Abstract
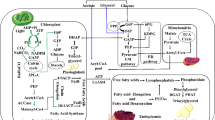
The widely distributed Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (A. ferrooxidans) lives in extremely acidic conditions by fixing CO2 and nitrogen, and by obtaining energy from Fe2+ oxidation with either downhill or uphill electron transfer pathway and from reduced sulfur oxidation. A. ferrooxidans exists as different genomovars and its genome size is 2.89–4.18 Mb. The chemotactic movement of A. ferrooxidans is regulated by quorum sensing. A. ferrooxidans shows weak magnetotaxis due to formation of 15–70 nm magnetite magnetosomes with surface functional groups. The room- and low-temperature magnetic features of A. ferrooxidans are different from other magnetotactic bacteria. A. ferrooxidans has potential for removing sulfur from solids and gases, metals recycling from metal-bearing ores, electric wastes and sludge, biochemical production synthesizing, and metal workpiece machining.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinci G, Guven DE (2011) Bioleaching of heavy metals contaminated sediment by pure and mixed cultures of Acidithiobacillus spp. Desalination 268(1):221–226
Aroca G, Urrutia H, Nunez D (2007) Comparison on the removal of hydrogen sulfide in biotrickling filters inoculated with Thiobacillus thioparus and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Electron J Biotechnol 10(4):514–520
Arshadi M, Mousavi S (2015) Multi-objective optimization of heavy metals bioleaching from discarded mobile phone PCBs: simultaneous Cu and Ni recovery using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Sep Purif Technol 147:210–219
Bajestani MI, Mousavi SM, Shojaosadati SA (2014) Bioleaching of heavy metals from spent household batteries using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans: statistical evaluation and optimization. Sep Purif Technol 132:309–316
Banderas A, Guiliani N (2013) Bioinformatic prediction of gene functions regulated by quorum sensing in the bioleaching bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Int J Mol Sci 14(8):16901–16916
Barrie JD, Hallberg KB (2009) Carbon, iron and sulfur metabolism in acidophilic microorganisms. Adv Microb Physiol 54:201–255
Barron JL, Lueking DR (1990) Growth and maintenance of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(9):2801–2806
Bassler BL (2016) Quorum sensing and its control. FASEB J 30(1):1
Biologie Ftfr (2011) Mechanism and regulation of magnetosomal iron uptake and biomineralization in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
Blake RC, Shute EA (1994) Respiratory enzymes of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Kinetic properties of an acid-stable iron: rusticyanin oxidoreductase. Biochemistry 33(31):9220–9228
Bosecker CGK (1999) Leaching heavy metals from contaminated soil by using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans or Thiobacillus thiooxidans. Geomicrobiol J 16(3):233–244
Brasseur G, Bruscella P, Bonnefoy V, Lemesle-Meunier D (2002) The bc 1 complex of the iron-grown acidophilic chemolithotrophic bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans functions in the reverse but not in the forward direction: is there a second bc 1 complex? Biochim Biophys Acta 1555(1–3):37–43
Brasseur G, Levicán G, Bonnefoy V, Holmes D, Jedlicki E, Lemesle-Meunier D (2004) Apparent redundancy of electron transfer pathways via bc 1 complexes and terminal oxidases in the extremophilic chemolithoautotrophic Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biochim Biophys Acta 1656(2–3):114–126
Brierley CL (2008) How will biomining be applied in future? T Nonferr Metal Soc 18(6):1302–1310
Campodonico MA, Vaisman D, Castro JF, Razmilic V, Mercado F, Andrews BA, Feist AM, Asenjo JA (2016) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans’s comprehensive model driven analysis of the electron transfer metabolism and synthetic strain design for biomining applications. Metab Eng Commun 3:84–96
Chakraborty R, Roy P (1992) Chemotaxis of chemolithotrophic Thiobacillus ferrooxidans toward thiosulfate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 98(1–3):9–12
Chen P, Yan L, Leng F, Nan W, Yue X, Zheng Y, Feng N, Li H (2011) Bioleaching of realgar by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans using ferrous iron and elemental sulfur as the sole and mixed energy sources. Bioresour Technol 102(3):3260–3267
Chen S, Yang Y, Liu C, Dong F, Liu B (2015) Column bioleaching copper and its kinetics of waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs) by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Chemosphere 141:162–168
