Abstract
The combustion of fossil fuels has resulted in rapidly increasing emissions of nitrogen oxide (NOx), which has caused serious human health and environmental problems. NO capture has become a research focus in gas purification because NO accounts for more than 90% of NOx and is difficult to remove. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), features the little secondary pollution and the broad-spectrum strong oxidation of hydroxyl radicals (•OH), are effective and promising strategies for NO removal from coal-fired flue gas. This review provides the state of the art of NO removal by AOPs, highlighting several methods for producing •OH and SO4•−. According to the main radicals responsible for NO removal, these processes are classified into two categories: hydroxyl radical-based AOPs (HR-AOPs) and sulfate radical-based AOPs (SR-AOPs). This paper also reviews the mechanisms of NO capture by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and SO4•− in various AOPs. A HiGee (high-gravity) enhanced AOP process for improving NO removal, characterized by intensified gas-liquid mass transfer and efficient micro-mixing, is then proposed and discussed in brief. We believe that this review will be useful for workers in this field.

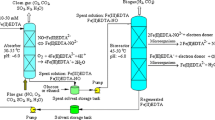
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AOPs:
-
advanced oxidation processes
- HR-AOPs:
-
hydroxy radical-based advanced oxidation processes
- SR-AOPs:
-
persulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes
- RPB:
-
rotating packed bed
- Fe2+ :
-
ferrous ion
- H2O2 :
-
hydrogen peroxide
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- NO2 :
-
nitrogen dioxide
- \( {\mathrm{NO}}_3^{-} \) :
-
nitrate ion
- \( {\mathrm{NO}}_2^{-} \) :
-
nitrite ion
- HO2• :
-
hydroperoxyl radical
- SO2 :
-
sulfur dioxide
- \( {\mathrm{S}}_2{\mathrm{O}}_8^{2\hbox{-} } \) :
-
peroxydisulfate
- \( {\mathrm{HSO}}_5^{\hbox{-} } \) :
-
PMS, peroxymonosulfate
- SO4•− :
-
sulfate radical
- rpm:
-
revolutions per minute
- k1-k9 :
-
rate constant
References
Adewuyi YG (2005a) Sonochemistry in environmental remediation. 1. Combinative and hybrid sonophotochemical oxidation processes for the treatment of pollutants in water. Environ Sci Technol 39:3409–3420. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049138y
Adewuyi YG (2005b) Sonochemistry in environmental remediation. 2. Heterogeneous sonophotocatalytic oxidation processes for the treatment of pollutants in water. Environ Sci Technol 39:8557–8570. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0509127
Adewuyi YG, Sakyi NY (2013a) Removal of nitric oxide by aqueous sodium persulfate simultaneously activated by temperature and Fe2+ in a lab-scale bubble reactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:14687–14697. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4025177
Adewuyi YG, Sakyi NY (2013b) Simultaneous absorption and oxidation of nitric oxide and sulfur dioxide by aqueous solutions of sodium persulfate activated by temperature. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:11702–11711. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie401649s
Adewuyi YG, Khan MA, Sakyi NY (2013) Kinetics and modeling of the removal of nitric oxide by aqueous sodium persulfate simultaneously activated by temperature and Fe2+. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:828–839. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie402801b
Adewuyi YG, Sakyi NY, Arif Khan M (2018) Simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 from flue gas by combined heat and Fe(2+) activated aqueous persulfate solutions. Chemosphere 193:1216–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.086
Andreozzi R, Caprio V, Insola A, Marotta R (1999) Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery. Catal Today 53:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0920-5861(99)00102-9
Baxendale JH, Wilson JA (1957) The photolysis of hydrogen peroxide at high light intensities. Trans Faraday Soc 53:344–356. https://doi.org/10.1039/tf9575300344
Bokare AD, Choi W (2014) Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J Hazard Mater 275:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.054
Boningari T, Smirniotis PG (2016) Impact of nitrogen oxides on the environment and human health: Mn-based materials for the NOx abatement. Curr Opin Chem Eng 13:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2016.09.004
