Abstract
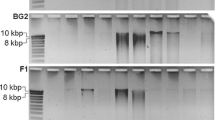
The anaerobic digestion (AD) of organic waste for biogas production has received much attention in recent years due to the increasing need for renewable energy and environmentally friendly waste management systems. Identification of the microbial community involved in AD aids in better understanding and optimising of the process. The choice of DNA extraction method is an integral step in any molecular biodiversity study. In the present study, potential biases introduced by DNA extraction methods were examined by comparing quality, quantity and representability of DNA extracted from AD samples using various extraction methods. In spite of the non-kit based method (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) yielding the largest quantity of DNA (approximately 44 µg DNA per gram dry weight), the extracted DNA contained PCR inhibitors. Furthermore, the quantity of extracted DNA was not proportional to species diversity. Diversity, determined using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE), was strongly linked to the type of extraction method used. The spin-column filter-based kit that incorporated mechanical and chemical lysis (Macherey-Nagel kit) gave the best results in terms of bacterial and archaeal diversity (Shannon–Wiener indices: average 2.5 and 2.6, respectively). Furthermore, this kit was the most effective at lysing hard-to-lyse bacterial and archaeal cells. The choice of DNA extraction method significantly influences the reliability and comparability of results obtained during AD microbial ecology investigations. Moreover, the careful selection of the DNA extraction method is of particular importance when analysing AD samples since these samples are rich in PCR inhibitors and hard-to-lyse cells such as archaea and gram-positive bacteria.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamowicz MS, Stasulli DM, Sobestanovich EM, Bille TW (2014) Evaluation of methods to improve the extraction and recovery of DNA from cotton swabs for forensic analysis. PLoS ONE 9(12):e116351
Albers SV, Meyer BH (2011) The archaeal cell envelope. Nat Rev Microbiol 9(6):414–426
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59(1):143–169
Ariefdjohan MW, Savaiano DA, Nakatsu CH (2010) Comparison of DNA extraction kits for PCR-DGGE analysis of human intestinal microbial communities from fecal specimens. J Nutr 9(1):1
Ariesyady HD, Ito T, Okabe S (2007) Functional bacterial and archaeal community structures of major trophic groups in a full-scale anaerobic sludge digester. Water Res 41(7):1554–1568
Bergmann I, Mundt K, Sontag M, Baumstark I, Nettmann E, Klocke M (2009) Influence of DNA isolation on Q-PCR-based quantification of methanogenic Archaea in biogas fermenters. Syst Appl Microbiol 33:78–84
Brownlow RJ, Dagnall KE, Ames CE (2012) A comparison of DNA collection and retrieval from two swab types (cotton and nylon flocked swab) when processed using three QIAGEN extraction methods. J Forensic Sci 57(3):713–717
Cabeen MT, Jacobs-Wagner C (2005) Bacterial cell shape. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(8):601–610
Carrigg C, Rice O, Kavanagh S, Collins G, O’Flaherty V (2007) DNA extraction method affects microbial community profiles from soils and sediment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77(4):955–964
Chaudhary PP, Sirohi SK, Kumar S (2011) Improved extraction of quality DNA from methanogenic archaea present in rumen liquor for PCR application. Asian J Anim Sci 5(3):166–174
Claassen S, du Toit E, Kaba M, Moodley C, Zar HJ, Nicol MP (2013) A comparison of the efficiency of five different commercial DNA extraction kits for extraction of DNA from faecal samples. J Microbiol Methods 94(2):103–110
Delmont TO, Robe P, Clark I, Simonet P, Vogel TM (2011) Metagenomic comparison of direct and indirect soil DNA extraction approaches. J Microbiol Methods 86(3):397–400
Endres HN, Johnson JA, Ross CA, Welp JK, Etzel MR (2003) Evaluation of an ion-exchange membrane for the purification of plasmid DNA. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 37(3):259–266