Chi A, Valenzuela L, Beard S, Mackey AJ, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Jerez CA (2007) Periplasmic proteins of the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans a high throughput proteomics analysis. Mol Cell Proteom 6(12):2239–2251
Crundwell FK (1997) The kinetics of the chemiosmotic proton circuit of the iron-oxidizing bacterium Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 43(1):115–122
Dastidar MG, Malik A, Roychoudhury PK (2000) Biodesulphurization of Indian (Assam) coal using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans (ATCC 13984). Energy Convers Manag 41(4):375–388
Dave SR, Gupta KH, Tipre DR (2008) Characterization of arsenic resistant and arsenopyrite oxidizing Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans from Hutti gold leachate and effluents. Bioresour Technol 99(16):7514–7520
DiSpirito AA, Tuovinen OH (1982) Uranous ion oxidation and carbon dioxide fixation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Arch Microbiol 133(1):28–32
Dixon R, Kahn D (2004) Genetic regulation of biological nitrogen fixation. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(8):621–631
Dong Y, Lin H, Xu X, Zhou S (2013) Bioleaching of different copper sulfides by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its adsorption on minerals. Hydrometallurgy 140:42–47
Esparza M, Cárdenas JP, Bowien B, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS (2010) Genes and pathways for CO2 fixation in the obligate, chemolithoautotrophic acidophile, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, carbon fixation in A. ferrooxidans. BMC Microbiol 10(1):229–244
Farah C, Vera M, Morin D, Haras D, Jerez CA, Guiliani N (2005) Evidence for a functional quorum-sensing type AI-1 system in the extremophilic bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):7033–7040
Gale NL, Beck JV (1967) Evidence for the Calvin cycle and hexose monophosphate pathway in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 94(4):1052–1059
Ghavidel A, Naji Rad S, Alikhani HA, Sharari M, Ghanbari A (2018) Bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge, direct action of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans or only the impact of pH? J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 20:1–9
Giaveno A, Donati E (2001) Bioleaching of heazelwoodite by Thiobacillus spp. Process Biochem 36(10):955–962
González A, Bellenberg S, Mamani S, Ruiz L, Echeverría A, Soulère L, Doutheau A, Demergasso C, Sand W, Queneau Y (2013) AHL signaling molecules with a large acyl chain enhance biofilm formation on sulfur and metal sulfides by the bioleaching bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(8):3729–3737
Gu W, Bai J, Dong B, Zhuang X, Zhao J, Zhang C, Wang J, Shih K (2017) Catalytic effect of graphene in bioleaching copper from waste printed circuit boards by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 171:172–178
Guiliani N, Jerez CA (2000) Molecular cloning, sequencing, and expression of omp-40, the gene coding for the major outer membrane protein from the acidophilic bacterium Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(6):2318–2324
Gupta A, Birendra K, Mishra R (2003) Study on the recovery of zinc from Moore cake: a biotechnological approach. Miner Eng 16(1):41–43
Haghshenas DF, Alamdari EK, Bonakdarpour B, Darvishi D, Nasernejad B (2009a) Kinetics of sphalerite bioleaching by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 99(3–4):202–208
Haghshenas DF, Alamdari EK, Torkmahalleh MA, Bonakdarpour B, Nasernejad B (2009b) Adaptation of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans to high grade sphalerite concentrate. Miner Eng 22(15):1299–1306
Haghshenas DF, Bonakdarpour B, Alamdari EK, Nasernejad B (2012) Optimization of physicochemical parameters for bioleaching of sphalerite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans using shaking bioreactors. Hydrometallurgy 111–112:22–28
Hedrich S, Schlömann M, Johnson DB (2011) The iron-oxidizing proteobacteria. Microbiology 157(6):1551–1564
Holmes DS, Bonnefoy V (2007) Genetic and bioinformatic insights into iron and sulfur oxidation mechanisms of bioleaching organisms. In: Rawlings DE, Johnson DB (eds) Biomining. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Hong FF, He H, Liu JY, Tao XX, Zheng L, Zhao YD (2013) Comparison analysis of coal biodesulfurization and coal’s pyrite bioleaching with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Sci World J 10:184964–184973