Buehler RE, Staehelin J, Hoigne J (1984) Ozone decomposition in water studied by pulse radiolysis. 1. Perhydroxyl (HO2)/hyperoxide (O2-) and HO3/O3- as intermediates. J Phys Chem 88:2560–2564. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150656a026
Burrows JP, Cliff DI, Harris Geoffrey W, Thrush Brian A, Wilkinson JPT (1979) Atmospheric reactions of the HO2 radical studied by laser magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proc Roy Soc Lond A Math Phys Sci 368:463–481. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1979.0141
Chen X, Hu X (2019) Removal of NOx and SO2 from the coal-fired flue gas using a rotating packed bed pilot reactor with peroxymonosulfate activated by Fe (II) and heating. Energy Fuel 33:6707–6716. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b00881
Chen L, Hsu C-H, Yang C-L (2005) Oxidation and absorption of nitric oxide in a packed tower with sodium hypochlorite aqueous solutions. Environ Prog 24:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10075
Chen L, Xu Z, He C, Wang Y, Liang Z, Zhao Q, Lu Q (2018a) Gas-phase total oxidation of nitric oxide using hydrogen peroxide vapor over Pt/TiO2. Appl Surf Sci 457:821–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.07.032
Chen L, Yang W, Wang Y, Liang Z, Zhao Q, Lu Q (2018b) Investigation on the NO removal from simulated flue gas by using H2O2 vapor over Fe2(MoO4)3. Energy Fuel 32:8605–8613. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b01487
Chen C, Feng H, Deng Y (2019) Re-evaluation of sulfate radical based-advanced oxidation processes (SR-AOPs) for treatment of raw municipal landfill leachate. Water Res 153:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.01.013
Cheng T, Zheng C, Yang L, Wu H, Fan H (2019) Effect of selective catalytic reduction denitrification on fine particulate matter emission characteristics. Fuel 238:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.086
Cooper CD, Clausen CA, Pettey L, Collins MM, de Fernandez MP (2002) Investigation of ultraviolet light-enhanced H2O2 oxidation of NOx emissions. J Environ Eng - Asce 128:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9372(2002)128:1(68)
Dalton JS, Janes PA, Jones NG, Nicholson JA, Hallam KR, Allen GC (2002) Photocatalytic oxidation of NOx gases using TiO2: a surface spectroscopic approach. Environ Pollut 120:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(02)00107-0
Daood SS, Yelland TS, Nimmo W (2017) Selective non-catalytic reduction–Fe-based additive hybrid technology. Fuel 208:353–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.07.019
Deng Y, Ezyske CM (2011) Sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for simultaneous removal of refractory organic contaminants and ammonia in landfill leachate. Water Res 45:6189–6194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.015
Deshwal BR, Lee SH, Jung JH, Shon BH, Lee HK (2008) Study on the removal of NOx from simulated flue gas using acidic NaClO2 solution. J Environ Sci 20:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(08)60004-2
Dewil R, Mantzavinos D, Poulios I, Rodrigo MA (2017) New perspectives for advanced oxidation processes. J Environ Manag 195:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.010
Ding J, Zhong Q, Zhang S (2014) Simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification of flue gas by catalytic ozonation over Ce-Ti catalyst. Fuel Process Technol 128:449–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.08.003
Ding J et al (2016a) Effect of fluoride doping for catalytic ozonation of low-temperature denitrification over cerium–titanium catalysts. J Alloys Compd 665:411–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.01.040
Ding J, Zhong Q, Cai H, Zhang S (2016b) Structural characterizations of fluoride doped CeTi nanoparticles and its differently promotional mechanisms on ozonation for low-temperature removal of NOx (x = 1, 2). Chem Eng J 286:549–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.055
Fang P, Cen C-p, Wang X-m, Tang Z-j, Tang Z-x, Chen D-s (2013) Simultaneous removal of SO2, NO and Hg0 by wet scrubbing using urea+KMnO4 solution. Fuel Process Technol 106:645–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2012.09.060
Fenton HJH (1894) LXXIII.-Oxidation of tartaric acid in presence of iron. J Chem Soc Trans 65:899–910. https://doi.org/10.1039/CT8946500899
