Abstract
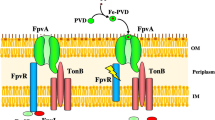
Iron is essential for all organisms. Bacteria have devolved sophisticated systems to maintain intracellular iron homeostasis. FpvCDEF(PA2407-2410) has been reported as an ABC transporter involved in pyoverdine-Fe uptake which does not affect growth under iron-limiting condition, when it is deleted in PAO1. In this study, we proved that fpvCDEF and fpvWXYZ(PA2403-2406) constituted an ABC transporter complex containing two operons: fpvWXYZCDE and fpvF. The operon fpvWXYZCDE was regulated by iron negatively and the single gene operon fpvF was constitutively expressed. Inactivation of any one of the components, fpvW, fpvC, fpvD, fpvE, and fpvF, led to increased expression of fpvWXYZCDE suggesting that each component of fpvWXYZCDEF could be involved in iron uptake. The ABC transporter complex encoded by fpvWXYZCDEF plays important roles in growth, oxidative stress resistance, and virulence, since the deletion of fpvWXYZCDEF resulted in defective growth, increased sensitivity to H2O2, and decreased virulence compared with PAO1(ΔfpvCDEF) and the wild type PAO1 under iron-limiting condition.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews SC, Robinson AK, Rodriguez-Quinones F (2003) Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:215–237
Bjarnason J, Southward CM, Surette MG (2003) Genomic profiling of iron-responsive genes in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium by high-throughput screening of a random promoter library. J Bacteriol 185:4973–4982
Brillet K et al (2012) An ABC transporter with two periplasmic binding proteins involved in iron acquisition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Chem Biol 7:2036–2045. doi:10.1021/cb300330v
Cairo G, Bernuzzi F, Recalcati S (2006) A precious metal: Iron, an essential nutrient for all cells. Genes Nutr 1:25–39. doi:10.1007/bf02829934
Carpenter C, Payne SM (2014) Regulation of iron transport systems in Enterobacteriaceae in response to oxygen and iron availability. J Inorg Biochem 133:110–117. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.01.007
Chang W, Small DA, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2005) Microarray analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals induction of pyocin genes in response to hydrogen peroxide. BMC Genom 6:115. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-6-115
Contreras H, Chim N, Credali A, Goulding CW (2014) Heme uptake in bacterial pathogens. Curr Opin Chem Biol 19:34–41. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.12.014
Cornelis P, Wei Q, Andrews SC, Vinckx T (2011) Iron homeostasis and management of oxidative stress response in bacteria. Metallomics 3:540–549. doi:10.1039/c1mt00022e
Cuiv PO, Clarke P, Lynch D, O’Connell M (2004) Identification of rhtX and fptX, novel genes encoding proteins that show homology and function in the utilization of the siderophores rhizobactin 1021 by Sinorhizobium meliloti and pyochelin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, respectively. J Bacteriol 186:2996–3005
Ditta G, Stanfield S, Corbin D, Helinski DR (1980) Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7347–7351
Duan K, Surette MG (2007) Environmental regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Las and Rhl quorum-sensing systems. J Bacteriol 189:4827–4836
Fetherston JD, Bertolino VJ, Perry RD (1999) YbtP and YbtQ: two ABC transporters required for iron uptake in Yersinia pestis. Mol Microbiol 32:289–299
Garau J, Gomez L (2003) Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Curr Opin Infect Dis 16:135–143. doi:10.1097/01.aco.0000065080.06965.86
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM (1984) Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem J 219:1–14
Hannauer M, Barda Y, Mislin GL, Shanzer A, Schalk IJ (2010) The ferrichrome uptake pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involves an iron release mechanism with acylation of the siderophore and recycling of the modified desferrichrome. J Bacteriol 192:1212–1220. doi:10.1128/jb.01539-09
Hider RC, Kong X (2010) Chemistry and biology of siderophores. Nat Prod Rep 27:637–657. doi:10.1039/b906679a
