Abstract
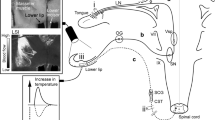
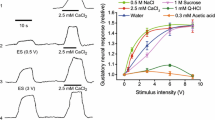
The present study was designed to examine whether there are parasympathetic vasodilator fibers in the lower lip of the guinea-pig. Electrical stimulation of the central cut end of the lingual nerve of guinea-pigs evoked intensity- and frequency-dependent decreases in lower lip blood flow and systemic arterial blood pressure (SABP). Pretreatment with guanethidine, a postganglionic sympathetic nerve blocker and antihypertensive drug (30 mg kg−1, s.c., 24 h prior to experiments), reduced the magnitude of the decrease in SABP while the intensity- and frequency-dependent increases of the lip blood flow occurred by the lingual nerve stimulation only on the side ipsilateral to stimulation. Increases in the lip blood flow evoked by lingual nerve stimulation in guanethidine pretreated guinea-pigs were reduced by hexamethonium (an autonomic ganglion cholinergic blocker) in a dose-dependent manner. When fluoro-gold (a retrograde neural tracer) was injected into the lower lip, labeled neurons were observed in the ipsilateral otic ganglion. The present study indicates the presence of parasympathetic vasodilator fibers originating from the otic parasympathetic ganglion in the guinea-pig lower lip, similar to those reported previously in rats, cats, rabbits and humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a.u.:
-
Arbitrary units
- SABP:
-
Systemic arterial blood pressure
References
Baranowski AP, Anand U, McMahon SB (1992) Retrograde labelling of dorsal root ganglion cells in the rat: a quantitative and morphological comparison of Fluoro-Gold with horseradish peroxidase labelling. Neurosci Lett 141:53–56
Beattie DT, Connor HE (1994) The influence of the trigeminal ganglion on carotid blood flow in anaesthetized guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol 112:262–266
Blessing WW, Nalivaiko E (2000) Regional blood flow and nociceptive stimuli in rabbits: patterning by medullary raphe, not ventrolateral medulla. J Physiol 524:279–292
Butler MJ, Britton BJ, Wood WG, Mainwaring-Burton R, Irving MH (1977) Plasma catecholamine concentrations during operation. Br J Surg 64:786–790
Date H, Kato M, Izumi H (2000) Involvement of two different mechanisms in trigeminal ganglion-evoked vasodilatation in the cat lower lip: role of experimental conditions. J Auton Nerv Syst 79:84–92
Dellow PG, Morgan MJ (1969) Trigeminal nerve inputs and central blood pressure change in the cat. Arch Oral Biol 14:295–300
Edwall B, Gazelius B, Berg JO, Edwall L, Hellander K, Olgart L (1987) Blood flow changes in the dental pulp of the cat and rat measured simultaneously by laser Doppler flowmetry and local 125I clearance. Acta Physiol Scand 131:81–91
Gibbins IL, Brayden JE, Bevan JA (1984) Perivascular nerves with immunoreactivity to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in cephalic arteries of the cat: distribution, possible origins and functional implications. Neuroscience 13:1327–1346
Gilman A, Rall T, Nies A, Taylor P (1990) Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 8th edn. Pergamon, New York, p 794
Heistad DD, Marcus ML (1978) Evidence that neural mechanisms do not have important effects on cerebral blood flow. Circ Res 42:295–302
Ishii H, Niioka T, Sudo E, Izumi H (2005) Evidence for parasympathetic vasodilator fibres in the rat masseter muscle. J Physiol 569:617–629
Ishii H, Niioka T, Watanabe H, Izumi H (2007) Inhibitory effects of excess sympathetic activity on parasympathetic vasodilatation in the rat masseter muscle. Am J Physiol 293:R729–R733
Ito Y, Izumi H, Sato M, Karita K, Iwatsuki N (1998) Suppression of parasympathetic reflex vasodilatation in the lower lip of the cat by isoflurane, propofol, ketamine and pentobarbital: implications for mechanisms underlying the production of anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 81:563–538
Izumi H (1995) Reflex parasympathetic vasodilatation in facial skin. Gen Pharmacol 26:237–244
Izumi H (1999a) Functional roles played by the sympathetic supply to lip blood vessels in the cat. Am J Physiol 277:R682–R689
Izumi H (1999b) Nervous control of blood flow in the orofacial region. Pharmacol Ther 81:141–161
Izumi H, Ishii H, Niioka T (2006) Parasympathetic vasodilator fibers in the orofacial region. J Oral Biosci 48:30–41
Izumi H, Ito Y (1998) Sympathetic attenuation of parasympathetic vasodilatation in oro-facial areas in the cat. J Physiol 510:915–921
