Abstract
An unmodified electrochemical biosensor has been constructed, which can directly detect DNA in homogeneous solution. The synthesized new compound tetraferrocene was used for signal amplification. The dual-hairpin probe DNA was tagged with a tetraferrocene at the 3′ terminal and a thiol at the 5′ terminal. Without being hybridized with target DNA, the loop of probe prevented the thiol from contacting the exposed gold electrode surface with an applied potential. After hybridization with the target DNA, the loop-stem structure of the probe was opened, which led to the formation of the hairpin DNA structure. Afterwards, the thiol easily contacted the electrode and accomplished potential-assisted Au-S self-assembly. Its current signal depends on the concentration of target DNA in the 1.8 × 10−13 to 1.8 × 10−9 M concentration range, and the detection limit is 0.14 pM. The technique is a meaningful study because of its high selectivity and sensitivity.

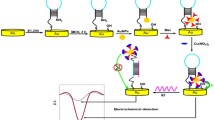
Schematic diagram of the electrochemical DNA sensor operation. Target DNA and probe DNA hybridization, resulting in the disappearance of the steric hindrance of the probe stem ring. A higher signal was generated when tetraferrocene reached the electrode. The electrochemical signals were determined by differential voltammetric pulses (DPV).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu YH, Deng HH, Li HN, Shi TF, Peng HP, Liu AL, Chen W, Hong GL (2018) A DNA electrochemical biosensor based on homogeneous hybridization for the determination of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Electroanal Chem 827:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.09.001
Zhang FT, Cai LY, Zhou YL, Zhang XX (2016) Immobilization-free DNA-based homogeneous electrochemical biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 85:17–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.08.012
Li X, Dou BT, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2019) Mismatched catalytic hairpin assembly and ratiometric strategy for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of microrna from tumor cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem 286:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.152
Park C, Park H, Lee HJ, Lee HS, Park KH, Choi CH, Na S (2019) Double amplified colorimetric detection of DNA using gold nanoparticles, enzymes and a catalytic hairpin assembly. Microchim Acta 186(1):34 https://xs.scihub.ltd/10.1007/s00604-018-3154-2
Lan L, Yao Y, Ping J, Ying Y (2019) Ultrathin transition-metal dichalcogenide nanosheet-based colorimetric sensor for sensitive and label-free detection of DNA. Sensors Actuators B Chem 290:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.016
Mandal TK, Parvin N, Mishra K, Mohandoss S, Lee YR (2019) Sensitive and selective fluorometric determination of DNA by using layered hexagonal nanosheets of a covalent organic framework prepared from p-phenylenediamine and benzene-1, 3, 5-tricarboxaldehyde. Microchim Acta 186(12):833 https://xs.scihub.ltd/10.1007/s00604-019-3944-1
Dadmehr M, Karimi MA, Korouzhdehi B (2019) A signal-on fluorescence based biosensing platform for highly sensitive detection of DNA methyltransferase enzyme activity and inhibition Spectrochim Acta A 117731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117731
Yang X, Liu Q, Wen D, Gao M, Zhang D, Jin Q, Zhang J (2019) Ultrasensitive fluorescence detection of sequence-specific DNA via labeling hairpin DNA probes for fluorescein o-acrylate polymers. Anal Chim Acta 1088:144–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.08.060
Karimi A, Husain SW, Hosseini M, Azar PA, Ganjali MR (2018) Rapid and sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide in milk by enzyme-free electrochemiluminescence sensor based on a polypyrrole-cerium oxide nanocomposite. Sensors Actuators B Chem 271:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.066
Li Y, Qi H, Peng Y, Gao Q, Zhang C (2008) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence aptamer-based method for the determination of thrombin incorporating quenching of tris (2, 2′-bipyridine) ruthenium by ferrocene. Electrochem Commun 10(9):1322–1325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2008.06.027
Huang L, Zhang L, Yang L, Yuan R, Yuan Y (2018) Manganese porphyrin decorated on DNA networks as quencher and mimicking enzyme for construction of ultrasensitive photoelectrochemistry aptasensor. Biosens Bioelectron 104:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.12.037
Miao X, Ling L, Shuai X (none) Sensitive detection of glucose in human serum with oligonucleotide modified gold nanoparticles by using dynamic light scattering technique. Biosens Bioelectron 41:880---883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.09.015
Chen JY, Liu ZJ, Wang XW, Ye CL, Zheng YJ, Peng HP, Zhong GX, Liu AL, Chen W, Lin XH (2019) Ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor developed by probe lengthening for detection of genomic DNA in human serum. Anal Chem 91(7):4552–4558. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05692
Wu X, Chai Y, Zhang P, Yuan R (2015) An electrochemical biosensor for sensitive detection of microRNA-155: combining target recycling with cascade catalysis for signal amplification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(1):713–720. https://doi.org/10.1021/am507059n
Hansen JA, Wang J, Kawde AN, Xiang Y, Gothelf KV, Collins G (2006) Quantum-dot/aptamer-based ultrasensitive multi-analyte electrochemical biosensor. J Am Chem Soc 128(7):2228–2229. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja060005h
Xiong E, Li Z, Zhang X, Zhou J, Yan X, Liu Y, Chen J (2017) Triple-helix molecular switch electrochemical ratiometric biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acids. Anal Chem 89(17):8830–8835. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01251
Hong N, Cheng L, Wei B, Chen C, He LL, Kong D, Ceng J, Cui HF, Fan H (2017) An electrochemical DNA sensor without electrode pre-modification. Biosens Bioelectron 91:110–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.10.008
