Summary
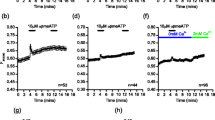
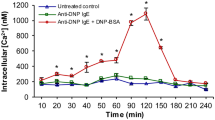
MC9 mast cells, sensitized with monoclonal IgE antibody specific for 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) group, were exposed to DNP-BSA and the pH and cytosolic calcium signals were recorded by using the fluorescent probes BCECF and Fura-2 respectively. DNP-BSA induced cell alkalinization was fully inhibited by azelastine with IC50 (1.6±0.5 μmol/l, mean±SEM, n = 5) similar to that required to inhibit histamine release (1.4 μmol/l), Conversely, high azelastine concentrations (> 100 μmol/l) were required to inhibit DNP-BSA-dependent cell calcium mobilization (IC50≈200 μmol/l, n = 3). Amiloride, but not the H1 histamine antagonist pyrilamine, was able to inhibit the DNP-BSA induced pH signal. In acidified mast cells, azelastine potently inhibited Na+:H+ exchange activity (IC50 = 7.7±3.6 × 10−6 M, mean±SEM, n = 3). Conversely, in mouse spleen lymphocytes azelastine was unable to inhibit the amiloride-sensitive pH signal induced by concanavalin A. In conclusion, the inhibition of histamine release by azelastine is not due to an interference with the cytosolic calcium signal. Conversely, azelastine potently antagonized the allergen-dependent Na+: H+ exchange activation, suggesting an action on the protein kinase C signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chand N, Pillar J, Diamantis W, Perhach JL, Sofia RD (1983) Inhibition of calcium ionophore (A 23187)-stimulated histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells by azelastine: Implications for its mode of action. Eur J Pharmacol 96:227–233
Chand N, Pillar J, Diamantis W, Sofia RD (1985) Inhibition of IgE-mediated allergic histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells by azelastine and selected antiallergic drugs. Agents and Actions 16:318–322
Fields DAS, Pillar J, Perhach JL, Sofia RD (1981) Inhibition of secretagogue-induced histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells in vitro by a novel antiallergic agent, 4-(p-chlorobenzyl)-2(hexahydro-1-methyl-1 H-azepine-4-yl)-1-(2H)-phtalazinone hydrochloride (azelastine). Pharmacologist 23:161
Fisher B, Schmutzler W (1981) Inhibition by azelastine of the immunologically-induced histamine release from isolated guinea pig mast cells. Arzneim Forsch 31:1193–1195
Foreman JC, Rihoux JP (1992) The antiallergic activity of H1 histamine receptor antagonists in relation to their actions on cell calcium. In: Church MK, Rihoux JP (eds) Therapeutic index of antihistamines. Hogrefe & Huber, New York, pp 32–46
Grinstein S, Dixon J (1989) Ion transport, membrane potential and cytoplasmic pH in lymphocytes: changes during activation. Physiological Rev 69:417–481
Grinstein S, Smith D, Rowatt C, Dixon J (1987) Mechanism of activation of lymphocyte Na+:H+ exchange by Concanavalin A. J Biol Chem 262:15277–15284
Heiman AS, Crews FT (1985) Characterization of the effects of phorbol esters on rat mast cell secretion. J Immunol 134:548–555
Katakami Y, Kaibuchi K, Sawamura M, Takai Y, Nishizuka Y (1984) Synergistic action of protein kinase C and calcium for histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 121:573–578
Katayama S, Akimoto N, Shionoya H, Morimoto T, Katah Y (1981) Antiallergic effect of azelastine hydrochloride on immediate type hypersensitivity reactions in vivo and in vitro. Arzneim Forsch 31:1196–1203
Metzger H, Alcaraz G, Hohman R, Kinet JP, Pribluda V, Quarto R (1986) The receptor with high affinity for immunoglobulin E. Annu Rev Immunol 4:419–470
Middleton E, Ferriola P, Drzewiecki G, Sofia RD (1989) The effect of azelastine and some other antiasthmatic and antiallergic drugs on calmodulin and protein kinase C. Agents and Actions 28:9–15
Nabel G, Fresno M, Chessman A, Cantor H (1981) Use of clonal populations on mouse lymphocytes to analyze cellular differentiation. Cell 23:19–28
Nakamura T, Nishizuka Y, Sato T, Yamato C (1988) Effect of azelastine on the intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol 148:35–41
Nishizuka Y (1984) The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature 308:693–698
Penner R (1988) Multiple signaling pathways control stimulus-secretion coupling in rat peritoneal mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:9856–9860
Razin E, Cordon-Cardo C, Good R (1981) Growth of a pure population of mast cells in vitro with conditioned medium derived from concanavalin A-stimulated splenocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:2559–2561
Rosati C, Jeanclos E, Cavalier S, Chabrier PE, Hannaert P, Braquet P, Garay RP (1990) Stimulatory action of endothelin-1 on membrane Na+ transport in vascular smooth muscle cells in culture. Am J Hypertens 3:711–713
Szelenyi I (1989) Pharmacological profile of Azelastine. Drugs of today 25 [Suppl 6]:3
Tasaka K, Akagi M (1979) Anti-allergic properties of a new histamine antagonist, 4-(p-chloro-benzyl)-2-[N-methyl-perhydroazepinyl-(4)]-1(2H)-phtalazinone hydrochloride (Azelastine). Arzneim Forsch Drug Res 29:488–493
White JR, Pluznik DH, Ishizaka K, Ishizaka T (1985) Antigen-induced increase in protein kinase C activity in plasma membrane of mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:8193–8197
Zechel HJ, Brock N, Lenke D, Achterrath-Tuckermann U (1981) Pharmacological and toxicological properties of azelastine, a novel antiallergic agent. Arzneim Forsch Drug Res 31:1184–1193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: R. P. Garay at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fanous, K., Garay, R.P. Azelastine and allergen transduction signal in MC9 mast cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 348, 515–519 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173212
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173212