Abstract
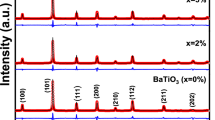
The polycrystalline ceramics of Sm3Fe5-xAlxO12 (x = 0, 0.5, 1, and 2) are prepared by the sol–gel method. The structure, dielectric, and magnetic properties are studied. The X-ray diffraction patterns indicate that the prepared samples crystallize in garnet phase. All of the samples exhibit relatively high-dielectric permittivity in the low-frequency range. With the increase of Al3+ content, the dielectric permittivity and the temperature and frequency stabilities at low frequency simultaneously decrease, which suggest the important role of Fe3+ for the dielectric property. Two sets of dielectric relaxation are observed in the available temperature from 300 to 700 K. With the increase of Al3+ concentration, the high-frequency relaxation peaks that originate from the carriers hopping between Fe2+ and Fe3+ shift toward the direction of low frequency, and the low-frequency relaxation processes that arise from the doubly ionized oxygen vacancies spread to high frequency. By measuring the hysteresis loops and the magnetization-temperature curves, it indicates that the magnetization is decreased and the magnetic property transforms from ferrimagnetism to paramagnetism with increasing the value of x at room temperature.

Large permittivity and ferrimagnetic property are observed in Sm3Fe5O12 and they are decreased via Al3+ doping, reflecting the crucial role of Fe3+ for the high performance.
Highlights
-
Sm3Fe5-xAlxO12 (x = 0, 0.5, 1, and 2) are fabricated via sol–gel method.
-
The dielectric relaxation processes are influenced by the content of iron ions.
-
Two magnetic anomalies are detected at low temperature.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kidoh H, Morimoto A, Shimizu T (1991) Synthesis of ferromagnetic Bi-substituted yttrium iron garnet films by laser ablation. Appl Phys Lett 59:237
Hansen P, Krumme JP (1984) Magnetic and magneto-optical properties of garnet films. Thin Solid Films 114:69–107
Sekijima T, Kishimoto H, Fujii T, Wakino K, Okada M (1999) Magnetic, optical and microwave properties of rare-earth-substituted fibrous yttrium iron garnet single crystals grown by floating zone method. Jpn J Appl Phys 38:5874–5878
Sugimoto M (1999) The past, present, and future of ferrites. J Am Ceram Soc 82:269–280
Dillon JF (1958) Optical properties of several ferrimagnetic garnets. J Appl Phys 29:539
Phan MH, Morales MB, Chinnasamy CN, Latha B, Harris VG, Srikanth H (2009) Magnetocaloric effect in bulk and nanostructured Gd3Fe5O12 materials. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:115007
Guillot M, Rodic D, Mitric M (1993) Temperature dependencies of the lattice constants and thermal expansion coefficients of Sm3Fe5O12 and Er3Fe5O12 single crystals. J Appl Phys 73:6304
Guillot M, Marchand A, Nekvasil Y, Tchéou F (1983) Anisotropic magnetic properties of samarium iron garnet in high magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 31–34:777–778
Harrison FW, Thompson JFA, Lang GK (1965) Single-crystal magnetization data for anisotropic rare-earth iron garnets at low temperatures. J Appl Phys 36:1014
Geller S, Balestrino G (1980) Magnetic phase transitions in samarium iron garnet. Phys Rev B 21:4055–4059
Hur N, Park S, Guha S, Borissov A, Kiryukhin V, Cheong SW (2005) Low-field magnetodielectric effect in terbium iron garnets. Appl Phys Lett 87:042901
Su J, Lu XM, Zhang C, Zhang JT, Sun H, Ju CC et al. (2012) Study on dielectric and magnetic properties of Ho3Fe5O12 ceramics. Phys B 407:485–488
Louca D, Kamazawa K, Proffen T (2009) Formation of local electric dipoles with no unique polar axis in Tb3Fe5O12. Phys Rev B 80:214406
Siao YJ, Qi X, Lin CR, Huang JCA (2012) Dielectric and magnetic properties of Y3-xTbxFe5O12 ferrimagnets. J Appl Phys 111:07A521
Wu H, Huang F, Lu X, Xu T, Lu X, Ti R et al. (2016) Grain size and Fe2+ concentration-dependent magnetic, dielectric, and magnetodielectric properties of Y3Fe5O12 ceramics. Phys Status Solidi A 1:146–153
Huang S, Shi LR, Sun HG, Li CL, Chen L, Yuan SL (2016) High temperature dielectric response in Sm3Fe5O12 ceramics. J Alloy Compd 674:341–346
Huang S, Su KP, Wang HO, Yuan SL, Huo DX (2017) High temperature dielectric response in R3Fe5O12 (R = Eu, Gd) ceramics. Mater Chem Phys 197:11–16
Su J, Lu X, Zhang J, Sun H, Zhang C, Jiang Z et al. (2012) The effect of Fe2+ ions on dielectric and magnetic properties of Yb3Fe5O12 ceramics. J Appl Phys 111:014112
