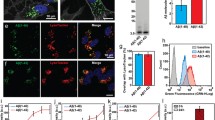
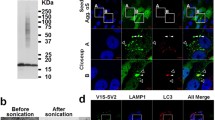
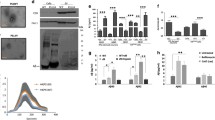
Abstract
Numerous pathological amyloid proteins spread from cell to cell during neurodegenerative disease, facilitating the propagation of cellular pathology and disease progression. Understanding the mechanism by which disease-associated amyloid protein assemblies enter target cells and induce cellular dysfunction is, therefore, key to understanding the progressive nature of such neurodegenerative diseases. In this study, we utilized an imaging-based assay to monitor the ability of disease-associated amyloid assemblies to rupture intracellular vesicles following endocytosis. We observe that the ability to induce vesicle rupture is a common feature of α-synuclein (α-syn) assemblies, as assemblies derived from WT or familial disease-associated mutant α-syn all exhibited the ability to induce vesicle rupture. Similarly, different conformational strains of WT α-syn assemblies, but not monomeric or oligomeric forms, efficiently induced vesicle rupture following endocytosis. The ability to induce vesicle rupture was not specific to α-syn, as amyloid assemblies of tau and huntingtin Exon1 with pathologic polyglutamine repeats also exhibited the ability to induce vesicle rupture. We also observe that vesicles ruptured by α-syn are positive for the autophagic marker LC3 and can accumulate and fuse into large, intracellular structures resembling Lewy bodies in vitro. Finally, we show that the same markers of vesicle rupture surround Lewy bodies in brain sections from PD patients. These data underscore the importance of this conserved endocytic vesicle rupture event as a damaging mechanism of cellular invasion by amyloid assemblies of multiple neurodegenerative disease-associated proteins, and suggest that proteinaceous inclusions such as Lewy bodies form as a consequence of continued fusion of autophagic vesicles in cells unable to degrade ruptured vesicles and their amyloid contents.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abounit S, Bousset L, Loria F, Zhu S, de Chaumont F, Pieri L, Olivo-Marin JC, Melki R, Zurzolo C (2016) Tunneling nanotubes spread fibrillar alpha-synuclein by intercellular trafficking of lysosomes. EMBO J 35:2120–2138. doi:10.15252/embj.201593411
Aits S, Kricker J, Liu B, Ellegaard AM, Hamalisto S, Tvingsholm S, Corcelle-Termeau E, Hogh S, Farkas T, Holm Jonassen A et al (2015) Sensitive detection of lysosomal membrane permeabilization by lysosomal galectin puncta assay. Autophagy 11:1408–1424. doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1063871
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Schapira AH, Gardiner C, Sargent IL, Wood MJ, Cooper JM (2011) Lysosomal dysfunction increases exosome-mediated alpha-synuclein release and transmission. Neurobiol Dis 42:360–367. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2011.01.029
Bourdenx M, Dehay B (2016) What lysosomes actually tell us about Parkinson’s disease? Ageing Res Rev. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2016.02.008
Bourdenx M, Bezard E, Dehay B (2014) Lysosomes and alpha-synuclein form a dangerous duet leading to neuronal cell death. Front Neuroanat 8:83. doi:10.3389/fnana.2014.00083
Bousset L, Pieri L, Ruiz-Arlandis G, Gath J, Jensen PH, Habenstein B, Madiona K, Olieric V, Bockmann A, Meier BH et al (2013) Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains. Nat Commun 4:2575. doi:10.1038/ncomms3575
Boza-Serrano A, Reyes JF, Rey NL, Leffler H, Bousset L, Nilsson U, Brundin P, Venero JL, Burguillos MA, Deierborg T (2014) The role of Galectin-3 in alpha-synuclein-induced microglial activation. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:156. doi:10.1186/s40478-014-0156-0
Chauhan S, Kumar S, Jain A, Ponpuak M, Mudd MH, Kimura T, Choi SW, Peters R, Mandell M, Bruun JA et al (2016) TRIMs and galectins globally cooperate and TRIM16 and Galectin-3 Co-direct autophagy in endomembrane damage homeostasis. Dev Cell 39:13–27. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2016.08.003
Chu Y, Dodiya H, Aebischer P, Olanow CW, Kordower JH (2009) Alterations in lysosomal and proteasomal markers in Parkinson’s disease: relationship to alpha-synuclein inclusions. Neurobiol Dis 35:385–398. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.05.023