Fernández-González R, Julián-López B, Cordoncillo E, Escribano P (2011) New insights on the structural and optical properties of Ce-Ti mixed oxidenanoparticles doped with praseodymium. J Mater Chem 21:497–504. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm01625j
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature, 1972 238(5358):37–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/238037a0
Gao F et al. (2017) A review on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 over Mn–based catalysts at low temperatures: catalysts, mechanisms, kinetics and DFT calculations. Catalysts 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7070199
Gao L et al (2018) Simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 from simulated flue gas over CoOx -CeO2 loaded biomass activated carbon derived from maize straw at low temperatures. Chem Eng J 342:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.100
Glaze WH, Kang JW (1989) Advanced oxidation processes—description of a kinetic-model for the oxidation of hazardous materials in aqueous-media with ozone and hydrogen-peroxide in a semibatch reactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 28:1573–1580. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00095a001
Glaze WH, Kang JW, Chapin DH (1987) The chemistry of water-treatment processes involving ozone, hydrogen-peroxide and ultraviolet-radiation. Ozone - Sci Eng 9:335–352
Goldstein S, Czapski G (1995) The reaction of no-center-dot with O-2(center-dot-) and HO2-center-dot—a pulse-radiolysis study. Free Radic Biol Med 19:505–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/08915849(95)00034u
Gu D et al (2019) Kinetic and mechanistic investigation on the decomposition of ketamine by UV-254 nm activated persulfate. Chem Eng J 370:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.093
Guerra SA, Olsen SR, Anderson JJ (2014) Evaluation of the SO2 and NOx offset ratio method to account for secondary PM2.5 formation. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 64:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2013.852636
Guo R-T et al (2014) Absorption of NO by aqueous solutions of KMnO4/H2SO4 separation. Sci Technol 49:2085–2089. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.907809
Guo L, Zhong Q, Ding J, Ou M, Lv Z, Song F (2016) Low-temperature NOx(x = 1, 2) removal with •OH radicals from catalytic ozonation over α-FeOOH ozone. Sci Eng 38:382–394. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2016.1198685
Guo L, Zhong Q, Ding J, Deng Z, Zhao W (2017) Catalytic ozonation for low-temperature NOx (x = 1,2) removal with OH radicals over Cu doped Ce0.90Co0.10O2-δ catalysts and mechanism analysis. Fuel Process Technol 167:545–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.07.033
Guo L, Han C, Zhang S, Zhong Q, Ding J, Zhang B, Zeng Y (2018) Enhancement effects of O2- and OH radicals on NOx removal in the presence of SO2 by using an O3/H2O2 AOP system with inadequate O3 ( O3/NO molar ratio = 0.5). Fuel 233:769–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.099
Haber F, Weiss J (1932) On the catalysis of hydroperoxide. Naturwissenschaften 20:948–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01504715
Haber F, Weiss J (1934) The catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iron salts. Proc R Soc:332–351
Han Y et al (2015) Abatement of SO2-NOx binary gas mixtures using a ferruginous active absorbent: Part I. Synergistic effects and mechanism. J Environ Sci (China) 30:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.10.012
Han Z et al (2017) New experimental results of NO removal from simulated flue gas by wet scrubbing using NaClO solution. Energy Fuel 31:3047–3054. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03062
Han C et al (2018) Ehanced catalytic ozonation of NO over black-TiO2 catalyst under inadequate ozone (O3/NO molar ratio = 0.6). Chem Eng Res Des 136:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2018.05.012
Han Z, Lan T, Han Z, Yang S (2019) NO removal from simulated diesel engine exhaust gas by cyclic scrubbing using NaClO2 solution in a rotating packed bed reactor. J Chem 2019:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3159524
Hao R, Yang S, Yuan B, Zhao Y (2017a) Simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification through an integrative process utilizing NaClO2/Na2S2O8. Fuel Process Technol 159:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.01.018
