Abstract
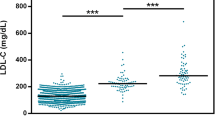
The uselfulness of the RFLPs of the LDL-receptor gene in early diagnosis of Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) was investigated in 122 FH-families. Four RFLPs, produced by digestion with the enzymes PvuII, ApaLI and AvaII/XbaI were able to detect the affected gene and to follow the inheritance of the disease in 72 out of 97 families (74%). In the remaining 25 families, unambiguous diagnosis was possible in 66% of the cases by use of PvuII, ApaLI and BstEII/EcoRI RFLPs. The RFLPs were also useful to distinguish true homozygotes from compound heterozygotes and to detect families where recombination events occurred or where hypercholesterolemia was not due to a defect of the LDL-receptor gene. In a normal population PvuII RFLP account for 9.6% of the total variance of the LDL cholesterol levels adjusted for confounding variables. The P2 allele was associated with lower LDL cholesterol concentrations (average excess −9.1 mg/dl). This finding allows us to presume there is a DNA sequence, close to the variable PvuII cutting site in intron 15, which could act as an enhancer of the LDL-receptor gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BotsteinD.,WhiteR.L.,SkolnickM. andDavisR.W. (1980): Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms -Am. J. Hum. Genet.32: 314–331.
ChakravartiA. andBuetowK.H. (1985): A strategy for using multiple linked markers for genetic counseling -Am. J. Hum. Genet.37: 984–997.
ChakravartiA.,BuetowK.H.,AntonarakisS.E.,WaberP.G.,BoehmC.D. andKazazianH.H. (1984): Nonuniform recombination within the human beta globin gene cluster - Am. J. Hum. Genet.36: 1239–1258.
ChakravartiA.,ElbeinS.C. andPermuttM.A. (1986): Evidence for increased recombination near the human insulin gene: implication for disease association studies - Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA83: 1045–1049.
DagaA.,FabbiM.,MattioniT.,BertoliniS. andCorteG. (1988): PvuII polymorphism of LDL receptor gene and Familial hypercholesterolemia - Arteriosclerosis8: 845–850.
DagaA.,MattioniT.,BalestreriR.,CovielloD.A.CorteG. andBertoliniS. (1990): Use of three DNA polymorphisms of the LDL receptor gene in the diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia - Hum. Genet.84: 412–416.
GeiselJ.,WeisshaarB.,OetteK. andDoerflerW. (1988): A new ApaLI restriction fragment length polymorphism in the low density lipoprotein receptor gene. - J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem.26: 429–433.
GoldsteinJ.L. andBrownM.S. (1989): Familial Hypercholesterolemia. In: Scriver C.R., Beaudet A.L., Sly W.S., Valle D. (eds). The metabolic basis of inherited disease, 6th ed, Mc Graw-Hill - New York -pp: 1215–1250.
HegeleR.A.,EmiM.,NakamuraY.,LalouelJ.M. andWhiteR. (1989): Three RFLPs upstream of the low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene - Nucleic Acids Res.17: 470.
HegeleR.A.PlaetkeR. andLalouelJ.M. (1990): Linkage disequilibrium between DNA markers at the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene - Genet. Epidemiol.7: 69–81.
HixsonJ.E.,KammererC.M.,CoxL.A. andMottG.E. (1989): Identification of LDL receptor gene marker associated with altered levels of LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B in baboons - Arteriosclerosis9: 829–835.
HobbsH.H.,LeitershdorfE.,LeffertC.C.,CryerD.R.,BrownM.S. andGoldsteinJ.L. (1989): Evidence for a dominant gene that suppresses hypercholesterolemia in a family with defective low density lipoprotein receptors - J. Clin. Invest.84: 656–664.
Humphries S.,Taylor R.,Jeenah M.,Dunning A.,Horsthemke B.,Seed M.,Schuster H. andWolfram G. (1989): Gene probes in diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia - Arteriosclerosis, Suppl. I,9: 59–65.
KajinamiK.,MabuchiH.,InazuA.,FujitaH.,KoizumiJ.,TakedaR.,MatsueT. andKibataM. (1990): Novel gene mutations at the low density lipoprotein receptor locus: FH-Kanazawa and FH-Okayama - J. Intern. Med.227: 247–251.
KellerC.,SpengelF.,WieczorekA.,WolframG. andZöllnerN. (1981): Familial hypercholesterolemia: a family with divergence of clinical phenotype and biochemical genotype based on fibroblast studies -Ann. Nutr. Metab.25: 79–84.
KotzeJ.,LangenhovenE.,RetiefA.E.,SeftelH.E.,HedersonH.E. andWeichH.F.H. (1989): Haplotypes identified by 10 DNA restriction fragment lenght polymorphisms at the human low density lipoprotein receptor gene locus - J. Med. Genet.26: 255–259.
Kwiterovich JrP.O. (1989): Pediatric implication of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia -Arteriosclerosis, Suppl. I,9: 111–120.
LeitersdorfE.,ChakravartiA. andHobbsH.H. (1989): Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the LDL receptor locus - Am. J. Hum. Genet.44: 409–421.
LeitersdorfE. andHobbsH.H. (1988): Human LDL receptor gene: HincII polymorphism detected by gene amplification - Nucleic Acids Res.16: 7215.
LeitersdorfE.,TobinE.J.,DavignonJ. andHobbsH.H. (1990): Common low-density lipoproteins receptor mutations in the French Canadian population - J. Clin. Invest.85: 1014–1023.
LewontinR.C. (1964): The interaction of selection and linkage. I. General considerations: heterotic models - Genetics49: 49–67.
ManiatisT.,FritschE.F. andSambrookJ. (eds) (1982): Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor - New York - pp. 458–459.
PedersenJ.C. andBergK. (1988): Normal DNA polymorphism at the low density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) locus associated with serum cholesterol levels - Clin. Genet.34: 306–312.
SchusterH.,HumphriesS.,RauhG.,HeldC.,KellerCh.,WolframG. andZöllnerN. (1990): Association of DNA-haplotypes in the human LDL receptor gene with normal serum cholesterol levels - Clin. Genet.38: 401–409.
SchusterH.,RauhG.,KormannB.,HeppT.,HumphriesS.,KellerC.,WolframG. andZöllnerN. (1990): Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100. Comparison with Familial Hypercholesterolemia in 18 cases detected in Munich - Arteriosclerosis10: 577–581.
SchusterH.,StiefenhoferB.,WolframG.,KellerC.,HumphriesS.,HuberA. andZöllnerN. (1989): Four DNA polymorphisms in the LDL-receptor gene and their use in diagnosis of Familial Hypercholesterolemia -Hum. Genet.82: 69–72.
SokalR.R. andRohlfG. (eds) (1983): Biometry, 2nd ed, Freeman - New York - pp: 208–270.
StettiA.A. (1989): A StuI RFLP upstream of the low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene - Nucleic Acids Res.17: 1786.
TempletonA.R.,SingC.F.,KesslingA. andHumphriesS. (1988): A cladistic analysis of phenotype associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping. II. The analysis of natural populations - Genetics -120: 1145–1154.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Corresponding author.
Supported by grant from the Italian CNR Target Project on Aging.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertolini, S., Coviello, D.A., Masturzo, P. et al. RFLPs of the LDL-receptor gene: Their use in the diagnosis of FH and in evaluation of different levels of gene expression on normal subjects. Eur J Epidemiol 8 (Suppl 1), 18–25 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00145345
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00145345