Abstract
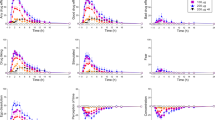
Noradrenaline (NA) plasma levels were examined in 18 healthy volunteers on 2 consecutive days after a single treatment with either lormetazepam (0.06 mg/kg) (LMZ group), flunitrazepam (0.03 mg/kg) (FNZ group) or placebo (PLA group) in combination with the benzodiazepine (BZ) antagonist Ro 15-1788 (0.1 mg/kg). Behavioural responses (mood changes, anxiety) were also investigated in parallel. Both BZ decreased NA plasma levels to 50% of the basal values 10 min after the injection; administration of Ro 15-1788 15 min later reinstated NA plasma levels to basal values. A second administration of Ro 15-1788 (0.1 mg/kg) 24 h after BZ or PLA treatment increased NA plasma levels, estimated 10 min after the injection in both the LMZ- and the FNZ groups, but not in the PLA group. Behavioural responses measured under the same treatment also indicated minor anxiety responses followed by mood impairment. These data suggest that a stressful situation may be precipitated by the antagonist Ro 15-1788 24 h after a single BZ treatment, which resembles a withdrawal response, and increases NA plasma levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackenheil M, Fröhler M, Goldig G, Rall G, Welter D (1982) Katecholamin-Bestimmung im Blut und Liquor mit Hochdruckflüssigkeitschromatographie und elektrochemischem Detektor. Arzneim Forsch (Drug Res) 32:893
Biggio G (1983) The action of stress, β-carbolines, diazepam and Ro 15–1788 on GABA receptors in the rat brain. In: Biggio G, Costa E, (eds) Advance in biochemical pharmacology. Raven Press, New York
Braestrup C, Squires RF (1977) Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterised by high-affinity (3H) diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3805–3804
Charney DS, Redmond DE Jr, Galloway MP, Kleber HD, Henniger GR, Murberg M, Roth RH (1984) Naltrexone precipitated opiate withdrawal in methadone addicted human subjects: Evidence for noradrenergic hyperactivity. Life Sci 35:1263–1272
Cooper JR, Bloom FE, Roth RH (1978) The biochemical basis for neuropharmacology. University Press, New York, pp 102–195
Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Hökfelt T (1967) The effect of some psychoactive drugs on central monoamine neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 1:363–368
Da Prada M, Pieri L, Picotti GB (1980) Effects of midazolam (a water soluble benzodiazepine) on stress-induced increase of plasma catecholamines. In: Usdin E, Kvetnansky R, Kopin IJ (eds) Catecholamines and stress: recent advances. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 231–236
Darragh A, Lambe R, Scully M, Brick I, O'Boyle C, Downie WW (1981) Investigation in man of the efficacy of a benzodiazepine antagonist, Ro 15–1788. Lancet ii:8–10
DeTurek K, Vogel WH (1982) Effects of acute ethanol on plasma and brain catecholamine levels in stressed and unstressed rats: Evidence for an ethanolstress interaction. J Pharm Expt Ther 223:348–354
Dionne RA, Goldstein DS, Wirdzek PR (1984) Effects of diazepam premedication and epinephrine-containing local anesthetic on cardiovascular and plasma catecholamine responses to oral surgery. Anesth-Analg 63:640–646
Dorow R, Seidler J, Schneider HH (1982) A radioreceptor assay to study the affinity of benzodiazepines and their receptor binding activity in human plasma including their active metabolites. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13:561–565
Dorow R, Doenicke A, Suttmann H, Gräf K-J, Grote B, Bretz Ch, Sarafoff M, Ott H (1983) Einfluβ verschiedener Narkosemethoden auf hormonelle Parameter und auf das sympathonervale System In: Doenicke A, Koenig KD (eds) Immunologie in Anästhesie und Intensivmedizin. Springer Verlag, New York
Elmadjian FJ, Hope M, Lamson ET (1957) Excretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine in various emotional states. J Clin Endocrinol 17:608–620
Emmett-Oglesby M, Spencer DG Jr, Lewis MW, Elmesallamy F, Lal H (1983) Anxiogenic aspects of diazepam withdrawal can be detected in animals. Eur J Pharmacol 92:127–130
File SE, Lister RG, Nutt DJ (1982) The anxiogenic action of benzodiazepine antagonists. Neuropharmacology 21:1033–1037
Fontaine R, Chouinard G, Annable L (1984) Rebound anxiety in anxious patients after abrupt withdrawal of benzodiazepine treatment. Am J Psychiatry 141:848–852