Fahle GA, Fischer SH (2000) Comparison of six commercial DNA extraction kits for recovery of cytomegalovirus DNA from spiked human specimens. J Clin Microbiol 38(10):3860–3863
Fang X, Willis RC, Burrell A, Evans K, Hoang Q, Xu W, Bounpheng M (2007) Automation of nucleic acid isolation on KingFisher magnetic particle processors. J Lab Autom 12(4):195–201
Garcia-Peña EI, Parameswaran P, Kang DW, Canul-Chan M, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2011) Anaerobic digestion and co-digestion processes of vegetable and fruit residues: process and microbial ecology. Bioresour Technol 102(20):9447–9455
Guo F, Zhang T (2013) Biases during DNA extraction of activated sludge samples revealed by high throughput sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol 97(10):4607–4616
Herrera A, Cockell CS (2007) Exploring microbial diversity in volcanic environments: a review of methods in DNA extraction. J Microbiol Methods 70(1):1–12
Ikenaga M, Asakawa S, Muraoka Y, Kimura M (2004) Methanogenic archaeal communities in rice roots grown in flooded soil pots: estimation by PCR-DGGE and sequence analyses. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 50(5):701–711
Jarrell KF, Faguy D, Hebert AM, Kalmokoff ML (1992) A general method of isolating high molecular weight DNA from methanogenic archaea (archaebacteria). Can J Microbiol 38(1):65–68
Kampmann K, Ratering S, Kramer I, Schmidt M, Zerr W, Schnell S (2012) Unexpected stability of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes communities in laboratory biogas reactors fed with different defined substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(7):2106–2119
Kishore R, Reef Hardy W, Anderson VJ, Sanchez NA, Buoncristiani MR (2006) Optimization of DNA extraction from low-yield and degraded samples using the BioRobot® EZ1 and BioRobot® M48. J Forensic Sci 51(5):1055–1061
Kojima K, Ozawa S (2002) US Patent No 20,020,192,667. Washington, DC, US Patent and Trademark Office
König H (1988) Archaeobacterial cell envelopes. Can J Microbiol 34(4):395–406
Krsek M, Wellington EMH (1999) Comparison of different methods for the isolation and purification of total community DNA from soil. J Microbiol Methods 39(1):1–16
Kubota K, Imachi H, Kawakami S, Nakamura K, Harada H, Ohashi A (2008) Evaluation of enzymatic cell treatments for application of CARD-FISH to methanogens. J Microbiol Methods 72(1):54–59
Leff LG, Dana JR, McArthur JV, Shimkets LJ (1995) Comparison of methods of DNA extraction from stream sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(3):1141–1143
Liesack W, Weyland H, Stackebrandt E (1991) Potential risks of gene amplification by PCR as determined by 16S rDNA analysis of a mixed-culture of strict barophilic bacteria. Microb Ecol 21(1):191–198
Magurran AE (1988) Ecological diversity and its measurement. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Mahalanabis M, Al-Muayad H, Kulinski MD, Altman D, Klapperich CM (2009) Cell lysis and DNA extraction of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria from whole blood in a disposable microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 9(19):2811–2817
Mertens B, Boon N, Verstraete W (2005) Stereospecific effect of hexachloro- cyclohexane on activity and structure of soil methanotrophic communities. Environ Microbiol 7:660–669
Miller DN, Bryant JE, Madsen EL, Ghiorse WC (1999) Evaluation and optimization of DNA extraction and purification procedures for soil and sediment samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(11):4715–4724
Minas K, McEwan NR, Newbold CJ, Scott KP (2011) Optimization of a high-throughput CTAB-based protocol for the extraction of qPCR-grade DNA from rumen fluid, plant and bacterial pure cultures. FEMS Microbiol Lett 325(2):162–169
Montpetit SA, Fitch IT, O’Donnell PT (2005) A simple automated instrument for DNA extraction in forensic casework. J Forensic Sci 50(3):555–563
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