Hao R, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Li Y, Yuan B, Mao X, Zhao Y (2017b) An advanced wet method for simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO from coal-fired flue gas by utilizing a complex absorbent. Chem Eng J 307:562–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.103
Howard JC (1980) Kinetic study of the equilibrium HO2• + NO⇌•OH + NO2 and the thermochemistry of HO2. J Am Chem Soc 102:6937–6941. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00543a006
Huang X, Ding J, Zhong Q (2015) Catalytic decomposition of H2O2 over Fe-based catalysts for simultaneous removal of NOx and SO2. Appl Surf Sci 326:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.11.088
Ji Y et al (2017) Ferrous-activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation of antimicrobial agent sulfaquinoxaline and structurally related compounds in aqueous solution: kinetics, products, and transformation pathways. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:19535–19545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9569-1
Jung Y, Pyo YD, Jang J, Kim GC, Cho CP, Yang C (2019) NO, NO2 and N2O emissions over a SCR using DOC and DPF systems with Pt reduction. Chem Eng J 369:1059–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.137
Kang Z, Yuan Q, Zhao L, Dai Y, Sun B, Wang T (2017) Study of the performance, simplification and characteristics of SNCR de-NOx in large-scale cyclone separator. Appl Therm Eng 123:635–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.04.122
Kang X, Ma X, Ja Y, Gao X (2018) A study on simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 by using sodium persulfate aqueous scrubbing. Chin J Chem Eng 26:1536–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.02.026
Kasper JM, Clausen CA III, Cooper CD (1996) Control of nitrogen oxide emissions by hydrogen peroxide-enhanced gas-phase oxidation of nitric oxide. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 46:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.1996.10467444
Khan NE, Adewuyi YG (2010) Absorption and oxidation of nitric oxide (NO) by aqueous solutions of sodium persulfate in a bubble column reactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:8749–8760. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie100607u
Khan S, He X, Khan HM, Boccelli D, Dionysiou DD (2016) Efficient degradation of lindane in aqueous solution by iron (II) and/or UV activated peroxymonosulfate. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 316:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2015.10.004
Kobayashi H, Takezawa N, Niki T (1977) Removal of nitrogen-oxides with aqueous-solutions of inorganic and organic-reagents. Environ Sci Technol 11:190–192. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60125a011
Kolthoff IM, Miller IK (1951) The Chemistry Of Persulfate .1. The kinetics and mechanism of the decomposition of the persulfate ion in aqueous medium. J Am Chem Soc 73:3055–3059. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01151a024
Kwan WP, Voelker BM (2003) Rates of hydroxyl radical generation and organic compound oxidation in mineral-catalyzed Fenton-like systems. Environ Sci Technol 37:1150–1158. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020874g
Lasek J, Yu Y-H, Wu JCS (2013) Removal of NOx by photocatalytic processes. J Photochem Photobiol C: Photochem Rev 14:29–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2012.08.002
Legrini O, Oliveros E, Braun AM (1993) Photochemical processes for water-treatment. Chem Rev 93:671–698. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00018a003
Li Y, Zhong W, Ju J, Wang T, Liu F (2014) Experiment on simultaneous absorption of NO and SO2 from sintering flue gas by oxidizing agents of KMnO4/NaClO. Int J Chem React Eng 12. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2014-0066
Li Y, Li D, Li J, Wang J, Hussain A, Ji H, Zhai Y (2015) Pretreatment of cyanided tailings by catalytic ozonation with Mn2+/O3. J Environ Sci (China) 28:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.05.038
Lin H, Wu J, Zhang H (2014) Degradation of clofibric acid in aqueous solution by an EC/Fe3+/PMS process. Chem Eng J 244:514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.01.099