Hou Q, Fang D, Liang J, Zhou L (2015) Significance of oxygen supply in jarosite biosynthesis promoted by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. PLoS One 10(3):e0120966
Huang B (2009) Study on removing low concentration SO2 from flue gas by immobilization technology of miroorganism. Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China
Ishii T, Kawaichi S, Nakagawa H, Hashimoto K, Nakamura R (2015) From chemolithoautotrophs to electrolithoautotrophs: CO2 fixation by Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria coupled with direct uptake of electrons from solid electron sources. Front Microbiol 6:994
Jadhav U, Hocheng H (2016) Study of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and enzymatic bio-Fenton process-mediated corrosion of copper–nickel alloy. Environ Technol 37(20):2669–2677
Jadhav U, Hong H (2013) Extraction of silver from spent silver oxide–zinc button cells by using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans culture supernatant. J Clean Prod 44(2):39–44
Jensen AB, Webb C (1995a) Ferrous sulphate oxidation using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: a review. Process Biochem 30(3):225–236
Jensen AB, Webb C (1995b) Treatment of H2S-containing gases: a review of microbiological alternatives. Enzyme Microb Technol 17(1):2–10
Jerez CA (2001) Chemotactic transduction in biomining microorganisms. Hydrometallurgy 59(2–3):347–356
Jiang G, Zhao S, Luo J, Wang Y, Yu W, Zhang C (2010) Microbial desulfurization for NR ground rubber by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Appl Polym Sci 116(5):2768–2774
Kappler U, Dahl C (2001) Enzymology and molecular biology of prokaryotic sulfite oxidation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 203(1):1–9
Karavaiko GI, Tat’yana PT, Kondrat’eva TF, Lysenko AM, Tat’yana VK, Ageeva SN, Muntyan LN, Tat’yana AP (2003) Phylogenetic heterogeneity of the species Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(1):113–119
Kernan T, Majumdar S, Li X, Guan J, West AC, Banta S (2016) Engineering the iron-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans for biochemical production. Biotechnol Bioeng 113(1):189–197
Kim SD, Baeb JE, Park HS, Cha DK (2005) Bioleaching of cadmium and nickel from synthetic sediments by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Environ Geochem Health 27(3):229–235
Ko MS, Park HS, Kim KW, Lee JU (2013) The role of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in arsenic bioleaching from soil. Environ Geochem Health 35(6):727–733
Kondratyeva TF, Muntyan LN, Karavaiko GI (1995) Zinc-and arsenic-resistant strains of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans have increased copy numbers of chromosomal resistance genes. Microbiology 141(5):1157–1162
Kurade MB, Murugesan K, Selvam A, Yu S-M, Wong JWC (2016) Sludge conditioning using biogenic flocculant produced by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans for enhancement in dewaterability. Bioresour Technol 217:179–185
Lambert F, Gaydardzhiev S, Léonard G, Lewis G, Bareel PF, Bastin D (2015) Copper leaching from waste electric cables by biohydrometallurgy. Miner Eng 76:38–46
Lee EY, Lee NY, Cho K-S, Ryu HW (2006) Removal of hydrogen sulfide by sulfate-resistant Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans AZ11. J Biosci Bioeng 101(4):309–314
Li Y, Li H (2014) Type IV pili of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans can transfer electrons from extracellular electron donors. J Basic Microbiol 54(3):226–231
Li J, Pan Y, Liu Q, Yu-Zhang K, Menguy N, Che R, Qin H, Lin W, Wu W, Petersen N, Xa Yang (2010a) Biomineralization, crystallography and magnetic properties of bullet-shaped magnetite magnetosomes in giant rod magnetotactic bacteria. Earth Planet Sci Lett 293(3–4):368–376
Li YQ, Wan DS, Huang SS, Leng FF, Yan L, Ni YQ, Li HY (2010b) Type IV Pili of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans are necessary for sliding, twitching motility, and adherence. Curr Microbiol 60(1):17–24
Li X, Mercado R, Berlinger S, Banta S, West AC (2014) Engineering Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans growth media for enhanced electrochemical processing. AIChE J 60(12):4008–4013
Li X, West AC, Banta S (2016) Enhancing isobutyric acid production from engineered Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cells via media optimization. Biotechnol Bioeng 113(4):790–796
Liang G, Li P, Liu W, Wang B (2016) Enhanced bioleaching efficiency of copper from waste printed circuit boards (PCBs) by dissolved oxygen-shifted strategy in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 18(4):742–751