Chu Y, Mickiewicz AL, Kordower JH (2011) alpha-Synuclein aggregation reduces nigral myocyte enhancer factor-2D in idiopathic and experimental Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 41:71–82. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2010.08.022
Clavaguera F, Bolmont T, Crowther RA, Abramowski D, Frank S, Probst A, Fraser G, Stalder AK, Beibel M, Staufenbiel M et al (2009) Transmission and spreading of tauopathy in transgenic mouse brain. Nat Cell Biol 11:909–913. doi:10.1038/ncb1901
Dehay B, Ramirez A, Martinez-Vicente M, Perier C, Canron MH, Doudnikoff E, Vital A, Vila M, Klein C, Bezard E (2012) Loss of P-type ATPase ATP13A2/PARK9 function induces general lysosomal deficiency and leads to Parkinson disease neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:9611–9616. doi:10.1073/pnas.1112368109
Dehay B, Martinez-Vicente M, Caldwell GA, Caldwell KA, Yue Z, Cookson MR, Klein C, Vila M, Bezard E (2013) Lysosomal impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 28:725–732. doi:10.1002/mds.25462
Desplats P, Lee HJ, Bae EJ, Patrick C, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Spencer B, Masliah E, Lee SJ (2009) Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13010–13015. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903691106
Dupont N, Lacas-Gervais S, Bertout J, Paz I, Freche B, Van Nhieu GT, van der Goot FG, Sansonetti PJ, Lafont F (2009) Shigella phagocytic vacuolar membrane remnants participate in the cellular response to pathogen invasion and are regulated by autophagy. Cell Host Microbe 6:137–149. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2009.07.005
Eisele YS, Obermuller U, Heilbronner G, Baumann F, Kaeser SA, Wolburg H, Walker LC, Staufenbiel M, Heikenwalder M, Jucker M (2010) Peripherally applied Abeta-containing inoculates induce cerebral beta-amyloidosis. Science 330:980–982. doi:10.1126/science.1194516
Freeman D, Cedillos R, Choyke S, Lukic Z, McGuire K, Marvin S, Burrage AM, Sudholt S, Rana A, O’Connor C et al (2013) Alpha-synuclein induces lysosomal rupture and cathepsin dependent reactive oxygen species following endocytosis. PLoS ONE 8:e62143. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062143
Gai WP, Yuan HX, Li XQ, Power JT, Blumbergs PC, Jensen PH (2000) In situ and in vitro study of colocalization and segregation of alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin, and lipids in Lewy bodies. Exp Neurol 166:324–333. doi:10.1006/exnr.2000.7527
Ghee M, Melki R, Michot N, Mallet J (2005) PA700, the regulatory complex of the 26S proteasome, interferes with alpha-synuclein assembly. FEBS J 272:4023–4033. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04776.x
Guo JL, Lee VM (2011) Seeding of normal Tau by pathological Tau conformers drives pathogenesis of Alzheimer-like tangles. J Biol Chem 286:15317–15331. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.209296
Guo JL, Lee VM (2014) Cell-to-cell transmission of pathogenic proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Med 20:130–138. doi:10.1038/nm.3457
Hansen C, Angot E, Bergstrom AL, Steiner JA, Pieri L, Paul G, Outeiro TF, Melki R, Kallunki P, Fog K et al (2011) alpha-Synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J Clin Invest 121:715–725. doi:10.1172/JCI43366
Iba M, Guo JL, McBride JD, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2013) Synthetic tau fibrils mediate transmission of neurofibrillary tangles in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s-like tauopathy. J Neurosci 33:1024–1037. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2642-12.2013
Jo E, McLaurin J, Yip CM, St George-Hyslop P, Fraser PE (2000) alpha-Synuclein membrane interactions and lipid specificity. J Biol Chem 275:34328–34334. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004345200
Jucker M, Walker LC (2013) Self-propagation of pathogenic protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 501:45–51. doi:10.1038/nature12481
Kaul S, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy AG (2005) Wild-type alpha-synuclein interacts with pro-apoptotic proteins PKCdelta and BAD to protect dopaminergic neuronal cells against MPP+-induced apoptotic cell death. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 139:137–152. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.05.022
