Summary
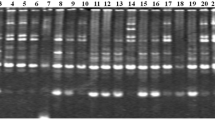
Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers combined with the Simple Matching index for calculating the distance matrix were used to determine the genetic diversity of African cassava clones. A preliminary study of three Manihot species using 20 primers clearly showed that RAPD markers were relevant for analyzing their genetic diversity. DNAs from 19 cultivars of Manihot esculenta Crantz (cassava) were amplified using 8 primers. Cultivars were well discriminated and coherently distributed, comparing to previous results from isozymes and RFLP studies. Genetic diversity analysis, characterization of collections and study of introgression are the domains that RAPD markers can contribute to the improvement of cassava.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PCR:
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- RAPD:
-
Randomly Amplified Polymorphic DNA
- RFLP:
-
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
References
Arnold, M.L., C.M. Buckner & J.J. Robinson, 1991. Pollen-mediated introgression and hybrid speciation in Louisiana irises. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 1398–1402.
Beeching, J.R., P. Marmey, M-C. Gavalda, M. Noirot, H.R. Hayson, M.A. Hughes & A. Charrier, 1993. An assessment of genetic diversity within a collection of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) germplasm using molecular markers. Annals of Botany 72: (6): 515–520.
Benzecri, J.P., 1973. L'analyse des données, tome 1, La Taxonomie, ed Dunod, Paris, 616 p.
Brizard, J.P., M. Noirot & F. Engelman, 1992. Conservation d'une vitrothèque de manioc (Manihot sp. en conditions de vie ralentie. ORSTOM report 23 p.
Bruijn de, G.H., 1971. Etude de caractère cyanogénétique du Manioc (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Thesis, Mendedelingen Landbouwhogeschool, Wageningen, 140 p.
Carlson, J.E., L.K. Tulsieram, J.C. Glaubitz, V.W.K. Luk, C. Kauffeldt & R. Rutledge, 1991. Segregation of random amplified DNA markers in F1 progeny of conifers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 194–200.
Cock, J.H., 1982. Cassava: a basic energy source in the tropics. Science 218: 755–762.
Cock, J.H., 1985. Cassava: new potential for a neglected crop. Westview Press, Inc., Boulder, CO. 191 p.
Dellaporta, S.L., J. Wood & J.B. Hicks, 1983. A plant DNA preparation. Version II. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 4: 19–21.
Hadrys, H., M. Balick & B. Scierwater, 1992. Applications of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) in molecular ecology. Mol. Ecol. 1: 55–63.
Hahn, S.K., A.K. Howland & E.R. Terry, 1980. Correlated resistance of cassava to mosaic and bacterial blight diseases. Euphytica 29: 305–311.
Hu, J. & C.F. Quiros, 1991. Identification of broccoli and cauliflower cultivars with RAPD markers. Plant Cell Reports 10: 505–511.
Hussain, A., W. Bushuk, H. Ramirez & W. Roca, 1987. Identification of cassava (Manihot Esculenta Crantz) cultivars by electrophoretic patterns of esterases enzymes. Seed Science and Technology 15: 19–21.
Jaccard, P., 1901. Etude comparative de la distribution florale dans une portion des Alpes et des Jura. Bull. Soc. Vaudoise Sci. Nat. 37: 547–579.
Jones, W.O., 1959. Manioc in Africa. Stanford University Press, 315 p.
Lashermes, P., J. Cros, P. Marmey & A. Charrier, 1993. Use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers to analyse genetic variability and relationships of Coffea species. Crop Evolution and Genetic Resources 40: 91–99.
Lefevre, F., 1989. Ressources génétiques et amélioration du Manioc, Manihot esculenta Crantz, en Afrique. Thesis, ORSTOM ed., coll TDM nEJ 57, Paris, 186 p.
Lefevre, F. & A. Charrier, 1993. Isozymes diversity within African Manihot germplasm. Euphytica 66: 73–80.
Plumbley, R.A. & J.E. Rickard, 1991. Post-harvest deterioration of cassava. Tropical Science 31: 1–32.
Quiros, C.F., J. Hu, P. This, A.M. Chevre & M. Delseny, 1991. Development and chromosal location of genome specific markers by polymerase chain reaction in Brassica. Theor. Appl. Genet. 82: 627–632.
Ramirez, H., A. Hussain, W. Roca & W. Bushuk, 1987. Isozymes electrophoregrams of sixteen enzymes in five tissues of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) varieties. Euphytica 36: 39–48.
Rogers, D.J. & S.G. Appan, 1973. Manihot-manihotoides (Euphorbiaceae). Flora Neotropica, Monograph 13, Hafner Press, New York, 272 p.
Silvestre, P. & M. Arraudeau, 1983. Le Manioc. ACCT collection: techniques agricoles et productions tropicales, Maisonneuve et Larose ed., 263 p.
Serres, E. & M. Rioux, 1986. Pratique de la classification automatique. L'exemple des Leishmania. p. 27–40. In: J.A. Rioux (Ed). Leishmania, Taxonomie et Phylogenèse. IMEEE, Montpellier.
Sokal, R. & C.D. Michener, 1958. A statistical method for evaluating systematic relationships. University of Kansas Science Bulletin 38: 1409–1438.
Vierling, R.A. & H. Nguyen, 1992. Use of RAPD markers to determine the genetic diversity of diploid wheat genotypes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 835–838.
Wilde, J., R. Waugh & W. Powell, 1992. Genetic fingerprinting of Theobroma clones using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 871–877.
Williams, J.G.K., A.R. Kubelik, K.J. Livak, J.A. Rafalski & S.V. Tingey, 1990. DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl. Acids Res. 18: 6531–6535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marmey, P., Beeching, J.R., Hamon, S. et al. Evaluation of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) germplasm collections using RAPD markers. Euphytica 74, 203–209 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040402
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040402