Abstract
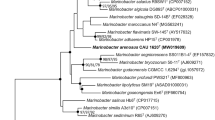
A novel Gram-stain-positive, coccoid-shaped, facultative anaerobic, motile and halophilic bacterium strain 5MT was isolated from Surajbari in India. Based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, it was identified as belonging to the genus Marinococcus and was most closely related to Marinococcus luteus KCTC 13214T (99.3 %, sequence similarity), Marinococcus halotolerans KCTC 19045T (99.0 %), Marinococcus halophilus LMG 17439T (98.8 %) and Marinococcus tarijensis LMG 26930T (98.7 %). However, the DNA–DNA relatedness of strain 5MT with M. luteus KCTC 13214T, M. halotolerans KCTC 19045T, M. halophilus LMG 17439T and M. tarijensis LMG 26930T was 42.6 ± 0.8, 48.6 ± 0.8, 40.9 ± 0.8 and 39.8 ± 0.9 %, respectively. Strain 5MT grows optimally at 5 % (w/v) NaCl, pH 7.5–8.5 and 37 °C. The cell-wall peptidoglycan of strain 5MT contains meso-diaminopimelic acid. Polar lipids of the strain 5MT include diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, a phospholipid and two unknown lipids. The predominant isoprenoid quinone was MK-7. DNA G+C content was 48.9 mol%, and anteiso-C15:0 (40.9 %) was the predominant fatty acid. The results of phylogenetic, biochemical tests and chemotaxonomic allowed a clear differentiation of strain 5MT from all of its nearest phylogenetic neighbours, which represents a novel member of the genus Marinococcus, for which the name Marinococcus salis sp., nov., is proposed. The type strain is 5MT (=KCTC 33743T = LMG 29101T = CGMCC 1.15385T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahal DR, Ventosa A (2002) Moderately halophilic and halotolerant species of Bacillus and related genera. In: Berkeley R, Heyndrickx M, Logan N, De Vos P (eds) Applications and systematics of Bacillus and relatives. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 83–99
Balderrama-Subieta A, Guzmán D, Minegishi H, Echigo A, Shimane Y, Hatada Y, Quillaguamán J (2013) Marinococcus tarijensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a salt mine. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3319–3323
Hao MV, Kocur M, Komogata K (1984) Marinococcus gen. nov., a new genus for motile cocci with meso-diaminopimelic acid in the cell wall; and Marinococcus albus sp. nov. and Marinococcus halophilus (Novitsky and Kushner) comb. nov. J Gen Appl Microbiol 30:449–459
Hasegawa T, Takizaea M, Tanida S (1983) A rapid analysis for chemical grouping of aerobic actinomycetes. J Gen Appl Microbiol 29:319–322
Kates M (1972) Techniques of lipidology. Elsevier, New York
Kates M (1986) Techniques of lipidology: isolation, analysis, and identification of lipids. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA Gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Li W-J, Schumann P, Zhang Y-Q, Chen G-Z, Tian X-P, Xu L-H, Stackebrandt E, Jiang C-L (2005) Marinococcus halotolerans sp. nov., isolated from Qinghai, North-West China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1801–1804
Logan NA, Berge O, Bishop AH, Busse H-J, De Vos P, Fritze D et al (2009) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of aerobic, endospore forming bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2114–2121
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Marquez MC, Ventosa A, Ruiz-Berraquero F (1990) Marinococcus hispanicus, a new species of moderately halophilic Gram-positive cocci. Int J Syst Bacteriol 40:165–169
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Gӧker M, Sprӧer C, Klenk H-P (2013) When should a DDH experiment be mandatory in microbial taxonomy? Arch Microbiol 195:413–418
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Novitsky TJ, Kushner DJ (1976) Planococcus halophilus sp. nov., a facultatively halophilic coccus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 26:53–57
Oren A (2002) Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28:56–63
Oren A, Duker S, Ritter S (1996) The polar lipid composition of Walsby’s square bacterium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 138:135–140
Parte AC (2016) List of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. http://www.bacterio.net
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Inc, Newark
Schleifer KH (1985) Analysis of the chemical composition and primary structure of murein. Methods Microbiol 18:123–156
Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1972) Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev 36:407–477
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1981) General characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA, Krieg NR, Phillips GB (eds) Manual of methods for general microbiology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 409–443
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P (ed) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 607–654
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 4:152–155
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Tamaoka J, Fujimura Y-K, Kuraishi H (1983) Analysis of bacterial menaquinone mixtures by high performance liquid chromatography. J Appl Microbiol 54:31–36
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tindall BJ (1990a) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66:199–202
Tindall BJ (1990b) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tourova TP, Antonov AS (1987) Identification of microorganisms by rapid DNA–DNA hybridization. Methods Microbiol 19:333–355
Ventosa A (2006) Unusual micro-organisms from unusual habitats: hypersaline environments. In: Logan NA, Lappin-Scott HM, Oyston PCF (eds) Prokaryotic diversity: mechanisms and significance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 223–254
Ventosa A, Quesada E, Rodriguez-Valera F, Ruiz-Berraquero F, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1982) Numerical taxonomy of moderately halophilic Gram-negative rods. J Gen Microbiol 128:1959–1968
Ventosa A, Marquez MC, Weiss N, Tindall BJ (1992) Transfer of Marinococcus hispanicus to the genus Salinicoccus as Salinicoccus hispanicus comb. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:530–534
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:504–544
Vishnuvardhan Reddy S, Aspana S, Tushar DL, Sasikala CH, Ramana V (2013) Spirochaeta sphaeroplastigenens sp. nov., a halo-alkaliphilic, obligately anaerobic spirochaete isolated from soda lake Lonar. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2223–2228
Wang Y, Cao L-L, Tang S-K, Lou K, Mao P-H, Jin X, Jiang C-L, Xu L-H, Li W-J (2009) Marinococcus luteus sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium isolated from a salt lake, and emended description of the genus Marinococcus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2875–2879
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Oh TK (2007) Reclassification of Marinococcus albus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2406–2411
Acknowledgments
S.V.R. and M.T. thank Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for providing FTSYS Project Grants (SB/FT/LS-115/2012 and SB/FT/LS-320/2012, respectively). M.F. also thanks DST for PA fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequences of strain 5MT is LN879357.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Two-dimensional thin-layer chromatogram of polar lipid extracts of strain 5MT and related Marinococcus species. The first direction was developed in CHCl3:CH3OH:H2O (75:32:4 by volume) and the second in CHCl3:CH3OH:CH3COOH:H2O (86:16:15:4 by volume). PG, phosphatidylglycerol; DPG, diphosphatidylglycerol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PL1, unknown phospholipid; and L1-7, unknown lipids (PDF 437 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vishnuvardhan Reddy, S., Thirumala, M., Farooq, M. et al. Marinococcus salis sp., nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a salt marsh. Arch Microbiol 198, 1013–1018 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1263-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1263-z