Abstract
-
1.
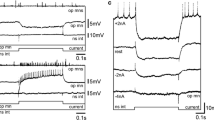
GABA, ACh, and other agents were applied by pressure ejection to the neuropil of the third abdominal ganglion in the isolated nerve cord of Manduca sexta. Intersegmental muscle motor neurons with dendritic arborizations in the same hemiganglion were inhibited by GABA (Fig. 2) and excited by ACh (Fig. 5).
-
2.
Picrotoxin was a potent antagonist of GABA (Fig. 4A). Bicuculline reduced GABA responses in some motor neurons (Fig. 4C), but had no effect on many other motor neurons. Curare reduced ACh responses (Fig. 6A). Bicuculline was an effective ACh antagonist in most motor neurons tested (Fig. 6B).
-
3.
Motor neurons with dendrites across the ganglion from the ejection pipette exhibited different responses to GABA and ACh. Contralateral motor neurons often showed smaller, delayed hyperpolarizing GABA responses (Fig. 7). On two occasions, contralateral motor neurons had excitatory responses (Fig. 8). Contralateral motor neurons were hyperpolarized by ACh (Fig. 9). The inhibitory responses had only slightly longer latencies than ipsilateral excitatory ACh responses (Fig. 10A). The contralateral inhibitory ACh responses, but not the ipsilateral excitatory ACh responses, were eliminated by TTX (Fig. 10B).
-
4.
A model, which includes inhibitory interneurons that cross the ganglionic midline to inhibit their contralateral homologs and motor neurons (Fig. 11), is proposed to account for contralateral responses to GABA and ACh and antagonistic patterns of activity of motor neurons during mechanosensory reflex responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GABA:
-
γ-amino butyric acid
- ACh:
-
acetylcholine
- TTX:
-
tetrodotoxin
- A2, A3,... 2nd, 3rd,...:
-
abdominal segment
- DNa:
-
anterior branch of the dorsal nerve
- DNp:
-
posterior branch of the dorsal nerve
References
Bate CM (1973a) The mechanism of the pupal gin trap. I. Segmental gradients and the connexions of the triggering sensilla. J Exp Biol 59:95–107
Bate CM (1973b) The mechanism of the pupal gin trap. II. The closure movement. J Exp Biol 59:109–119
Bell RA, Joachim FA (1976) Techniques for rearing laboratory colonies of tobacco hornworms and pink bollworms. Ann Entomol Soc Am 69:365–373
Benson JA (1988) Bicuculline blocks the response to acetylcholine and nicotine but not muscarine or GABA in isolated insect neuronal somata. Brain Res 458:65–71
Benson JA (1992) Electrophysiological pharmacology of the nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic responses of isolated neuronal somata from locust thoracic ganglia. J Exp Biol 170:203–233
Booker R, Truman JW (1987) Postembryonic neurogenesis in the CNS of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. I. Neuroblast arrays and the fate of their progeny during metamorphosis. J Comp Neurol 255:548–559
Bowery NG, Hill DR, Hudson AL (1983) Characteristics of GABAB receptor binding sites on rat whole brain synaptic membranes. Br J Pharmacol 78:191–206
Friesen WO, Stent GS (1977) Generation of a locomotory rhythm by a neural network with recurrent cyclic inhibition. Biol Cybern 28:27–40
Kent KS, Levine RB (1988) Neural control of leg movements in a metamorphic insect: persistence of the larval leg motor neurons to innervate the adult legs of Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 276:30–43
Kent KS, Levine RB (1993) Dendritic reorganization of an identified neuron during metamorphosis in the moth Manduca sexta: the influence of interactions with the periphery. J Neurobiol 24:1–22
Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Johnston GAR, Curtis DR, Game CJA, McCulloch RM (1975) Structure and biological activity of a series of conformationally restricted analogues of GABA. J Neurochem 25:803–809
Lees G, Beadle DJ, Neumann R, Benson JA (1987) Responses to GABA by isolated insect neuronal somata: pharmacology and modulation by a benzodiazepine and a barbiturate. Brain Res 401:267–278
Levine RB, Truman JW (1985) Dendritic reorganization of abdominal motoneurons during metamorphosis of the moth, Manduca sexta. J Neurosci 5:2424–2431