Lin FW, Wang ZH, Ma Q et al (2016a) N2O5 formation mechanism during the ozone-based low-temperature oxidation deNOx. Process Energy Fuels 30(6):5101–5107. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00824
Lin FW, Wang ZH, Ma Q, Yang Y, Whiddon R, Zhu Y, Cen K (2016b) Catalytic deep oxidation of NO by ozone over MnOx loaded spherical alumina catalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 198:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.05.058
Lin FW, Wang ZH, Shao JM et al (2017) Catalyst tolerance to SO2 and water vapor of Mn based bimetallic oxides for NO deep oxidation by ozone. RSC Adv 7(40):25132–25143. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra04010e
Lin FW, Wang ZH, Zhang ZM et al (2020) Flue gas treatment with ozone oxidation: An overview on NOx, organic pollutants, and mercury. Chem Eng J 382:123030
Liu Y, Adewuyi YG (2016) A review on removal of elemental mercury from flue gas using advanced oxidation process: chemistry and process. Chem Eng Res Des 112:199–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2016.06.024
Liu Y, Wang Y (2017) Simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 using aqueous peroxymonosulfate with coactivation of Cu2+/Fe3+ and high temperature. AIChE J 63:1287–1302. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.15503
Liu Y, Wang Y (2018) Elemental mercury removal from flue gas using heat and Co2+/Fe2+ coactivated oxone oxidation system. Chem Eng J 348:464–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.171
Liu Y, Wang Y (2019) Gaseous elemental mercury removal using VUV and heat coactivation of Oxone/H2O/O2 in a VUV-spraying reactor. Fuel 243:352–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.01.130
Liu Y, Zhang J (2017) Removal of NO from flue gas using UV/S2O82- process in a novel photochemical impinging stream reactor. AIChE J 63:2968–2980. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.15633
Liu Y, Zhang J, Sheng C, Zhang Y, Zhao L (2010a) Preliminary study on a new technique for wet removal of nitric oxide from simulated flue gas with an ultraviolet (UV)/H2O2. Process Energy Fuels 24:4925–4930. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef1006325
Liu Y, Zhang J, Sheng C, Zhang Y, Zhao L (2010b) Simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 from coal-fired flue gas by UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Chem Eng J 162:1006–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.07.009
Liu Y, Zhang J, Sheng C (2011) Kinetic model of NO removal from SO2-containing simulated flue gas by wet UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Chem Eng J 168:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.061
Liu CS, Shih K, Sun CX, Wang F (2012a) Oxidative degradation of propachlor by ferrous and copper ion activated persulfate. Science of The Total Environment 416:507–512
Liu Y, Pan J, Zhang J, Tang A, Liu Y (2012b) Study on mass transfer-reaction kinetics of NO removal from flue gas by using a UV/Fenton-like reaction. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:12065–12072. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie300883f
Liu Y, Zhang J, Pan J, Tang A (2012c) Investigation on the removal of NO from SO2-containing simulated flue gas by an ultraviolet/Fenton-like reaction. Energy Fuel 26:5430–5436. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef3008568
Liu Y, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Pan J, Wang Q, Zhang J (2015) Removal of Hg0 and simultaneous removal of Hg0/SO2/NO in flue gas using two Fenton-like reagents in a spray reactor. Fuel 145:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.12.084
Liu Y, Wang Q, Pan J (2016) Novel process of simultaneous removal of nitric oxide and sulfur dioxide using a vacuum ultraviolet (VUV)-activated O2/H2O/H2O2 system in a wet VUV-spraying reactor. Environ Sci Technol 50:12966–12975. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02753
Liu Y, Wang Y, Liu Z, Wang Q (2017a) Oxidation removal of nitric oxide from flue gas using UV photolysis of aqueous hypochlorite. Environ Sci Technol 51:11950–11959. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03628
Liu Y, Xu W, Pan J, Wang Q (2017b) Oxidative removal of NO from flue gas using ultrasound, Mn2+/Fe2+ and heat coactivation of Oxone in an ultrasonic bubble reactor. Chem Eng J 326:1166–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.026
