Summary
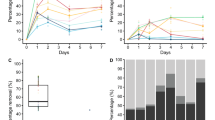
In the presence of iron, which is always associated with natural sulphide ores, the percentages of copper dissolution in the bioleaching of covellite were 34 and 45 % when Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Thiobacillus ferrooxidans were used together and when an indirect bioleaching with attached bacteria was performed respectively. In the latter, the percentage of copper dissolution was still higher than the percentages obtained with pure cultures (36 % with a T. thiooxidans culture and 40 % with a T. ferrooxidans culture).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curutchet, G., Pogliani, C., and Donati, E.R. (1995). Biotech. Lett. 17, 1251–1256.
Donati, E.R., Curutchet, G., Pogliani, C., and Tedesco, P.H. (1996). Process Biochem. 31, 129–134.
Ehrlich, H.L. (1981). Geomicrobiology, New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.
Pistorio, M, Curutchet, G., Donati, E.R., and Tedesco, P.H. (1994). Biotech. Lett. 16, 419–424.
Silverman, M., and Lundgren, D. (1959). J. Bacteriol. 77, 642–647.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curutchet, G., Tedesco, P. & Donati, E. Combined degradation of covellite by Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Thiobacillus ferrooxidans . Biotechnol Lett 18, 1471–1476 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00129357
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00129357