Abstract
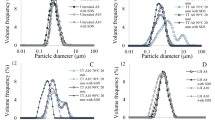
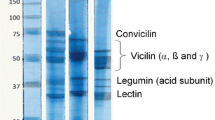
The article considers the influence of the thermal hydrolysis process on emulsifying properties and viscosity of potato protein isolates. During the study, there was demonstrated a significant improvement in emulsifying properties of the protein isolates as a result of denaturation. Thermal hydrolysis process includes high temperature and pressure. The improvement in emulsion stability maintained in some variants up to a week has been observed. Significant correlations were found between emulsification activity and emulsion stability after 1 week (p > 0.05). The rheological measurement showed an increase in viscosity after HPP. As the proposed method of the protein isolate modification does not affect the chemical composition of the protein solution, but only its molecular structure, it enables to increase the emulsifying properties in a simple and cost-effective way.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baier AK, Knorr D (2015) Influence of high isostatic pressure on structural and functional characteristics of potato protein. Food Res Int 77:753–761
Barba FJ, Terefe NS, Buckow R, Knorr D, Orlien V (2015) New opportunities and perspectives of high pressure treatment to improve health and safety attributes of foods. A review. Food Res Int 77:725–742
Bárta J, Bártová V (2008) Patatin, the major protein of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers, and its occurrence as genotype effect: processing versus table potatoes. Czech J Food Sci 26(5):347–359
Chao D, Aluko RE (2018) Modification of the structural, emulsifying, and foaming properties of an isolated pea protein by thermal pretreatment. CyTA J Food 16(1):357–366
Creusot N, Gruppen H (2007) Enzyme-induced aggregation and gelation of proteins. Biotechnol Adv 25(6):597–601
Damodaran S (2017) Food proteins and their applications. Routledge, New York
David S, Livney YD (2016) Potato protein based nanovehicles for health promoting hydrophobic bioactives in clear beverages. Food Hydrocolloids 57:229–235
Dziubiński M, Kiljański T (2002) Podstawy reologii i reometrii płynów nienewtonowskich. Inżynieria i Aparatura Chemiczna, pp 3–8
Galazka VB, Dickinson E, Ledward DA (2000) Influence of high pressure on interactions of 11S globulin Vicia faba with ι-carrageenan in bulk solution and at interfaces. Food Hydrocolloids 14(6):551–560
Gannasin SP, Ramakrishnan Y, Adzahan NM, Muhammad K (2012) Functional and preliminary characterisation of hydrocolloid from tamarillo (Solanum betaceum Cav.) puree. Molecules 17(6):6869–6885
Holm F, Eriksen S (1980) Emulsifying properties of undenatured potato protein concentrate. Int J Food Sci Technol 15(1):71–83
Itzhaki RF, Gill DM (1964) A micro-biuret method for estimating proteins. Anal Biochem 9(4):401–410
Khan NM, Mu TH, Zhang M, Arogundade LA (2014) The effects of pH and high hydrostatic pressure on the physicochemical properties of a sweet potato protein emulsion. Food Hydrocolloids 35:209–216
Khan NM, Mu TH, Ali F, Arogundade LA, Khan ZU, Zhang M, Sun HN (2015a) Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on emulsifying properties of sweet potato protein in model protein–hydrocolloids system. Food Chem 169:448–454
Khan NM, Mu TH, Sun HN, Zhang M, Chen JW (2015b) Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on secondary structure and emulsifying behavior of sweet potato protein. High Press Res 35(2):189–202
McClements DJ (2005) Food emulsions: principles, practice, and techniques. CRC Press, Washington
Miedzianka J, Pęksa A, Aniołowska M (2012) Properties of acetylated potato protein preparations. Food Chem 133(4):1283–1291
Nishinari K, Fang Y, Guo S, Phillips GO (2014) Soy proteins: a review on composition, aggregation and emulsification. Food Hydrocolloids 39:301–318
Pihlanto A (2017) Potato and other root crops. Fruit and vegetable phytochemicals: chemistry and human health, 2nd edn, pp 1195–1214
Ralet MC, Guéguen J (2000) Fractionation of potato proteins: solubility, thermal coagulation and emulsifying properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 33(5):380–387
Samaranayaka AG, Li-Chan EC (2011) Food-derived peptidic antioxidants: a review of their production, assessment, and potential applications. J Funct Foods 3(4):229–254
Ustunol Z (ed) (2014) Applied food protein chemistry. Wiley, Hoboken
Van Koningsveld GA, Walstra P, Voragen AG, Kuijpers IJ, Van Boekel MA, Gruppen H (2006) Effects of protein composition and enzymatic activity on formation and properties of potato protein stabilized emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 54(17):6419–6427
Wegener CB, Jansen G, Jurgens HU (2014) Influence of drought and wounding stress on soluble phenols and proteins in potato tubers. Sustain Agric Res 3(3):1
Xia C, Zhang S, Shi SQ, Cai L, Garcia AC, Rizvi HR, D’Souza NA (2016) Property enhancement of soy protein isolate-based films by introducing POSS. Int J Biol Macromol 82:168–173
Zhang Z, Arrighi V, Campbell L, Lonchamp J, Euston SR (2016) Properties of partially denatured whey protein products 2: solution flow properties. Food Hydrocolloids 56:218–226
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drozłowska, E., Weronis, M. & Bartkowiak, A. The influence of thermal hydrolysis process on emulsifying properties of potato protein isolate. J Food Sci Technol 57, 1131–1137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04148-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04148-z