Liu Y, Xu W, Zhao L, Wang Y, Zhang J (2017c) Absorption of NO and simultaneous absorption of SO2/NO using a vacuum ultraviolet light/ultrasound/KHSO5 system. Energy Fuel 31:12364–12375. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b01274
Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang Y, Yin Y, Pan J, Zhang J, Wang Q (2018a) Simultaneous absorption of SO2 and NO from flue gas using ultrasound/Fe2+/heat coactivated persulfate system. J Hazard Mater 342:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.08.042
Liu Y, Liu Z, Zhao L, Wang Y, Pan J, Wang Q, Zhang J (2018b) Removal of NO in flue gas using vacuum ultraviolet light/ultrasound/chlorine in a VUV-US coupled reactor. Fuel Process Technol 169:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.10.011
Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang Q, Pan J, Zhang J (2018c) Simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 using vacuum ultraviolet light (VUV)/heat/peroxymonosulfate (PMS). Chemosphere 190:431–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.020
Liu Y, Wang Y, Xu W, Yang W, Pan Z, Wang Q (2018d) Simultaneous absorption–oxidation of nitric oxide and sulfur dioxide using ammonium persulfate synergistically activated by UV-light and heat. Chem Eng Res Des 130:321–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.12.043
Liu Y, Li Y, Xu H, Xu J (2019) Oxidation removal of gaseous Hg0 using enhanced-Fenton system in a bubble column reactor. Fuel 246:358–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.03.018
Liu Y, Shan Y, Wang Y (2020) Novel simultaneous removal technology of NO and SO2 using a semi-dry microwave activation persulfate system. Environ Sci Technol 54:2031–2042. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07221
Ma Q, Wang ZH, Lin FW et al (2016) Characteristics of O3 oxidation for simultaneous desulfurization and denitration with limestone-gypsum wet scrubbing: application in a carbon black drying kiln furnace. Energy Fuel 30(3):2302–2308. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b02717
Martinez-Oviedo A, Ray SK, Nguyen HP, Lee SW (2019) Efficient photo-oxidation of NOx by Sn doped blue TiO2 nanoparticles. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 370:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.10.032
Mechakra H, Sehili T, Kribeche MA, Ayachi AA, Rossignol S, George C (2016) Use of natural iron oxide as heterogeneous catalyst in photo-Fenton-like oxidation of chlorophenylurea herbicide in aqueous solution: reaction monitoring and degradation pathways. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 317:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2015.11.019
Mellouki A, Wallington TJ, Chen J (2015) Atmospheric chemistry of oxygenated volatile organic compounds: impacts on air quality and climate. Chem Rev 115:3984–4014. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500549n
Mondal MK, Chelluboyana VR (2013) New experimental results of combined SO2 and NO removal from simulated gas stream by NaClO as low-cost absorbent. Chem Eng J 217:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.002
Pan W, Zhang X, Guo R, Zhou Y, Jin Q, Ren J (2015) A thermodynamic study of simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO by a KMnO4/ammonia solution energy sources, part A: recovery, utilization, and environmental effects. Energy Sources A Recovery Util Environ Effects 37:721–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2011.592919
Peyton GR, Glaze WH (1988) Destruction of pollutants in water with ozone in combination with ultraviolet-radiation .3. Photolysis of aqueous ozone. Environ Sci Technol 22:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00172a003
Pham AL-T, Lee C, Doyle FM, Sedlak DL (2009) A silica-supported iron oxide catalyst capable of activating hydrogen peroxide at neutral pH values. Environ Sci Technol 43:8930–8935. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902296k
Raghunath CV, Mondal MK (2017) Experimental scale multi component absorption of SO2 and NO by NH3/NaClO scrubbing. Chem Eng J 314:537–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.011
Roy S, Hegde MS, Madras G (2009) Catalysis for NOx abatement. Appl Energy 86:2283–2297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.03.022
Sada E, Kumazawa H, Hayakawa N, Kudo I, Kondo T (1977) Absorption of NO in aqueous-solutions of KMNO4. Chem Eng Sci 32:1171–1175. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(77)80049-3