Kordower JH, Chu Y, Hauser RA, Freeman TB, Olanow CW (2008) Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Med 14:504–506. doi:10.1038/nm1747
Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108. doi:10.1038/ng0298-106
Lasagna-Reeves CA, Castillo-Carranza DL, Sengupta U, Guerrero-Munoz MJ, Kiritoshi T, Neugebauer V, Jackson GR, Kayed R (2012) Alzheimer brain-derived tau oligomers propagate pathology from endogenous tau. Sci Rep 2:700. doi:10.1038/srep00700
Le MN, Kim W, Lee S, McKee AC, Hall GF (2012) Multiple mechanisms of extracellular tau spreading in a non-transgenic tauopathy model. Am J Neurodegener Dis 1:316–333
Lee HJ, Suk JE, Bae EJ, Lee JH, Paik SR, Lee SJ (2008) Assembly-dependent endocytosis and clearance of extracellular alpha-synuclein. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1835–1849. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2008.01.017
Lee SJ, Desplats P, Lee HJ, Spencer B, Masliah E (2012) Cell-to-cell transmission of alpha-synuclein aggregates. Methods Mol Biol 849:347–359. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-551-0_23
Lee HJ, Cho ED, Lee KW, Kim JH, Cho SG, Lee SJ (2013) Autophagic failure promotes the exocytosis and intercellular transfer of alpha-synuclein. Exp Mol Med 45:e22. doi:10.1038/emm.2013.45
Lesage S, Anheim M, Letournel F, Bousset L, Honore A, Rozas N, Pieri L, Madiona K, Durr A, Melki R et al (2013) G51D alpha-synuclein mutation causes a novel parkinsonian-pyramidal syndrome. Ann Neurol 73:459–471. doi:10.1002/ana.23894
Li JY, Englund E, Holton JL, Soulet D, Hagell P, Lees AJ, Lashley T, Quinn NP, Rehncrona S, Bjorklund A et al (2008) Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson’s disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat Med 14:501–503. doi:10.1038/nm1746
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 338:949–953. doi:10.1126/science.1227157
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Intracerebral inoculation of pathological alpha-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative alpha-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 209:975–986. doi:10.1084/jem.20112457
Maejima I, Takahashi A, Omori H, Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Saitoh T, Yamamoto A, Hamasaki M, Noda T, Isaka Y et al (2013) Autophagy sequesters damaged lysosomes to control lysosomal biogenesis and kidney injury. EMBO J 32:2336–2347. doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.171
Maier O, Marvin SA, Wodrich H, Campbell EM, Wiethoff CM (2012) Spatiotemporal dynamics of adenovirus membrane rupture and endosomal escape. J Virol 86:10821–10828. doi:10.1128/JVI.01428-12
Makky A, Bousset L, Polesel-Maris J, Melki R (2016) Nanomechanical properties of distinct fibrillar polymorphs of the protein alpha-synuclein. Sci Rep 6:37970. doi:10.1038/srep37970
Masuda-Suzukake M, Nonaka T, Hosokawa M, Oikawa T, Arai T, Akiyama H, Mann DM, Hasegawa M (2013) Prion-like spreading of pathological alpha-synuclein in brain. Brain 136:1128–1138. doi:10.1093/brain/awt037
Mazzulli JR, Xu YH, Sun Y, Knight AL, McLean PJ, Caldwell GA, Sidransky E, Grabowski GA, Krainc D (2011) Gaucher disease glucocerebrosidase and alpha-synuclein form a bidirectional pathogenic loop in synucleinopathies. Cell 146:37–52. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.001
Mazzulli JR, Zunke F, Isacson O, Studer L, Krainc D (2016) alpha-Synuclein-induced lysosomal dysfunction occurs through disruptions in protein trafficking in human midbrain synucleinopathy models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:1931–1936. doi:10.1073/pnas.1520335113
Mazzulli JR, Zunke F, Tsunemi T, Toker NJ, Jeon S, Burbulla LF, Patnaik S, Sidransky E, Marugan JJ, Sue CM et al (2016) Activation of beta-glucocerebrosidase reduces pathological alpha-synuclein and restores lysosomal function in Parkinson’s patient midbrain neurons. J Neurosci 36:7693–7706. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0628-16.2016
Meyer-Luehmann M, Coomaraswamy J, Bolmont T, Kaeser S, Schaefer C, Kilger E, Neuenschwander A, Abramowski D, Frey P, Jaton AL et al (2006) Exogenous induction of cerebral beta-amyloidogenesis is governed by agent and host. Science 313:1781–1784. doi:10.1126/science.1131864
Mok SW, Riemer C, Madela K, Hsu DK, Liu FT, Gultner S, Heise I, Baier M (2007) Role of galectin-3 in prion infections of the CNS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 359:672–678. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.163