Rashid JIA, Yusof NA (2017) The strategies of DNA immobilization and hybridization detection mechanism in the construction of electrochemical DNA sensor: a review. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research 16:19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2017.09.001
Yang Z, d’Auriac MA, Goggins S, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Thomas KV, Frost CG, Estrela P (2015) A novel DNA biosensor using a ferrocenyl intercalator applied to the potential detection of human population biomarkers in wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 49(9):5609–5617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00637
Sha Y, Zhang Y, Xu E, Wang Z, Zhu T, Craig SL, Tang C (2018) Quantitative and mechanistic mechanochemistry in ferrocene dissociation. ACS Macro Lett 7(10):1174–1179. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.8b00625
Li W, Liu X, Hou T, Li H, Li F (2015) Ultrasensitive homogeneous electrochemical strategy for DNA methyltransferase activity assay based on autonomous exonuclease III-assisted isothermal cycling signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 70:304–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.03.060
Hou T, Li W, Liu X, Li F (2015) Label-free and enzyme-free homogeneous electrochemical biosensing strategy based on hybridization chain reaction: a facile, sensitive, and highly specific microRNA assay. Anal Chem 87(22):11368–11374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02790
Balaji Viswanath K, Krithiga N, Jayachitra A, Sheik Mideen AK, Amali AJ, Vasantha VS (2018) Enzyme-free multiplex detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aeromonas hydrophila with ferrocene and thionine-labeled antibodies using ZIF-8/Au NPs as a platform. ACS Omega 3(12):17010–17022. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02183
Rasheed PA, Sandhyarani N (2017) Electrochemical DNA sensors based on the use of gold nanoparticles: a review on recent developments. Microchim Acta 184(4):981–1000 https://xs.scihub.ltd/10.1007/s00604-017-2143-1
Hua X, Zhou X, Guo S, Zheng T, Yuan R, Xu W (2019) Determination of Alzheimer biomarker DNA by using an electrode modified with in-situ precipitated molybdophosphate catalyzed by alkaline phosphatase-encapsulated DNA hydrogel and target recycling amplification. Microchim Acta 186(3):158 https://xs.scihub.ltd/10.1007/s00604-019-3283-2
Yan T, Zhu L, Ju H, Lei J (2018) DNA-walker-induced allosteric switch for tandem signal amplification with palladium nanoparticles/metal-organic framework tags in electrochemical biosensing. Anal Chem 90(24):14493–14499. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04338
Cui L, Wu J, Li J, Ju H (2015) Electrochemical sensor for lead cation sensitized with a DNA functionalized porphyrinic metal–organic framework. Anal Chem 87(20):10635–10641. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03287
Kou B, Chai Y, Yuan Y, Yuan R (2018) Dynamical regulation of enzyme cascade amplification by a regenerated DNA nanotweezer for ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA detection. Anal Chem 90(18):10701–10706. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00477
Yang S, You M, Yang L, Zhang F, Wang Q, He P (2016) A recyclable electrochemical sensing platform for breast cancer diagnosis based on homogeneous DNA hybridization and host-guest interaction between cucurbit [7] uril and ferrocene-nanosphere with signal amplification. J Electroanal Chem 783:161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.11.027
Van Staveren DR, Metzler-Nolte N (2004) Bioorganometallic chemistry of ferrocene. Chem Rev 104(12):5931–5986.2. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0101510
Zhu J, Gan H, Wu J, Ju H (2018) Molecular machine powered surface programmatic chain reaction for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of protein. Anal Chem 90(8):5503–5508. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01217
Deng C, Pi X, Qian P, Chen X, Wu W, Xiang J (2016) High-performance ratiometric electrochemical method based on the combination of signal probe and inner reference probe in one hairpin-structured DNA. Anal Chem 89(1):966–973. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04209
Cinti S, Proietti E, Casotto F, Moscone D, Arduini F (2018) Based strips for the electrochemical detection of single and double stranded DNA. Anal Chem 90(22):13680–13686. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04052
Tan Y, Wei X, Zhao M, Qiu B, Guo L, Lin Z, Yang HH (2015) Ultraselective homogeneous electrochemical biosensor for DNA species related to oral cancer based on nicking endonuclease assisted target recycling amplification. Anal Chem 87(18):9204–9208. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01470
Fu C, Liu C, Li Y, Guo Y, Luo F, Wang P, Lin Z (2016) Homogeneous electrochemical biosensor for melamine based on DNA triplex structure and exonuclease III-assisted recycling amplification. Anal Chem 88(20):10176–10182 https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02753
Liu Y, Ge Z, Chen M, He H, Zhang X, Wang S (2019) Ratiometric electrochemical biosensor based on Exo III-assisted recycling amplification for the detection of CAG trinucleotide repeats. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111537
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81860682, 81872968, 81560625, 81660658) and Jiangxi Provincial Graduate Innovation special fund project (YC2019-S364).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1007 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, T., Liao, F., Cui, H. et al. A homogeneous electrochemical DNA sensor on the basis of a self-assembled thiol layer on a gold support and by using tetraferrocene for signal amplification. Microchim Acta 187, 340 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04274-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04274-y