Hoang TT, Karkhoff-Schweizer RR, Kutchma AJ, Schweizer HP (1998) A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212:77–86
Hoang TT, Kutchma AJ, Becher A, Schweizer HP (2000) Integration-proficient plasmids for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: site-specific integration and use for engineering of reporter and expression strains. Plasmid 43:59–72
Holloway BW, Romling U, Tummler B (1994) Genomic mapping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Microbiology 140(Pt 11):2907–2929
Imlay JA, Chin SM, Linn S (1988) Toxic DNA damage by hydrogen peroxide through the Fenton reaction in vivo and in vitro. Science 240:640–642 (New York, NY)
Jang HJ, Nde C, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2009) Microarray analysis of Mycobacterium bovis BCG revealed induction of iron acquisition related genes in response to hydrogen peroxide. Environ Sci Technol 43:9465–9472. doi:10.1021/es902255q
Janulczyk R, Ricci S, Bjorck L (2003) MtsABC is important for manganese and iron transport, oxidative stress resistance, and virulence of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun 71:2656–2664
Kehrer JP (2000) The Haber-Weiss reaction and mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicology 149:43–50
Kochan I, Kvach JT, Wiles TI (1977) Virulence-associated acquisition of iron in mammalian serum by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis 135:623–632
Koster W (2001) ABC transporter-mediated uptake of iron, siderophores, heme and vitamin B12. Res Microbiol 152:291–301
Lau CK, Krewulak KD, Vogel HJ (2016) Bacterial ferrous iron transport: the Feo system. FEMS Microbiol Rev 40:273–298. doi:10.1093/femsre/fuv049
Llamas MA, Mooij MJ, Sparrius M, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, Ratledge C, Bitter W (2008) Characterization of five novel Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell-surface signalling systems. Mol Microbiol 67:458–472. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06061.x
Mademidis A, Killmann H, Kraas W, Flechsler I, Jung G, Braun V (1997) ATP-dependent ferric hydroxamate transport system in Escherichia coli: periplasmic FhuD interacts with a periplasmic and with a transmembrane/cytoplasmic region of the integral membrane protein FhuB, as revealed by competitive peptide mapping. Mol Microbiol 26:1109–1123
Minandri F et al (2016) Role of iron uptake systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and airway. Infect Immun 84:2324–2335. doi:10.1128/iai.00098-16
Nicolaou SA, Fast AG, Nakamaru-Ogiso E, Papoutsakis ET (2013) Overexpression of fetA (ybbL) and fetB (ybbM), encoding an iron exporter, enhances resistance to oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:7210–7219. doi:10.1128/aem.02322-13
Ochsner UA, Wilderman PJ, Vasil AI, Vasil ML (2002) GeneChip expression analysis of the iron starvation response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of novel pyoverdine biosynthesis genes. Mol Microbiol 45:1277–1287
Palma M, Worgall S, Quadri LE (2003) Transcriptome analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa response to iron. Arch Microbiol 180:374–379. doi:10.1007/s00203-003-0602-z
Perry RD, Fetherston JD (2011) Yersiniabactin iron uptake: mechanisms and role in Yersinia pestis pathogenesis. Microbes Infect 13:808–817. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2011.04.008
Porcheron G, Dozois CM (2015) Interplay between iron homeostasis and virulence: Fur and RyhB as major regulators of bacterial pathogenicity. Vet Microbiol 179:2–14. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.03.024
Ravel J, Cornelis P (2003) Genomics of pyoverdine-mediated iron uptake in pseudomonads. Trends Microbiol 11:195–200
Rodriguez GM, Smith I (2006) Identification of an ABC transporter required for iron acquisition and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol 188:424–430. doi:10.1128/jb.188.2.424-430.2006
Sabri M, Leveille S, Dozois CM (2006) A SitABCD homologue from an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain mediates transport of iron and manganese and resistance to hydrogen peroxide. Microbiology 152:745–758. doi:10.1099/mic.0.28682-0