Monsellier E, Redeker V, Ruiz-Arlandis G, Bousset L, Melki R (2015) Molecular interaction between the chaperone Hsc70 and the N-terminal flank of huntingtin exon 1 modulates aggregation. J Biol Chem 290:2560–2576. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.603332
Olanow CW, Perl DP, DeMartino GN, McNaught KS (2004) Lewy-body formation is an aggresome-related process: a hypothesis. Lancet Neurol 3:496–503. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00827-0
Pan T, Kondo S, Le W, Jankovic J (2008) The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:1969–1978. doi:10.1093/brain/awm318
Papadopoulos C, Kirchner P, Bug M, Grum D, Koerver L, Schulze N, Poehler R, Dressler A, Fengler S, Arhzaouy K et al (2017) VCP/p97 cooperates with YOD1, UBXD1 and PLAA to drive clearance of ruptured lysosomes by autophagy. EMBO J 36:135–150. doi:10.15252/embj.201695148
Paz I, Sachse M, Dupont N, Mounier J, Cederfur C, Enninga J, Leffler H, Poirier F, Prevost MC, Lafont F et al (2010) Galectin-3, a marker for vacuole lysis by invasive pathogens. Cell Microbiol 12:530–544. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01415.x
Peelaerts W, Bousset L, Van der Perren A, Moskalyuk A, Pulizzi R, Giugliano M, Van den Haute C, Melki R, Baekelandt V (2015) alpha-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature 522:340–344. doi:10.1038/nature14547
Pieri L, Madiona K, Bousset L, Melki R (2012) Fibrillar alpha-synuclein and huntingtin exon 1 assemblies are toxic to the cells. Biophys J 102:2894–2905. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2012.04.050
Pieri L, Chafey P, Le Gall M, Clary G, Melki R, Redeker V (2016) Cellular response of human neuroblastoma cells to alpha-synuclein fibrils, the main constituent of Lewy bodies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1860:8–19. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.10.007
Pieri L, Madiona K, Melki R (2016) Structural and functional properties of prefibrillar alpha-synuclein oligomers. Sci Rep 6:24526. doi:10.1038/srep24526
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R et al (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Randow F, Munz C (2012) Autophagy in the regulation of pathogen replication and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol 33:475–487. doi:10.1016/j.it.2012.06.003
Ray K, Bobard A, Danckaert A, Paz-Haftel I, Clair C, Ehsani S, Tang C, Sansonetti P, Tran GV, Enninga J (2010) Tracking the dynamic interplay between bacterial and host factors during pathogen-induced vacuole rupture in real time. Cell Microbiol 12:545–556. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01428.x
Ren PH, Lauckner JE, Kachirskaia I, Heuser JE, Melki R, Kopito RR (2009) Cytoplasmic penetration and persistent infection of mammalian cells by polyglutamine aggregates. Nat Cell Biol 11:219–225. doi:10.1038/ncb1830
Rey NL, Petit GH, Bousset L, Melki R, Brundin P (2013) Transfer of human alpha-synuclein from the olfactory bulb to interconnected brain regions in mice. Acta Neuropathol 126:555–573. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1160-3
Rey NL, Steiner JA, Maroof N, Luk KC, Madaj Z, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Brundin P (2016) Widespread transneuronal propagation of alpha-synucleinopathy triggered in olfactory bulb mimics prodromal Parkinson’s disease. J Exp Med 213:1759–1778. doi:10.1084/jem.20160368
Ruiz-Arlandis G, Pieri L, Bousset L, Melki R (2016) Binding, internalization and fate of Huntingtin Exon1 fibrillar assemblies in mitotic and nonmitotic neuroblastoma cells. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 42:137–152. doi:10.1111/nan.12258
Samuel F, Flavin WP, Iqbal S, Pacelli C, Sri Renganathan SD, Trudeau LE, Campbell EM, Fraser PE, Tandon A (2016) Effects of serine 129 phosphorylation on alpha-synuclein aggregation, membrane association, and internalization. J Biol Chem 291:4374–4385. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.705095
Sanders DW, Kaufman SK, DeVos SL, Sharma AM, Mirbaha H, Li A, Barker SJ, Foley AC, Thorpe JR, Serpell LC et al (2014) Distinct tau prion strains propagate in cells and mice and define different tauopathies. Neuron 82:1271–1288. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.04.047
