Abstract
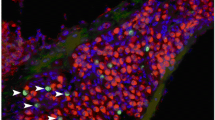
The expression of S-100 protein was analyzed in the human fetal inner ear using immunohistochemical methods. In the 11-week-old human fetus, the cochlea was almost negative for S-100 protein, whereas in the 14- and 15-week-old fetuses, the spiral ligament, Reissner's membrane and spiral limbus were positive for the protein. These results suggest that S-100 protein may be a reliable marker for determining functional maturation of the fetal cochlea and the inner ear. In the l l-, 14- and 15-week fetuses, the epithelial cells of the endolymphatic sac were labelled with S-100 protein. These findings demonstrate that the endolymphatic sac, spiral limbus and spiral ligament in the fetal inner ear have a high activity of S-100 protein, with this presence possibly related to fluid and ion transport of endolymph.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anniko M, Arnold W (1990) Analytical electron microscopy and monoclonal antibody techniques applied to the human inner ear. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 45:1–45
Donato R (1991) Perspectives in S-100 protein biology. Cell Calcium 12:713–726
Foster JD, Drescher MJ, Hatfield JS, Drescher DG (1994) Immunohistochemical localization of S-100 protein in auditory and vestibular end organs of the mouse and hamster. Hear Res 74:67–76
Lauriola L, Coli A, Cocchia D, Tallini G, Michetti F (1987) Comparative study by S-100 and GFAP immunohistochemistry of glial cell populations in the early stages of human spinal cord development. Dev Brain Res 37:251–255
Ludwin SK, Kosek JC, Eng LF (1976) The topographical distribution of S-100 and GFA proteins in the adult rat brain: an immunohistochemical study using horseradish peroxidase labelled antibodies. J Comp Neurol 165:197–208
Moore BW (1965) A soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 19:739–744
Persechini A, Moncrief ND, Kretsinger RH (1989) The EFhand family of calcium-modulated proteins. Trends Neurosci 12:462–467
Saidel WM, Presson JC, Chang JS (1990) S-100 protein immunoreactivity identifies a subunit of hair cells in the utricle and saccule of a fish. Hear Res 47:139–146
Shi S-R, Tandon AK, Cóte C, Kalra KL (1992) S-100 protein in human inner ear: use of a novel immunohistochemical technique on routinely processed, celloidin-embedded human temporal bone sections. Laryngoscope 102:734–738
Streeter GL (1906) On the development of the membranous labyrinth and the acoustic and facial nerves in the human embryo. Am J Anat 6:139–165
Yamashita H, Bagger-Sjöbäck D (1992) Calmodulin binding sites in the endolymphatic sac and stria vascularis of the human fetus and the guinea pig. ORL 54:117–120
Yamashita H, Bagger-Sjöbdäck D, Wersäll J, Sekitani T (1991) Glycocojugates in the human fetal endolymphatic sac as detected by lectins. J Laryngol Otol 105:711–715
Yamashita H, Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Sekitani T (1992) Expression of carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes in the developing endolymphatic sac of the human fetus and the mouse embryo. J Laryngol Otol 106:98–102
Yamashita H, Sekitani T, Bagger-Sjöbäck D (1992) Expression of carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme-like immunoreactivity in the limbus spiralis of the human fetal cochlea. Hear Res 64:118–122
Zuckerman JE, Herschman HR, Levine L (1970) Appearance of a brain specific antigen (the S-100 protein) during human foetal development. J Neurochem 17:247–251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, H., Takahashi, M. & Bagger-Sjöbäck, D. Expression of S-100 protein in the human fetal inner ear. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 252, 312–315 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185396
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185396