Izumi H, Ito Y, Sato M, Karita K, Iwatsuki N (1997) Effects of inhalation anesthetics on parasympathetic reflex vasodilation in the lower lip and palate of the cat. Am J Physiol 273:R168–R174
Izumi H, Karita K (1992) Somatosensory stimulation causes autonomic vasodilatation in cat lip. J Physiol 450:191–202
Izumi H, Karita K (1990) The effects of capsaicin applied topically to inferior alveolar nerve on antidromic vasodilatation in cat gingiva. Neurosci Lett 112:65–69
Izumi H, Karita K (1993a) Innervation of the cat lip by two groups of parasympathetic vasodilator fibres. J Physiol 465:501–512
Izumi H, Karita K (1993b) Reflex vasodilatation in the cat lip elicited by stimulation of nasal mucosa by chemical irritants. Am J Physiol 265:R733–R738
Izumi H, Karita K (1994a) The parasympathetic vasodilator fibers in the trigeminal portion of the distal lingual nerve in the cat tongue. Am J Physiol 266:R1517–R1522
Izumi H, Karita K (1994b) Parasympathetic-mediated reflex salivation and vasodilatation in the cat submandibular gland. Am J Physiol 267:R747–R753
Izumi H, Karita K (1995) Low-frequency subthreshold sympathetic stimulation augments maximal reflex parasympathetic salivary secretion in cats. Am J Physiol 268:R1188–R1195
Izumi H, Mizuta K, Kuchiiwa S (2002) Simultaneous measurement of parasympathetic reflex vasodilator and arterial blood pressure responses in the cat. Brain Res 952:61–70
Izumi H, Nakamura I, Karita K (1995) Effects of clonidine and yohimbine on parasympathetic reflex salivation and vasodilatation in cat SMG. Am J Physiol 268:R1196–R1202
Kaji A, Shigematsu H, Fujita K, Maeda T, Watanabe S (1991) Parasympathetic innervation of cutaneous blood vessels examined by retrograde tracing in the rat lower lip. J Auton Nerv Syst 32:153–158
Kaji A, Maeda T, Watanabe S (1988) Parasympathetic innervation of cutaneous blood vessels by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive and acetylcholinesterase-positive nerves: histochemical and experimental study on rat lower lip. Neuroscience 25:353–262
Kim S, Liu M, Markowitz K, Bilotto G, Dorscher-Kim J (1990) Comparison of pulpal blood flow in dog canine teeth determined by the laser Doppler and the 133xenon washout methods. Archs Oral Biol 35:41141–41143
Koeda S, Yasuda M, Izumi H (2003) Species differences in the reflex effects of lingual afferent nerve stimulation on lip blood flow and arterial pressure. J Comp Physiol [B] 173:629–636
Kuchiiwa S, Izumi H, Karita K, Nagasawa S (1992) Origins of parasympathetic postganglionic vasodilator fibers supplying the lips and gingivae; an WGA-HRP study in the cat. Neurosci Lett 142:237–240
Kumada M, Dampney RA, Reis DJ (1975) The trigeminal depressor response: a cardiovascular reflex originating from the trigeminal system. Brain Res 92:485–489
Lambert GA, Bogduk N, Goadsby PJ, Duckworth JW, Lance JW (1984) Decreased carotid arterial resistance in cats in response to trigeminal stimulation. J Neurosurg 61:307–315
Matthews B, Robinson PP (1980) The course of post-ganglionic sympathetic fibres distributed with the trigeminal nerve in the cat. J Physiol 303:391–401
Mizuta K, Kuchiiwa S, Saito T, Mayanagi H, Karita K, Izumi H (2002) Involvement of trigeminal spinal nucleus in parasympathetic reflex vasodilatation in cat lower lip. Am J Physiol 282:R492–R500
Mizuta K, Izumi H (2004) Bulbar pathway for contralateral lingual nerve-evoked reflex vasodilatation in cat palate. Brain Res 1020:86–94
Mizuta K, Mizuta F, Takahashi M, Ishii H, Niioka T, Izumi H (2006) Effects of isoflurane on parasympathetic vasodilatation in the rat submandibular gland. J Dent Res 85:379–383
Schmued LC, Fallon JH (1986) Fluoro-Gold: a new fluorescent retrograde axonal tracer with numerous unique properties. Brain Res 377:147–154
Stern MD, Lappe DL, Bowen PD, Chimosky JE, Holloway GA Jr, Keiser HR, Bowman RL (1977) Continuous measurement of tissue blood flow by laser-Doppler spectroscopy. Am J Physiol 232:H441–H448
Weissman C (1990) The metabolic response to stress: an overview and update. Anesthesiology 73:308–327
Yasuda M, Izumi H (2003) Trigeminal nerve-mediated reflex arterial blood pressure decrease and vasodilatation in lower lip of the rabbit. Brain Res 987:59–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by I.D. Hume.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, H., Ishii, H., Niioka, T. et al. Occurrence of parasympathetic vasodilator fibers in the lower lip of the guinea-pig. J Comp Physiol B 178, 297–305 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-007-0222-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-007-0222-z