Liu W-B, Wu H-Y, Liu X-D, Liu X-X (2008) Influence of different Fe sources and concentrations on formation of magnetosomes in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. T Nonferr Metal Soc 18(6):1379–1385
Lombardi AT, Garcia O (2002) Biological leaching of Mn, Al, Zn, Cu and Ti in an anaerobic sewage sludge effectuated by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and its effect on metal partitioning. Water Res 36(13):3193–3202
Mahmoud A, Cézac P, Hoadley AFA, Contamine F, D’Hugues P (2017) A review of sulfide minerals microbially assisted leaching in stirred tank reactors. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 19:118–146
Makita M, Esperón M, Pereyra B, López A, Orrantia E (2004) Reduction of arsenic content in a complex galena concentrate by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. BMC Biotechnol 4(1):22–44
Mamani S, Moinier D, Denis Y, Soulère L, Queneau Y, Talla E, Bonnefoy V, Guiliani N (2016) Insights into the quorum sensing regulon of the acidophilic Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans revealed by transcriptomic in the presence of an Acyl homoserine lactone superagonist analog. Front Microbiol 7:1365
Mannivannan T, Sandhya S, Pandey RA (2008) Microbial desulfurization of coal by chemoautotrophic Thiobacillus ferrooxidans—an iron mine isolate. J Environ Sci Health Part A 29(10):2045–2061
Martínez-Bussenius C, Navarro CA, Orellana L, Paradela A, Jerez CA (2016) Global response of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 to high concentrations of copper: a quantitative proteomics approach. J Proteom 145:37–45
Mousavi SM, Yaghmaei S, Vossoughi M, Jafari A, Roostaazad R (2006) Zinc extraction from Iranian low-grade complex zinc–lead ore by two native microorganisms: Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Sulfobacillus. Int J Miner Process 80(2):238–243
Mukherjee C, Jones FS, Bigham JM, Tuovinen OH (2016) Synthesis of argentojarosite with simulated bioleaching solutions produced by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Mater Sci Eng C 66:164–169
Muñoz JA, Ballester A, González F, Blázquez ML (1995) A study of the bioleaching of a Spanish uranium ore. Part II: orbital shaker experiments. Hydrometallurgy 38(1):59–78
Murugesan K, Ravindran B, Selvam A, Kurade MB, Yu S-M, Wong JWC (2014) Enhanced dewaterability of anaerobically digested sewage sludge using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans culture as sludge conditioner. Bioresour Technol 169:374–379
Nan W, Zhi D, Leng F, Yan L, Chen P, Yue X, Li H (2011) Quorum-sensing system in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans involved in its resistance to Cu2+. Lett Appl Microbiol 53(1):84–91
Nguyen VK, Lee MH, Park HJ, Lee J-U (2015) Bioleaching of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings by pure and mixed cultures of Acidithiobacillus spp. J Ind Eng Chem 21:451–458
Ni YQ, Yang Y, Bao JT, He KY, Li HY (2007) Inter- and intraspecific genomic variability of the 16S–23S intergenic spacer regions (ISR) in representatives of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 270(1):58–66
Nie H, Zhu N, Cao Y, Xu Z, Wu P (2015) Immobilization of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on cotton gauze for the bioleaching of waste printed circuit boards. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177(3):675–688
Nowaczk NR, Harwart S, Melles M (2000) A rock magnetic record from Lama Lake, Taymyr Peninsula, northern Central Siberia. J Paleolimnol 23(3):227–241
Ohmura N, Tsugita K, Koizumi JI, Saika H (1996) Sulfur-binding protein of flagella of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 178(19):5776–5780
Oprime MEAG, Garcia O, Cardoso AA (2001) Oxidation of H2S in acid solution by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Thiobacillus thiooxidans. Process Biochem 37(2):111–114
Osorio H, Mangold S, Denis Y, Ñancucheo I, Esparza M, Johnson DB, Bonnefoy V, Dopson M, Holmes DS (2013) Anaerobic sulfur metabolism coupled to dissimilatory iron reduction in the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(7):2172–2181
Pal S, Pradhan D, Das T, Sukla LB, Chaudhury GR (2010) Bioleaching of low-grade uranium ore using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Indian J Microbiol 50(1):70–75
Patel MJ, Tipre DR, Dave SR (2011) Isolation, identification, characterization and polymetallic concentrate leaching studies of tryptic soy- and peptone-resistant thermotolerant Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans SRDSM2. Bioresour Technol 102(2):1602–1607
