Abstract
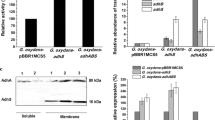
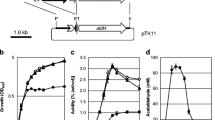
In contrast to D-glyceric acid (D-GA) production with 99% enantiomeric excess (ee) by Acetobacter tropicalis NBRC 16470, Gluconobacter sp. CHM43 produced 19.6 g L−1 of D-GA with 73.7% ee over 4 days of incubation in flask culture. To investigate the reason for this enantiomeric composition of GA, the genes encoding membrane-bound alcohol dehydrogenase (mADH) of A. tropicalis NBRC 16470, composed of three subunits (adhA, adhB, and adhS), were cloned using the broad-host-range vector pBBR1MCS-2 and heterologously expressed in Gluconobacter sp. CHM43 and its ΔadhAB ΔsldBA derivative TORI4. Reverse-transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction demonstrated that adhABS genes from A. tropicalis were expressed in TORI4 transformants, and their membrane fraction exhibited mADH activities of 0.13 and 0.31 U/mg with or without AdhS, respectively. Compared with the GA production of TORI4-harboring pBBR1MCS-2 (1.23 g L−1), TORI4 transformants expressing adhABS and adhAB showed elevated GA production of 2.46 and 3.67 g L−1, respectively, suggesting a negative effect of adhS gene expression on GA production as well as mADH activity in TORI4. Although TORI4 was found to produce primarily L-GA with 42.5% ee, TORI4 transformants expressing adhABS and adhAB produced D-GA with 27.6% and 49.0% ee, respectively, demonstrating that mADH of A. tropicalis causes a sharp increase in the enantiomeric composition of D-GA. These results suggest that one reason for D-GA production with 73.7% ee in Gluconobacter spp. might be a property of the host, which possibly produces L-GA intracellularly.
Key points
• Membrane-bound ADH from Acetobacter tropicalis showed activity in Gluconobacter sp.
• D-GA production from glycerol was performed using recombinant Gluconobacter sp.
• Enantiomeric excess of D-GA was affected by both membrane and intracellular ADHs.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Gluconobacter sp. (formerly Gluconobacter frateurii) CHM43 has been deposited in the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (NITE) NBRC under accession number NBRC 101,659.
References
Ameyama M, Shinagawa E, Matsushita K, Adachi O (1981) D-Fructose dehydrogenase of Gluconobacter industrius: purification, characterization, and application to enzymatic microdetermination of D-fructose. J Bacteriol 145:814–823. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.145.2.814-823.1981
Armstrong JM (1964) The molar extinction coefficient of 2,6-dichlorophenol indophenol. Biochim Biophys Acta – Gen Subj 86:194–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(64)90180-1
Claude S (1999) Research of New Outlets for Glycerol: Recent Developments in France Fett/lipid 101:101–104. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527624720.ch12
da Silva GP, Mack M, Contiero J (2009) Glycerol: a promising and abundant carbon source for industrial microbiology. Biotechnol Adv 27:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.07.006
Demirbas MF, Balat M (2006) Recent advances on the production and utilization trends of bio-fuels: a global perspective. Energy Convers Manage 47:2371–2381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2005.11.014
Ferraro DJ, Okerlund AL, Mowers JC, Ramaswamy S (2006) Structural basis for regioselectivity of product formation by naphthalene 1,2-dioxygenase. J Bacteriol 188:6986–6994. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00707-06
Habe H, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D, Sakaki K (2009a) Application of electrodialysis to glycerate recovery from a glycerol containing model solution and culture broth. J Biosci Bioeng 107:425–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2008.12.008
Habe H, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D, Sakaki K (2009b) Biotransformation of glycerol to d-glyceric acid by Acetobacter tropicalis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:1033–1039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1737-2
Habe H, Fukuoka T, Morita T, Kitamoto D, Yakushi T, Matsushita K, Sakaki K (2010) Disruption of the membrane-bound alcohol dehydrogenase-encoding gene improved glycerol use and dihydroxyacetone productivity in Gluconobacter oxydans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:1391–1395. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.100068
Habe H, Shimada Y, Yakushi T, Hattori H, Ano Y, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D, Itagaki M, Watanabe K, Yanagishita H, Matsushita K, Sakaki K (2009c) Microbial production of glyceric acid, an organic acid that can be mass produced from glycerol. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7760–7766. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01535-09
Hekmat D, Bauer R, Fricke J (2003) Optimization of the microbial synthesis of dihydroxyacetone from glycerol with Gluconobacter oxydans. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 26:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-003-0338-9
Kondo K, Horinouchi S (1997) Characterization of the genes encoding the three-component membrane-bound alcohol dehydrogenase from Gluconobacter suboxydans and their expression in Acetobacter pasteurianus. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1131–1138. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.63.3.1131-1138.1997
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(95)00584-1