Silas K, Ghani WAWAK, Choong TSY, Rashid U (2018) Carbonaceous materials modified catalysts for simultaneous SO2/NOx removal from flue gas: a review. Catal Rev 61:134–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/01614940.2018.1482641
Song Z et al (2018) Effect of Ti doping on heterogeneous oxidation of NO over Fe3O4 (111) surface by H2O2: a density functional study. Chem Eng J 354:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.042
Staehelin J, Hoigne J (1982) Decomposition of ozone in water: rate of initiation by hydroxide ions and hydrogen peroxide. Environ Sci Technol 16:676–681. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00104a009
Staehelin J, Hoigne J (1985) Decomposition of ozone in water in the presence of organic solutes acting as promoters and inhibitors of radical chain reactions. Environ Sci Technol 19:1206–1213. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00142a012
Sun WY, Ding SL, Zeng SS, Su SJ, Jiang WJ (2011) Simultaneous absorption of NOx and SO2 from flue gas with pyrolusite slurry combined with gas-phase oxidation of NO using ozone. J Hazard Mater 192:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.104
Tang L, Nagashima T, Hasegawa K, Ohara T, Sudo K, Itsubo N (2015) Development of human health damage factors for PM2.5 based on a global chemical transport model. Int J Life Cycle Assess 23:2300–2310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-014-0837-8
Teramoto M, Ikeda M, Teranishi H (1977) Absorption of dilute NO in mixed aqueous-solutions of KMNO4 and NAOH. Int Chem Eng 17:265–270
Tokumura M, Morito R, Hatayama R, Kawase Y (2011) Iron redox cycling in hydroxyl radical generation during the photo-Fenton oxidative degradation: dynamic change of hydroxyl radical concentration. Appl Catal B Environ 106:565–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.06.017
Vorontsov AV (2019) Advancing Fenton and photo-Fenton water treatment through the catalyst design. J Hazard Mater 372:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.033
Wang ZH, Zhou JH, Zhu YQ et al (2007) Simultaneous removal of NOx, SO2 and Hg in nitrogen flow in a narrow reactor by ozone injection: Experimental results. Fuel Process Technol 88(8):817–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2007.04.001
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Tan Z, Li Q (2018) A wet process for oxidation-absorption of nitric oxide by persulfate/calcium peroxide. Chem Eng J 350:767–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.145
Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu Y (2019) Elimination of nitric oxide using new Fenton process based on synergistic catalysis: optimization and mechanism. Chem Eng J 372:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.122
Wu J, Cheng Y (2006) In situ FTIR study of photocatalytic NO reaction on photocatalysts under UV irradiation. J Catal 237:393–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2005.11.023
Wu B, Xiong Y (2018) A novel low-temperature NO removal approach with •OH from catalytic decomposition of H2O2 over La1-xCaxFeO3 oxides. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5317
Wu B, Xiong Y, Ru J, Feng H (2016) Enhancement of NO absorption in ammonium-based solution using heterogeneous Fenton reaction at low H2O2 consumption. Korean J Chem Eng 33:3407–3416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0195-2
Wu B, Xiong Y, Ge Y (2018) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO from flue gas with OH from the catalytic decomposition of gas-phase H2O2 over solid-phase Fe2(SO4)3. Chem Eng J 331:343–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.097
Wydeven T, Wood P, Tsuji O (2000) An improved UV/ozone oxidation system ozone. Sci Eng 22:427–440. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919510009408785
Xi H, Zhou S, Zhou J (2019) New experimental results of NO removal from simulated marine engine exhaust gases by Na2S2O8/urea solutions. Chem Eng J 362:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.002
Xia D et al (2011) A novel wet-scrubbing process using Fe(VI) for simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO. J Environ Monit 13:864–870. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0em00647e