Pogaku R, Kodali B (2006) Optimization of bacterial oxidation process parameters for selective leaching of nickel by Thiobacillus Ferrooxidans. Int J Chem React Eng 4(1):1–14
Popa R, Fang W, Nealson KH, Souza-Egipsy V, Berquó TS, Banerjee SK, Penn LR (2009) Effect of oxidative stress on the growth of magnetic particles in Magnetospirillum magneticum. Int Microbiol 12(1):49–57
Pósfai M, Moskowitz BM, Arató B, Schüler D, Flies C, Bazylinski DA, Frankel RB (2006) Properties of intracellular magnetite crystals produced by Desulfovibrio magneticus strain RS-1. Earth Planet Sci Lett 249(3–4):444–455
Qiu G, Li Q, Yu R, Sun Z, Liu Y, Chen M, Yin H, Zhang Y, Liang Y, Xu L (2011) Column bioleaching of uranium embedded in granite porphyry by a mesophilic acidophilic consortium. Bioresour Technol 102(7):4697–4702
Quatrini R, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS (2005) Genomic insights into the iron uptake mechanisms of the biomining microorganism Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32(11–12):606–614
Quatrini R, Appia-Ayme C, Denis Y, Ratouchniak J, Veloso F, Valdes J, Lefimil C, Silver S, Roberto F, Orellana O (2006) Insights into the iron and sulfur energetic metabolism of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans by microarray transcriptome profiling. Hydrometallurgy 83(1–4):263–272
Quatrini R, Appia-Ayme C, Denis Y, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS, Bonnefoy V (2009) Extending the models for iron and sulfur oxidation in the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. BMC Genom 10(1):394–412
Rai C (1985) Microbial desulfurization of coals in a slurry pipeline reactor using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biotechnol Prog 1(3):200–204
Ramírez P, Guiliani N, Valenzuela L, Beard S, Jerez CA (2004) Differential protein expression during growth of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on ferrous iron, sulfur compounds, or metal sulfides. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(8):4491–4498
Rastegar SO, Mousavi SM, Shojaosadati SA (2014) Cr and Ni recovery during bioleaching of dewatered metal-plating sludge using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Bioresour Technol 167:61–68
Rastegar SO, Mousavi SM, Shojaosadati SA, Sarraf Mamoory R (2015) Bioleaching of V, Ni, and Cu from residual produced in oil fired furnaces using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 157:50–59
Rawlings DE (2005) Characteristics and adaptability of iron- and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms used for the recovery of metals from minerals and their concentrates. Microb Cell Fact 4(1):13–27
Rivas M, Seeger M, Holmes DS, Jedlicki E (2005) A Lux-like quorum sensing system in the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biol Res 38(2–3):283–297
Rivas M, Seeger M, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS (2007) Second Acyl homoserine lactone production system in the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(10):3225–3231
Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (2006) The genus Thiobacillus. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes, vol 5. Proteobacteria: alpha and beta subclasses. Springer, New York, pp 812–827
Rohwerder T, Gehrke T, Kinzler K, Sand W (2003) Bioleaching review part A: progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(3):239–248
Sampson MI, Phillips CV, Ii RCB (2000) Influence of the attachment of acidophilic bacteria during the oxidation of mineral sulfides. Miner Eng 13(4):373–389
Sandy Jones F, Bigham JM, Gramp JP, Tuovinen OH (2014) Synthesis and properties of ternary (K, NH4, H3O)-jarosites precipitated from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cultures in simulated bioleaching solutions. Mater Sci Eng C 44:391–399
Schrader JA, Holmes DS (1988) Phenotypic switching of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 170(9):3915–3923
Schrenk MO, Edwards KJ, Goodman RM, Hamers RJ, Banfield JF (1998) Distribution of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans: implications for generation of acid mine drainage. Science 279(5356):1519–1522
Shah MB, Tipre DR, Dave SR (2014) Chemical and biological processes for multi-metal extraction from waste printed circuit boards of computers and mobile phones. Waste Manag Res 32(11):1134–1141
Shah MB, Tipre DR, Purohit MS, Dave SR (2015) Development of two-step process for enhanced biorecovery of Cu–Zn–Ni from computer printed circuit boards. J Biosci Bioeng 120(2):167–173