Levine RB, Weeks JC (1990) Hormonally mediated changes in simple reflex circuits during metamorphosis in Manduca. J Neurobiol 21:1022–1036
Levine RB, Pak C, Linn D (1985) The structure, function, and metamorphic reorganization of somatotopically projecting sensory neurons in Manduca sexta larvae. J Comp Physiol A 157:1–13
Levine RB, Truman JW, Linn D, Bate CM (1986) Endocrine regulation of the form and function of axonal arbors during insect metamorphosis. J Neurosci 6:293–299
Levine RB, Waldrop B, Tamarkin D (1989) The use of hormonally induced mosaics to study alterations in the synaptic connections made by persistent sensory neurons during insect metamorphosis. J Neurobiol 20:326–338
Miyazaki S (1980) The ionic mechanism of action potentials in neurosecretory and non-neurosecretory cells of the silkworm. J Comp Physiol 140:43–52
Nistri A, Constanti A (1979) Pharmacological characterization of different types of GABA and glutamate receptors in vertebrates and invertebrates. Prog Neurobiol 13:117–235
Olsen RW, Ban M, Miller T (1976) Studies on the neuro-pharmacological activity of bicuculline and related compounds. Brain Res 102:283–299
Rauh JJ, Lummis SCR, Sattelle DB (1990) Pharmacological and biochemical properties of insect GABA receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11:325–329
Sattelle DB (1988) Synaptic and extrasynaptic neuronal nicotinic receptors of insects. In: Clementi F, Gotti C, Sher E (eds) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the nervous system. Springer, Berlin, pp 241–256
Sattelle DB (1990) GABA receptors of insects. Adv Insect Physiol 22:1–113
Schmidt J, Calabrese RL (1992) Evidence that acetylcholine is an inhibitory transmitter of heart interneurons in the leech. J Exp Biol 171:329–347
Simmonds MK (1983) Multiple GABA receptors and associated regulatory sites. Trends Neurosci 6:279–281
Trimmer BA, Weeks JC (1993) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors modulate the excitability of an identified insect motoneurone. J Neurophysiol 69:1821–1836
Truman JW, Thorn RS, Robinson SN (1992) Programmed neuronal death in insects. J Neurobiol 23:1295–1311
Wagner JG (1968) Kinetics of pharmacologic response. I. Proposed relationships between response and drug concentration in the intact animal and man. J Theor Biol 20:173–201
Waldrop B (1991) Physiological and pharmacological properties of GABA receptors on motor neurons in the moth Manduca sexta. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17:275
Waldrop B, Hildebrand JG (1989) Physiology and pharmacology of acetylcholinergic responses of interneurons in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 164:433–441
Waldrop B, Levine RB (1989) Development of the gin trap reflex in Manduca sexta: a comparison of larval and pupal motor responses. J Comp Physiol A 165:743–754
Waldrop B, Levine RB (1992) Intersegmental interneurons serving larval and pupal mechanosensory reflexes in the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 171:195–205
Waldrop B, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1987) GABA-mediated synaptic inhibition of projection neurons in the antennal lobes of the sphinx moth, Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 161:23–32
Weeks JC, Ernst-Utzschneider K (1989) Respecification of larval proleg motoneurons during metamorphosis of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta: segmental dependence and hormonal regulation. J Neurobiol 20:569–592
Weeks JC, Jacobs GA (1987) A reflex behavior mediated by monosynaptic connections between hair afferents and motoneurons in the larval tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 160:315–329
Weeks JC, Levine RB (1990) Postembryonic neuronal plasticity and its hormonal control during insect metamorphosis. Annu Rev Neurosci 13:183–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waldrop, B. Physiological and pharmacological properties of responses to GABA and ACh by abdominal motor neurons in Manduca sexta . J Comp Physiol A 174, 775–785 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192727
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192727