Yang W, Liu Y, Xu W, Wang Q, Zhao L, Pan J (2017) Oxidation-separation kinetics of nitric oxide from flue gas using ferrate (VI) reagent in a spraying reactor. Can J Chem Eng 95:1364–1372. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.22778
Yang S, Xiong Y, Ge Y, Zhang S (2018) Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of nitric oxide by magnetite: kinetics and mechanism. Mater Lett 218:257–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.01.171
Zhang J, Ayusawa T, Minagawa M, Kinugawa K, Yamashita H, Matsuoka M, Anpo M (2001) Investigations of TiO2 photocatalysts for the decomposition of NO in the flow system. J Catal 198:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.2000.3076
Zhang L-L, Wang J-X, Sun Q, Zeng X-F, Chen J-F (2012) Removal of nitric oxide in rotating packed bed by ferrous chelate solution. Chem Eng J 181-182:624–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.12.027
Zhang J et al (2014) Simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 from flue gas by ozone oxidation and NaOH absorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:6450–6456. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie403423p
Zhang K, Zhao J, Zhu Y (2018a) MPC case study on a selective catalytic reduction in a power plant. J Process Control 62:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2017.11.010
Zhang P et al (2018b) A study on simultaneous catalytic ozonation of Hg0 and NO using Mn–TiO2 catalyst at low flue gas temperatures. Chem Pap 72:1347–1361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0388-8
Zhao Y, Hao R (2014) Denitrification utilizing a vaporized enhanced-Fenton reagent: kinetics and feasibility. RSC Adv 4:46060–46067. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra07879a
Zhao Y, Guo T-x, Chen Z-y, Du Y-r (2010) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO using M/NaClO2 complex absorbent. Chem Eng J 160:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.02.060
Zhao D, Liao X, Yan X, Huling SG, Chai T, Tao H (2013) Effect and mechanism of persulfate activated by different methods for PAHs removal in soil. J Hazard Mater 254-255:228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.056
Zhao Y, Han Y, Guo T, Ma T (2014a) Simultaneous removal of SO2, NO and Hg0 from flue gas by ferrate (VI) solution. Energy 67:652–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.01.081
Zhao Y, Wen X, Guo T, Zhou J (2014b) Desulfurization and denitrogenation from flue gas using Fenton reagent. Fuel Process Technol 128:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.07.006
Zhao Y, Hao R-L, Guo Q, Feng Y-N (2015) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO by a vaporized enhanced-Fenton reagent. Fuel Process Technol 137:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.04.003
Zhao W, Zhang S, Ding J, Deng Z, Guo L, Zhong Q (2016) Enhanced catalytic ozonation for NOx removal with CuFe2O4 nanoparticles and mechanism analysis. J Mol Catal A Chem 424:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.08.007
Zhao Y, Yuan B, Hao R, Tao Z (2017) Low-temperature conversion of NO in flue gas by vaporized H2O2 and nanoscale zerovalent iron. Energy Fuel 31:7282–7289. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b00588
Zhao Y, Han Y, Zhao Z (2018) Removal of NO from flue gas by a heterogeneous Fenton-like process. Chem Eng Technol 41:2203–2211. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201700717
Zhao Y, Han Y, Wang T, Sun Z, Fang C (2019) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO from flue gas using iron-containing polyoxometalates as heterogeneous catalyst in UV-Fenton-like process. Fuel 250:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.03.151
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the funding received from the University of Chinese Academy of Science for financial assistance via Grant Y8540XX222. The institution and program is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding sources
This study was supported by the University of Chinese Academy of Science (No. Y8540XX222).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 86 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Wang, C., Zhang, J. et al. NOx attenuation in flue gas by •OH/SO4•--based advanced oxidation processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 37468–37487 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09782-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09782-1