Masud U, Matsushita K, Theeragool G (2010) Cloning and functional analysis of adhS gene encoding quinoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase subunit III from Acetobacter pasteurianus SKU1108. Int J Food Microbiol 138:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.12.027
Matsushita K, Ameyama M (1982) D-Glucose dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens, membrane-bound. Methods Enzymol 89:149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89026-5
Matsushita K, Fujii Y, Ano Y, Toyama H, Shinjoh M, Tomiyama N, Miyazaki T, Sugisawa T, Hoshino T, Adachi O (2003) 5-Keto-D-gluconate production is catalyzed by a quinoprotein glycerol dehydrogenase, major polyol dehydrogenase, in Gluconobacter species. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1959–1966. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.69.4.1959-1966.2003
Matsushita K, Toyama H, Yamada M, Adachi O (2002) Quinoproteins: structure, function, and biotechnological applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-001-0851-1
Matsushita K, Yakushi T, Toyama H, Shinagawa E, Adachi O (1996) Function of multiple heme c moieties in intramolecular electron transport and ubiquinone reduction in the quinohemoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase-cytochrome c complex of Gluconobacter suboxydans. J Biol Chem 271:4850–4857. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.9.4850
Moonmangmee D, Adachi O, Ano Y, Shinagawa E, Toyama H, Theeragool G, Lotong N, Matsushita K (2002) Isolation and characterization of thermotolerant Gluconobacter strains catalyzing oxidative fermentation at higher temperatures. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:2306–2315. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.64.2306
Morrison RJ, Dekock PC. (1959) Glyceric acid in broad bean (Vicia faba L.). Nature 184: 819. https://doi.org/10.1038/184819a0
Nguyen TM, Naoki K, Kataoka N, Matsutani M, Ano Y, Adachi O, Matsushita K, Yakushi T (2021) Characterization of a cryptic, pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent dehydrogenase of Gluconobacter sp. strain CHM43. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 85:998–1004. https://doi.org/10.1093/bbb/zbab005
Pagliaro M, Ciriminna R, Kimura H, Rossi M, Della PC (2007) From glycerol to value-added products. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:4434–4440. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200604694
Palmer JK (1956) Occurrence of d-glyceric acid in tobacco leaves. Science 123:415. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.123.3193.415
Richter N, Neumann M, Liese A, Wohlgemuth R, Eggert T, Hummel W (2009) Characterisation of a recombinant NADP-dependent glycerol dehydrogenase from Gluconobacter oxydans and its application in the production of L-glyceraldehyde. ChemBioChem 10:1888–1896. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200900193
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Schweiger P, Volland S, Deppenmeier U (2007) Overproduction and characterization of two distinct aldehyde-oxidizing enzymes from Gluconobacter oxydans 621H. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 13:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1159/000103606
Švitel J, Šturdík E (1994) Product yield and by-product formation in glycerol conversion to dihydroxyacetone by Gluconobacter oxydans. J Ferment Bioeng 78:351–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/0922-338X(94)90279-8
Yakushi T, Matsushita K (2010) Alcohol dehydrogenase of acetic acid bacteria: structure, mode of action, and applications in biotechnology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1257–1265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2529-z
Yakushi T, Terada Y, Ozaki S, Kataoka N, Akakabe Y, Adachi O, Matsutani M, Matsushita K (2018) Aldopentoses as new substrates for the membrane-bound, pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glycerol (polyol) dehydrogenase of Gluconobacter sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:3159–3171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8848-1
Zhang H, Shi L, Lin J, Sun M, Wei D (2016) Effective improvement of the activity of membrane-bound alcohol dehydrogenase by overexpression of adhS in Gluconobacter oxydans. Biotechnol Lett 38:1131–1138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2084-5
Zhou C-H, Beltramini JN, Fan Y-X, Lu GQ (2008) Chemoselective catalytic conversion of glycerol as a biorenewable source to valuable commodity chemicals. Chem Soc Rev 37:527–549. https://doi.org/10.1039/b707343g
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Shohei Kawamoto and Yukihiro Kaneko for their technical support.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Program through Target-driven R&D (A-STEP) of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript and have read and approved the final manuscript. HH, KM, and TY conceived and designed research. YS and HT performed GA production and RT-qPCR. MM contributed data analysis. KT and GT contributed mADH enzyme assay.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habe, H., Sato, Y., Tani, H. et al. Heterologous expression of membrane-bound alcohol dehydrogenase–encoding genes for glyceric acid production using Gluconobacter sp. CHM43 and its derivatives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 6749–6758 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11535-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11535-0