Abstract
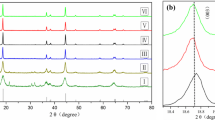
Nickel-rich cathode materials is becoming one of the most promising cathode materials for electronic cars and other electronic devices. It is mainly due to their high reversible capacity, high tap density and low cost. However, its inherent defects such as poor capacity retention and safety performance problems limit its rapid development. In this article, the Mg2+ has been doped into the crystal lattice homogeneously via co-precipitation method to enhance the poor cyclic and rate behavior of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2. The result of X-ray diffraction illustrates that the samples possess a layered α-NaFeO2 structure, and belong to R-3m space group. The content of cation mixing in the sample with Mg2+ dopants is much lower than that of pristine sample. the electrochemical features are evaluated by charge and discharge studies, CV and EIS. The initial capacity of NCMM811 sample is 197.06 mAh/g, and after cycling 100 times, the capacity retention still remains at 91.88%, while the capacity retention of pristine sample is only 80.85% at the same circumstances.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Atar, T. Eren, M. Yola, H. Gerengi, S. Wang, Ionics 21, 3185 (2015)
T. Eren, N. Atar, M. Yola, H. Karimi-Maleh, A. Çolak, A. Olgun, Ionics 21, 2193 (2015)
N. Atar, T. Eren, M. Yola, Thin Solid Films 590, 156 (2015)
X. Xiong, Z. Wang, X. Yin, H. Guo, X. Li, Mater. Lett. 110, 4 (2013)
C. Zhang, J. Qi, H. Zhao, Mater. Lett. 201, 1 (2017)
S. Jan, S. Nurgul, X. Shi, H. Xia, H. Pang, Electrochim. Acta 149, 86 (2014)
J. Kang, H. Pham, D. Kang, H. Park, S. Song, J. Alloy. Compd. 657, 464 (2016)
X. Li, X. Xiong, Z. Wang, Q. Chen, Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 24, 4023 (2014)
Y. Ding, D. Mu, B. Wu, R. Wang, Z. Zhao, F. Wu, Appl. Energy 195, 586 (2017)
C. Pan, Y. Zhu, Y. Yang et al., Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 26, 1396 (2016)
T. Li, X. Li, Z. Wang, H. Guo, J. Power Sources 342, 495 (2017)
K. Liu, G. Yang, Y. Dong, T. Shi, L. Chen, J. Power Sources 281, 370 (2015)
Z. Zhang, D. Chen, C. Chang, RSC Adv. 7, 51721 (2017)
Z. Zheng, X. Guo, Y. Zhong, Electrochim. Acta 188, 336 (2016)
H. Liu, Y. Ding, B. Yang, Z. Liu, Q. Liu, X. Zhang, Sens. Actuators B 271, 336 (2018)
J. Lian, P. Liu, X. Li, Colloids Surf. A 565, 1 (2019)
J. Wang, C. Du, C. Yan, Electrochim. Acta 174, 1185 (2015)
Q. Qiu, X. Huang, Y. Chen, Y. Tan, W. Lv, Ceram. Int. 40, 10511 (2014)
X. Liu, D. Li, H. Li, Electrochim. Acta 148, 26 (2014)
P. Ilango, T. Subburaj, K. Prasanna, Y. Jo, C. Lee, Mater. Chem. Phys. 158, 45 (2015)
S. Sun, N. Wan, Q. Wu, Solid State Ionics 278, 85 (2015)
T. Liu, S. Zhao, K. Wang, L. Gou, C. Nan, Appl. Surf. Sci. 355, 1222 (2015)
E. Zhao, X. Liu, Z. Hu, L. Sun, X. Xiao, J. Power Sources 294, 141 (2015)
Y. Huang, F. Jin, F. Chen, L. Chen, J. Power Sources 256, 1 (2014)
H. Liu, Y. Ding, B. Yang, Z. Liu, X. Zhang, Q. Liu, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 14383 (2018)
Y. Ding, H. Liu, L. Gao, J. Alloy. Compd. 785, 1189 (2019)
P. Yue, Z. Wang, X. Li, Electrochim. Acta 95, 112 (2013)
S. Liu, Z. Dang, D. Liu, C. Zhang, T. Huang, A. Yu, J. Power Sources 396, 288 (2018)
Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, J. Lei, Ceram. Int. 41, 9069 (2015)
M. Chen, E. Zhao, D. Chen, Inorg. Chem. 56, 14 (2017)
S. Do, P. Santhoshkumar, S. Kang, K. Prasanna, Y. Jo, C. Lee, Ceram. Int. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.196
X. Cui, L. Ai, L. Mao, Ionics 25, 411 (2019)
Y. Gao, K. Wu, H. Li, Sens. Actuators B 273, 1635 (2018)
L. Liang, G. Hu, Y. Cao, J. Alloy. Compd. 635, 92 (2015)
Z. Qiu, Y. Zhang, P. Dong, S. Xia, Y. Yao, Solid State Ionics 307, 73 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51834004, 51774076 and 51704063); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. N172507011) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2018MB041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, Y., Yi, W. et al. Improved electrochemical performance of cathode material LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 by doping magnesium via co-precipitation method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 7490–7496 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01062-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01062-0