Frankenhaeuser M (1971) Behavior and circulating catecholamines. Brain Res 31:241–262
Goldstein DS, Dionne R, Sweet J, Gracely R, Brewer HB Jr, Gregg R, Keiser HR (1982) Circulatory, plasma catecholamine, cortisol, lipid, and psychological responses to a real-life stress (third molar extractions): Effects of diazepam sedation and of inclusion of epinephrine with the local anesthetic. Psychosom Med 44:259–272
Goodman Gilman A, Goodman LS, Rall TW, Murad F (eds) (1985) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 7th edition. MacMillan Publishing Company, New York
Hossmann V, Maling TJB, Hamilton CA, Reid JL, Dollery CT (1980) Sedative and cardiovascular effects of clonidine and nitrazepam. Clin Pharmacol Ther 28:167–176
Hunkeler W, Mohler H, Pieri L, Polc P, Bonetti EP, Cumin R, Schaffner R, Haefely W (1981) Selective antagonists of benzodiazepines. Nature 290:514–516
Kales A, Soldatos CR, Bixler EO, Kales JD (1983) Rebound insomnia and rebound anxiety: A review. Pharmacology 26:121–137
Klotz U, Duka T, Dorow R, Doenicke A (1985) Flunitrazepam and lormetazepam do not affect the pharmacokinetics of the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15–1788. Br J Clin Pharmacol 19:95–98
Kopin I (1981) Catecholamines, adrenal hormones, and stress. In: Krieger H (ed) Neuroendocrinology. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, pp 159–166
Krohne HW (1974) Untersuchungen mit einer deutschen Form der Repression-Sensitization-Skala. Z Klin Psychol Psychother 3:238–260
Levi L (1961) A new stress tolerance test with simultaneous study of physiological and psychological variables. Acta Endocrinol (Kbh) 37:38–44
Levi L (1972) Stress and distress in response to psychosocial stimuli. Acta Med Scand 528 suppl:151–156
Lukas SE, Griffiths RR (1984) Precipitated diazepam withdrawal in baboons: Effects of dose and duration of diazepam exposure. Eur J Pharmacol 100:163–171
Major LF, Hawley RJ, Linnoila M (1984) The role of the central noradrenergic nervous system in the mediation of the ethanol intoxication and ethanol withdrawal syndrome. Psychopharmacol Bull 20:487
Michalova C, Hrubes V, Benes V (1966) The influence of chlordiazepoxide on biochemical reactions to experimental stress in rats. Activ Nerv Sup (Praha) 8:458–459
Pellow S, File SE (1984) Multiple sites of action for anxiogenic drugs: Behavioural, electrophysiological and biochemical correlations. Psychopharmacology 83:304–315
Petursson H, Lader MH (1981) Withdrawal from long-term benzodiazepine treatment. Br Med J 283:643–645
Picotti GB, Corli O, Galva MD, Bondiolotti GP, Carruba MO (1982) Effects of oral chlordemethyldiazepam on plasma adrenaline and noradrenaline and cardiovascular reactivity in preoperative patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 23:383–388
Schöpf J (1983) Withdrawal phenomena after long-term administration of benzodiazepines. A review of recent investigations. Pharmacopsychiatr 16:1–8
Schöpf J, Laurian S, Le PK and Gaillard JM (1984) Intrinsic activity of the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15–1788 in man: An electrophysiological investigation. Pharmacopsychiatr 17:79–83
Smith DE (1979) Importance of grandual dosage reduction following low dose benzodiazepine therapy. Newslett Calif Soc Treat Alcohol Drug Depend 6:1–3
Taylor KM, Laverty R (1969) The effect of chloridiazepoxide, diazepam and nitrazepam on catecholamine metabolism in regions of the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 8:296–301
Timm U, Zell M (1983) Determination of the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15–1788 in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. Arzneim Forsch (Drug Res) 33:358–362
Vogel WH, Miller J, DeTurck H and Routzahn B (1984) Effects of psychoactive drugs on plasma catecholamines during stress in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:1105–1108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duka, T., Ackenheil, M., Noderer, J. et al. Changes in noradrenaline plasma levels and behavioural responses induced by benzodiazepine agonists with the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788. Psychopharmacology 90, 351–357 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00179190
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00179190