Sugio T, Hirayama K, Inagaki K, Tanaka H, Tano T (1992a) Molybdenum oxidation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(5):1768–1771
Sugio T, Hirose T, Ye L-Z, Tano T (1992b) Purification and some properties of sulfite: ferric ion oxidoreductase from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 174(12):4189–4192
Takeuchi F, Iwahori K, Kamimura K, Negishi A, Maeda T, Sugio T (2001) Volatilization of mercury under acidic conditions from mercury-polluted soil by a mercury-resistant Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans SUG 2-2. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65(9):1981–1986
Temple KL, Colmer AR (1951) The autotrophic oxidation of iron by a new bacterium, Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 62(5):605–611
Tipre DR, Dave SR (2004) Bioleaching process for Cu–Pb–Zn bulk concentrate at high pulp density. Hydrometallurgy 75(1):37–43
Tipre DR, Vora SB, Dave SR (2004) Medium optimization for bioleaching of metals from Indian bulk polymetallic concentrate. Indian J Biotechnol 3:86–91
Ulloa R, Moya-Beltrán A, Issotta F, Nuñez H, Covarrubias PC, Donati ER, Quatrini R, Giaveno A (2017) Metagenome-derived draft genome sequence of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans RV1 from an abandoned gold tailing in Neuquén, Argentina. Solid State Phenom 262:339–442
Valdés J, Veloso F, Jedlicki E, Holmes D (2003) Metabolic reconstruction of sulfur assimilation in the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans based on genome analysis. BMC Genom 4(1):51–65
Valdés J, Pedroso I, Quatrini R, Dodson RJ, Tettelin H, Blake R, Eisen JA, Holmes DS (2008) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans metabolism: from genome sequence to industrial applications. BMC Genom 9(1):597–620
Waltenbury DR, Leduc LG, Ferroni GD (2005) The use of RAPD genomic fingerprinting to study relatedness in strains of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Microbiol Methods 62(1):103–112
Wang Y, Yu W, Zhao S, Jiang G (2011) Isolation and identification of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its desulfurization reclamation of ground tyre rubber. J B Univ Chem Technol 38(1):105–109
Wang Y, Li H, Li D (2013) Biosynthesis of natrojarosite by immobilized iron-oxidizing bacteria. Int J Miner Process 120:35–38
Wang H, Ju L-K, Castaneda H, Cheng G, B-M Zhang Newby (2014) Corrosion of carbon steel C1010 in the presence of iron oxidizing bacteria Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Corros Sci 89:250–257
Watling HR (2008) The bioleaching of nickel-copper sulfides. Hydrometallurgy 91(1–4):70–88
Weiss BP, Kim SS, Kirschvink JL, Kopp RE, Sankaran M, Kobayashi A, Komeili A (2004) Magnetic tests for magnetosome chains in Martian meteorite ALH84001. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(22):8281–8284
Xenofontos E, Feidiou A, Constantinou M, Constantinides G, Vyrides I (2015) Copper biomachining mechanisms using the newly isolated Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans B1. Corros Sci 100:642–650
Xia L, Dai S, Yin C, Hu Y, Liu J, Qiu G (2009) Comparison of bioleaching behaviors of different compositional sphalerite using Leptospirillum ferriphilum, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36(6):845–851
Xie J, Liu X, Liu W, Qiu G (2005) Extraction of magnetosome from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biomagnetism 5(3):7–10
Xiong H, Liao Y, Zhou L, Xu Y, Wang S (2008) Biosynthesis of nanocrystal akaganéite from FeCl2 solution oxidized by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cells. Environ Sci Technol 42(11):4165–4169
Yamanaka T (2008) Oxidation and reduction of iron by bacteria, vol 5. Springer, Tokyo
Yan L, Yin H, Zhang S, Duan J, Li Y, Chen P, Li H (2010a) Organoarsenic resistance and bioremoval of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Bioresour Technol 101(16):6572–6575
Yan L, Yin HH, Zhang SA, Leng FF, Nan WB, Li HY (2010b) Biosorption of inorganic and organic arsenic from aqueous solution by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans BY-3. J Hazard Mater 178(1–3):209–217
Yan L, Yue X, Zhang S, Chen P, Xu Z, Li Y, Li H (2012a) Biocompatibility evaluation of magnetosomes formed by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Mater Sci Eng C 32(7):1802–1807
Yan L, Zhang S, Li X, Xinxin T, Zi Y (2012b) Magnetic properties of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and the effects of iron sources on magnetosome formation. J Heilongjiang Bayi Agric Univ 24(1):23–27
Yan L, Zhang S, Chen P, Wang W, Wang Y, Li H (2013) Magnetic properties of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Mater Sci Eng C 33(7):4026–4031
