Abstract
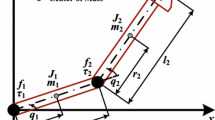
A robustness analysis and synthesis for incomplete nonlinear decoupling for a class of nonlinear systems is discussed. Rigid and elastic-joint robot models belong to this class. For the elastic case, a transformation facilitates the robustness analysis under a weak assumption. Charts with H 1- and H ∞- norms of closed-loop disturbance transfer functions of the nonlinear-decoupled system are presented for a robust pole assignment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, N. and Grimm, W.M., 1988, On L2- and L∞-Stability approaches for the robust control of robot manipulators, IEEE Trans. Automat. Control. AC-33, 118–122.
Becker, N. and Grimm, W.M., 1988, Design of robust controllers for robots. Part 1: Theoretical fundamentals. Part 2: Application to the design of P-PI cascade and PI-P state-feedback controllers (in German), Automatisierungstechnik 36 Nos. 3 and 4, 101–108 and 129–132.
De Luca, A., 1988, Dynamic control of robots with joint elasticity, Proc. IEEE Internat. Conf. Robot. Automat., Philadelphia, pp. 152–158.
De Luca, A. and Isidori, A., 1987, Feedback linearization of invertible systems, 2nd Duisburger Colloquium on Automation and Robotics. Duisburg.
Freund, E., 1973, Decoupling and pole assignment in nonlinear systems, Electron. Lett. 9, 373–374.
Freund, E., 1982, Fast nonlinear control with arbitrary pole-placement for industrial robots and manipulators, Internat. J. Robot. Res. 1, 65–78.
Grimm, W.M., 1989, Robustness analysis of nonlinear decoupling for elastic-joint robots, IEEE J. Robot. Automat. submitted for publication.
Grimm, W.M., Becker, N., and Frank, P.M., 1988, A robust stability design method for the control of robot manipulators, Int. Workshop on Robot Control, University of Oxford, April 11–12, in Robot Control-Theory and Applications, IEE Control Engineering Series 36 (eds. K., Warwick and A., Pugh), P. Peregrinus Ltd., London, Chapter 18, pp. 167–175.
Grimm, W.M., Becker, N., and Frank, P.M., 1988, Robust stability design framework for robot manipulator control, IEEE Internat. Conf. Robot. and Automat. Philadelphia, pp. 1042–1047 (1988).
Grimm, W.M., Berlin, F., and Frank, P.M., 1988, Robust control of robots with joint elasticities, Symposium on Robot Control, SYROCO' 88, Karlsruhe, pp. 58.1–6.
Grimm, W.M. and Frank, P.M., 1989, Methods for the norm estimation of non-linearities in equations of movements for robots (in German), Robotersysteme 5, 85–96.
Grimm, W.M. and Frank, P.M., 1989, Robust control of flexible-joint robot arms, 1989 IEEE Internat. Conf. on Control and Applications, ICCON'89, Jerusalem, pp. 1–6, TA-3-1.
Grimm, W.M. and Frank, P.M., 1990, Robustness analysis and synthesis of model-based elastic-joint robot manipulator control, Internal. J. Control Comput., IASTED, submitted for publication.
Isidori, A., Moog, C.H., and De Luca, A., 1986, A sufficient condition for full linearization via dynamic state feedback, 25th IEEE Conf. on Decision and Control, Athens, pp. 203–208.
Isidori, A. and Ruberti, A., 1984. On the synthesis of linear input-output responses for nonlinear systems, Systems Control Lett. 4, 17–22.
Kuntze, H.-B., Jacubasch, A.H.K., Richalet, J., and Arber, Ch., 1986, On the predictive functional control of an elastic industrial robot, Proc. 25th IEEE Conf. on Decision and Control, Athens, pp. 1877–1881.
Luh, J.Y.S., 1983, Conventional controller design for industrial robots—A tutorial, IEEE Trans. System, Man and Cybernet. SMC-13, 298–316.
Nicosia, S., Nicolo, F., and Lentini, D., 1981, Dynamical control of industrial robots with elastic and dissipative joints, IFAC 8th World Congress on Autom. Contr., Kyoto, pp. 1933–1940.
Otter, M. and Türk, S., 1988, The DFVLR Models 1 and 2 of the MANUTEC R3 Robot, DFVLR-Mitt. 88-13, Oberpfaffenhofen.
Seliger, R., 1988, Robuste Polvorgabe für die Regelung von starren und elastischen Robotern, Studienarbeit at the Fachgebiet MRT of the Universität Duisburg.
Spong, W.M., 1987, Modeling and control of elastic joint robots, ASME J. Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Contr. 109, 310–319.
Spong, M.W., 1989, Adaptive control of flexible-joint manipulators, System Control Lett. submitted for publication.
Spong, M.W. and Vidyasagar, M., 1985, Robust linear compensator design for nonlinear robotic control, Proc. IEEE Internat. Conf. on Robot. Automat. St. Louis, pp. 954–959.
Spong, M.W., and Vidyasagar, M., 1985, Robust nonlinear control of robot manipulators, Proc. 24th IEEE Conf. Decision and Control, Ft. Lauderdale, pp. 1767–1772.
Tarn, T., Bejczy, A.K., Isidori, A., and Chen, Y., 1984, Nonlinear feedback in robot arm control, 23rd IEEE Conf. Decision and Control, Las Vegas. pp. 736–751.
Türk, S., 1988 Dynamische Robotermodelle am Beispiel des MANUTEC R3, DFVLR-Mitt. 88–16, Institut für Dynamik der Flugsysteme, Oberpfaffenhofen.
Vidyasagar, M., 1978, Nonlinear Systems Analysis, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grimm, W.M., Frank, P.M. Robust pole assignment for incomplete nonlinear decoupling applied to robots. J Intell Robot Syst 3, 259–289 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126073
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126073