Riviere D, Desvignes V, Pelletier E, Chaussonnerie S, Guermazi S, Weissenbach J, Sghir A (2009) Towards the definition of a core of microorganisms involved in anaerobic digestion of sludge. ISME J 3(6):700–714
Roh C, Villatte F, Kim BG, Schmid RD (2006) Comparative study of methods for extraction and purification of environmental DNA from soil and sludge samples. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 134:97–112
Roopnarain A, Adeleke R (2017) Current status, hurdles and future prospects of biogas digestion technology in Africa. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 67:1162–1179
Salonen A, Nikkilä J, Jalanka-Tuovinen J, Immonen O, Rajilić-Stojanović M, Kekkonen RA, de Vos WM (2010) Comparative analysis of fecal DNA extraction methods with phylogenetic microarray: effective recovery of bacterial and archaeal DNA using mechanical cell lysis. J Microbiol Methods 81(2):127–134
Shaw KJ, Thain L, Docker PT, Dyer CE, Greenman J, Greenway GM, Haswell SJ (2009) The use of carrier RNA to enhance DNA extraction from microfluidic-based silica monoliths. Anal Chim Acta 652(1):231–233
Sironen A, Uimari P, Vilkki J (2008) Comparison of different DNA extraction methods from hair root follicles to genotype Finnish Landrace boars with the Illumina PorcineSNP60 BeadChip. Agric Food Sci 20(2):143–150
Slana I, Pribylova R, Kralova A, Pavlik I (2011) Persistence of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis at a farm-scale biogas plant supplied with manure from paratuberculosis-affected dairy cattle. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(9):3115–3119
Sundberg C, Al-Soud WA, Larsson M, Alm E, Yekta SS, Svensson BH, Karlsson A (2013) 454 pyrosequencing analyses of bacterial and archaeal richness in 21 full-scale biogas digesters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 85(3):612–626
Tan SC, Yiap BC (2009) DNA, RNA, and protein extraction: the past and the present. Biomed Res Int. doi:10.1155/2009/574398
Theron J, Cloete TE (2000) Molecular techniques for determining microbial diversity and community structure in natural environments. Crit Rev Microbiol 26(1):37–57
Vanysacker L, Declerck SA, Hellemans B, De Meester L, Vankelecom I, Declerck P (2010) Bacterial community analysis of activated sludge: an evaluation of four commonly used DNA extraction methods. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88(1):299–307
Watanabe T, Asakawa S, Nakamura A, Nagaoka K, Kimura M (2004) DGGE method for analyzing 16S rDNA of methanogenic archaeal community in paddy field soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 232(2):153–163
Weiss A, Jerome V, Freitag R (2007) Comparison of strategies for the isolation of PCR-compatible, genomic DNA from a municipal biogas plants. J Chromatogr B 853:190–197
Wintzingerode FV, Göbel UB, Stackebrandt E (1997) Determination of microbial diversity in environmental samples: pitfalls of PCR-based rRNA analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21(3):213–229
Xu Z, Zhao M, Miao H, Huang Z, Gao S, Ruan W (2014) In situ volatile fatty acids influence biogas generation from kitchen wastes by anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 163:186–192
Yeates C, Gillings MR, Davison AD, Altavilla N, Veal DA (1998) Methods for microbial DNA extraction from soil for PCR amplification. Biol Proced Online 1(1):40–47
Acknowledgements
Biogas research at ARC-ISCW, South Africa is supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF; Grant Number 96735), the South Africa—Norway Research Co-operation (SANCOOP; Grant Number RCN 234203) and the Water Research Commission (WRC; Grant Number K5/2543). Opinions expressed and conclusions reached are those of the authors and not necessarily endorsed by the NRF, SANCOOP or WRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roopnarain, A., Mukhuba, M., Adeleke, R. et al. Biases during DNA extraction affect bacterial and archaeal community profile of anaerobic digestion samples. 3 Biotech 7, 375 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1009-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1009-x