Sangsuwan A, Kawasaki H, Iwasaki Y (2016) Thiolated-2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine protected silver nanoparticles as novel photo-induced cell-killing agents. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 140:128–134
Schalk IJ, Guillon L (2013) Fate of ferrisiderophores after import across bacterial outer membranes: different iron release strategies are observed in the cytoplasm or periplasm depending on the siderophore pathways. Amino Acids 44:1267–1277. doi:10.1007/s00726-013-1468-2
Schweizer HP (1993) Two plasmids, X1918 and Z1918, for easy recovery of the xylE and lacZ reporter genes. Gene 134:89–91
Sharp R, Jansons IS, Gertman E, Kropinski AM (1996) Genetic and sequence analysis of the cos region of the temperate Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage, D3. Gene 177:47–53
Shea CM, McIntosh MA (1991) Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the ferric enterobactin transport system: homology to other periplasmic binding protein-dependent systems in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 5:1415–1428
Shen L, Gao X, Wei J, Chen L, Zhao X, Li B, Duan K (2012) PA2800 plays an important role in both antibiotic susceptibility and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Curr Microbiol 65:601–609
Sigel SP, Stoebner JA, Payne SM (1985) Iron-vibriobactin transport system is not required for virulence of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun 47:360–362
Staudenmaier H, Van Hove B, Yaraghi Z, Braun V (1989) Nucleotide sequences of the fecBCDE genes and locations of the proteins suggest a periplasmic-binding-protein-dependent transport mechanism for iron(III) dicitrate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 171:2626–2633
Taudte N, German N, Zhu YG, Grass G, Rensing C (2016) Restoration of growth by manganese in a mutant strain of Escherichia coli lacking most known iron and manganese uptake systems. Biometals 29:433–450. doi:10.1007/s10534-016-9927-3
Visca P, Leoni L, Wilson MJ, Lamont IL (2002) Iron transport and regulation, cell signalling and genomics: lessons from Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas. Mol Microbiol 45:1177–1190
Visca P, Imperi F, Lamont IL (2007) Pyoverdine siderophores: from biogenesis to biosignificance. Trends Microbiol 15:22–30. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2006.11.004
Wei Y, Murphy ER (2016) Shigella iron acquisition systems and their regulation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 6:18. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2016.00018
Wirth C, Meyer-Klaucke W, Pattus F, Cobessi D (2007) From the periplasmic signaling domain to the extracellular face of an outer membrane signal transducer of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: crystal structure of the ferric pyoverdine outer membrane receptor. J Mol Biol 368:398–406. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.023
Wyckoff EE, Payne SM (2011) The Vibrio cholerae VctPDGC system transports catechol siderophores and a siderophore-free iron ligand. Mol Microbiol 81:1446–1458. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07775.x
Wyckoff EE, Mey AR, Payne SM (2007) Iron acquisition in Vibrio cholerae Biometals: an international journal on the role of metal ions in biology, biochemistry, and medicine 20:405–416. doi:10.1007/s10534-006-9073-4
Wyckoff EE, Boulette ML, Payne SM (2009) Genetics and environmental regulation of Shigella iron transport systems Biometals: an international journal on the role of metal ions in biology, biochemistry, and medicine 22:43–51. doi:10.1007/s10534-008-9188-x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSFC (81171620, 31570131), NSERC Canada (No. 402943-2011 RGPIN), PCSIRT (IRT 15R55), and Science and Technology Overall Innovation Project of Shaanxi Province China (2016KTCQ03-18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, L., Guo, Z., Wang, Y. et al. The Two-Operon-Coded ABC Transporter Complex FpvWXYZCDEF is Required for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Growth and Virulence Under Iron-Limiting Conditions. J Membrane Biol 251, 91–104 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-017-9979-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-017-9979-5