1986) Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide synergistically modulate the gain of the nociceptive flexor withdrawal reflex in the rat. Neurosci Lett 66:226–230
Yoshida S, Matsuda Y (1979) Studies on sensory neurons of the mouse with intracellular-recording and horseradish peroxidase-injection techniques. J Neurophysiol 42:1134–1145
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoheisel, U., Mense, S. & Scherotzke, R. Calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactivity in functionally identified primary afferent neurones in the rat. Anat Embryol 189, 41–49 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193128
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193128