Shrivastava AN, Redeker V, Fritz N, Pieri L, Almeida LG, Spolidoro M, Liebmann T, Bousset L, Renner M, Lena C et al (2015) alpha-synuclein assemblies sequester neuronal alpha3-Na+/K+-ATPase and impair Na+ gradient. EMBO J 34:2408–2423. doi:10.15252/embj.201591397
Steiner JA, Angot E, Brundin P (2011) A deadly spread: cellular mechanisms of alpha-synuclein transfer. Cell Death Differ 18:1425–1433. doi:10.1038/cdd.2011.53
Stohr J, Watts JC, Mensinger ZL, Oehler A, Grillo SK, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB, Giles K (2012) Purified and synthetic Alzheimer’s amyloid beta (Abeta) prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:11025–11030. doi:10.1073/pnas.1206555109
Tanik SA, Schultheiss CE, Volpicelli-Daley LA, Brunden KR, Lee VM (2013) Lewy body-like alpha-synuclein aggregates resist degradation and impair macroautophagy. J Biol Chem 288:15194–15210. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.457408
Thurston TL, Wandel MP, von Muhlinen N, Foeglein A, Randow F (2012) Galectin 8 targets damaged vesicles for autophagy to defend cells against bacterial invasion. Nature 482:414–418. doi:10.1038/nature10744
Tofaris GK (2012) Lysosome-dependent pathways as a unifying theme in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27:1364–1369. doi:10.1002/mds.25136
Verasdonck J, Bousset L, Gath J, Melki R, Bockmann A, Meier BH (2016) Further exploration of the conformational space of alpha-synuclein fibrils: solid-state NMR assignment of a high-pH polymorph. Biomol NMR Assign 10:5–12. doi:10.1007/s12104-015-9628-9
Vila M, Bove J, Dehay B, Rodriguez-Muela N, Boya P (2011) Lysosomal membrane permeabilization in Parkinson disease. Autophagy 7:98–100
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Patel TP, Tanik SA, Riddle DM, Stieber A, Meaney DF, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2011) Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron 72:57–71. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.033
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Lee VM (2014) Addition of exogenous alpha-synuclein preformed fibrils to primary neuronal cultures to seed recruitment of endogenous alpha-synuclein to Lewy body and Lewy neurite-like aggregates. Nat Protoc 9:2135–2146. doi:10.1038/nprot.2014.143
Wolfe DM, Lee JH, Kumar A, Lee S, Orenstein SJ, Nixon RA (2013) Autophagy failure in Alzheimer’s disease and the role of defective lysosomal acidification. Eur J Neurosci 37:1949–1961. doi:10.1111/ejn.12169
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B et al (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55:164–173. doi:10.1002/ana.10795
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Michael Sobieraj for assistance with construct generation and protein purification, Oksana I. Zhurbich for assistance with electron microscopy, and Sean C. Liebscher for assistance with assembly characterization, as well as all laboratory members for discussion. EMC was funded by the Michael J. Fox foundation, RRI award. JHK was funded in part by a Center Grant from the Parkinson’s disease Foundation. RM and LB were funded by Grants from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-14-CE13-0031) and the EC Joint Programme on Neurodegenerative Diseases (JPND-NeuTARGETs-ANR-14-JPCD-0002-02; JPND-SYNACTION-ANR-15-JPWG-0012-03), the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, France Parkinson (Contract 113344), the Fondation de France (Contract 2015-00060936), The Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (Contract DEQ 20160334896), a “Coup d’Elan a la Recherche Francaise” award from Fondation Bettencourt-Schueller and the Fondation Simone et Cino Del Duca of the Institut de France. WPF was supported by the Illinois Chapter of the ARCS Foundation, the Arthur J. Schmitt Foundation, and a fund from the Dean of the Stritch School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (MP4 824 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (MP4 861 kb)
Supplementary material 4 (MP4 829 kb)
Supplementary material 5 (MP4 659 kb)
Supplementary material 6 (MP4 451 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flavin, W.P., Bousset, L., Green, Z.C. et al. Endocytic vesicle rupture is a conserved mechanism of cellular invasion by amyloid proteins. Acta Neuropathol 134, 629–653 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1722-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1722-x