Su J, Lu X, Zhang C, Zhang J, Peng S, Wu X et al. (2011) The effect of sintering temperature on magnetic and dielectric properties of Ho3Fe5O12 ceramics. J Mater Sci 46:3488–3492
Wu YJ, Yu C, Chen XM, Li J (2012) Effects of Al substitution on dielectric response and magnetic behavior of yttrium iron garnet ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 95:1671–1675
Wu YJ, Gao Y, Chen XM (2007) Dielectric relaxations of yttrium iron garnet ceramics over a broad temperature range. Appl Phys Lett 91:092912
Lunkenheimer P, Krohns S, Riegg S, Ebbinghaus SG, Reller A, Loidl A (2010) Colossal dielectric constants in transition-metal oxides. Eur Phys J Spec Top 180:61–89
Wu X, Wang X, Liu Y, Cai W, Peng S, Huang F et al. (2009) Study on dielectric and magnetodielectric properties of Lu3Fe5O12 ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 95:182903
Yamasaki Y, Kohara Y, Tokura Y (2009) Quantum magnetoelectric effect in iron garnet. Phys Rev B 80:140412. (R)
Kohara Y, Yamasaki Y, Onose Y, Tokura Y (2010) Excess-electron induced polarization and magnetoelectric effect in yttrium iron garnet. Phys Rev B 82:104419
Sinclair DC, Adams TB, Morrison FD, West AR (2002) CaCu3Ti4O12: One-step internal barrier layer capacitor. Appl Phys Lett 80:2153
Lunkenheimer P, Fichtl R, Ebbinghaus SG, Loidl A (2004) Nonintrinsic origin of the colossal dielectric constants in CaCu3Ti4O12. Phys Rev B 70:172102
Guillot M, Chinnasamy CN, Greneche JM, Harris VG (2012) Tuning the cation distribution and magnetic properties of single phase nanocrystalline Dy3Fe5O12 garnet. J Appl Phys 111:07A517
Kim CS, Min BK, Kim SJ, Yoon SR, Uhm YR (2003) Crystallographic and magnetic properties of Y3Fe5-xAlxO12. J Magn Magn Mater 254-255:553–555
Thongmee S, Winotai P, Tang IM (1999) Local field fluctuations in the substituted aluminum iron garnets, Y3Fe5-xAlxO12. Solid State Commun 109:471–476
Siao YJ, Qi X, Lin CR, Huang JCA (2011) Dielectric relaxation and magnetic behavior of bismuth-substituted yttrium iron garnet. J Appl Phys 109:07A508
Skaudzius R, Sakirzanovas S, Kareiva A (2018) On the samarium substitution effects in Y3-xSmxAl5O12 (x = 0.1-3.0). J Electron Mater 47:3951–3956
Silva KLD, Šepelák V, Paesano A Jr., Litterst FJ, Becker K-D (2010) Structural studies of Bi2(FexAl1-x)4O9 solid solutions (0.1 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) prepared by a combined mechanochemical/thermal synthesis Z Anorg Allg Chem 636:1018–1025
Cole KS, Cole RH (1941) Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics I. Alternating current characteristics. J Chem Phys 9:341–351
Costantini JM, Salvetat JP, Brisard F (1997) Dielectric and transport properties of magnetic insulators irradiated with GeV heavy ions. J Appl Phys 82:5063
Zhang J, Li Y, Zhang D, Qi HC, Xu XX, Huang ZF et al. (2016) Giant dielectric behavior in CaLaAlO4 ceramics. Mater Lett 168:163–165
Liu LJ, Shi DP, Zheng SY, Huang YM, Wu SS, Li YH et al. (2013) Polaron relaxation and non-ohmic behavior in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics with different cooling methods. Mater Chem Phys 139:844–850
Jonscher AK (1977) The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267:673–679
Jonscher AK (1999) Dielectric relaxation in solids. J Phys D Appl Phys 32:57–70
Mahato DK, Rudra M, Sinha TP (2016) Structural and electrical features of rare earth based double perovskite oxide: Pr2NiZrO6. J Alloy Compd 689:617–624
Ang C, Yu Z, Cross LE (2000) Oxygen-vacancy-related low-frequency dielectric relaxation and electrical conduction in Bi:SiTiO3. Phys Rev B 62:228–236
Sun XJ, Deng JM, Liu LJ, Liu SS, Shi DP, Fang L et al. (2016) Dielectric properties of BiAlO3-modified (Na, K, Li)NbO3 lead-free ceramics. Mater Res Bull 73:437–445
Sasaki M, Jӧnsson PE, Takayama H, Mamiya H (2005) Aging and memory effects in superparamagnets and superspin glasses. Phys Rev B 71:104405
Su Y, Zhang J, Feng Z, Li L, Li B, Zhou Y et al. (2010) Magnetization reversal and Yb3+/Cr3+ spin ordering at low temperature for perovskite YbCrO3 chromites. J Appl Phys 108:013905
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11704091, 51601049, and 11604067), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11574066, 11747014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Feng, L., Shi, W. et al. The structural, dielectric, and magnetic properties of Al3+ doped Sm3Fe5O12 ceramics. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 90, 611–620 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04944-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04944-1