Yan L, Zhang S, Liu H, Wang W, Chen P, Li H (2016) Optimization of magnetosome production by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans using desirability function approach. Mater Sci Eng C 59:731–739
Yan L, Hu H, Zhang S, Chen P, Wang W, Li H (2017a) Arsenic tolerance and bioleaching from realgar based on response surface methodology by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans isolated from Wudalianchi volcanic lake, northeast China. Electron J Biotechnol 25:50–57
Yan S, Zheng G, Meng X, Zhou L (2017b) Assessment of catalytic activities of selected iron hydroxysulphates biosynthesized using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans for the degradation of phenol in heterogeneous Fenton-like reactions. Sep Purif Technol 185:83–93
Yang C, Qin W, Lai S, Wang J, Zhang Y, Jiao F, Ren L, Zhuang T, Chang Z (2011) Bioleaching of a low grade nickel–copper–cobalt sulfide ore. Hydrometallurgy 106(1–2):32–37
Yang Y, Chen S, Li S, Chen M, Chen H, Liu B (2014) Bioleaching waste printed circuit boards by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its kinetics aspect. J Biotechnol 173(6):24–30
Yang C, Zhu N, Shen W, Zhang T, Wu P (2017) Bioleaching of copper from metal concentrates of waste printed circuit boards by a newly isolated Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain Z1. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 19(1):247–255
Yarzábal A, Brasseur G, Bonnefoy V (2002) Cytochromes c of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 209(2):189–195
Yarzábal A, Duquesne K, Bonnefoy V (2003) Rusticyanin gene expression of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 33020 in sulfur-and in ferrous iron media. Hydrometallurgy 71(1–2):107–114
Yarzábal A, Appia-Ayme C, Ratouchniak J, Bonnefoy V (2004) Regulation of the expression of the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans rus operon encoding two cytochromes c, a cytochrome oxidase and rusticyanin. Microbiology 150(7):2113–2123
Yu Z, Huang B, Wang Y (2007) Studying advance in flue gas desulfurization by Thiobacillus ferroxidans. Acta Agric Jiangxi 19(6):121–124
Zammit CM, Mangold S, Rao Jonna V, Mutch LA, Watling HR, Dopson M, Watkin ELJ (2012) Bioleaching in brackish waters—effect of chloride ions on the acidophile population and proteomes of model species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(1):319–329
Zeng G, Deng X, Luo S, Luo X, Zou J (2012) A copper-catalyzed bioleaching process for enhancement of cobalt dissolution from spent lithium–ion batteries. J Hazard Mater 199–200:164–169
Zeng G, Luo S, Deng X, Li L, Au C (2013) Influence of silver ions on bioleaching of cobalt from spent lithium batteries. Miner Eng 49(8):40–44
Zhang S, Yan L, Li H, Liu H (2012) Optimal conditions for growth and magnetosome formation of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Afr J Microbiol 6(32):6142–6151
Zhu J, Gan M, Zhang D, Hu Y, Chai L (2013) The nature of schwertmannite and jarosite mediated by two strains of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans with different ferrous oxidation ability. Mater Sci Eng C 33(5):2679–2685
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41471201, 31100006), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (QC2014C023), University Nursing Program for Young Scholars with Creative Talents in Heilongjiang Province (UNPYSCT-2015086), Open Foundation of the Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Environmental Microbiology and Recycling of Argo-Waste in Cold Region (201704), Scientific Research Staring Foundation in HBAU (XZR2014-15) and Technology Program of Land Reclamation General Bureau of Heilongjiang (HNK135-04-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This manuscript is original and has not been submitted elsewhere for publication, in whole or in part, and no data was fabricated or manipulated (including images) in this work. The submission has been received explicitly from all co-authors. All the authors listed have contributed sufficiently to the scientific work and therefore share collective responsibility and accountability for the results.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Albers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Yan, L., Xing, W. et al. Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its potential application. Extremophiles 22, 563–579 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1024-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1024-9