Abstract
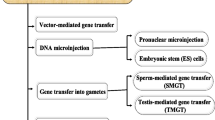
Transgenic animal technology is one of the fastest growing biotechnology areas. It is used to integrate exogenous genes into the animal genome by genetic engineering technology so that these genes can be inherited and expressed by offspring. The transgenic efficiency and precise control of gene expression are the key limiting factors in the production of transgenic animals. A variety of transgenic technologies are available. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages and needs further study because of unresolved technical and safety issues. Further studies will allow transgenic technology to explore gene function, animal genetic improvement, bioreactors, animal disease models, and organ transplantation. This article reviews the recently developed animal transgenic technologies, including the germ line stem cell-mediated method to improve efficiency, gene targeting to improve accuracy, RNA interference-mediated gene silencing technology, zinc-finger nuclease gene targeting technology and induced pluripotent stem cell technology. These new transgenic techniques can provide a better platform to develop transgenic animals for breeding new animal varieties and promote the development of medical sciences, livestock production, and other fields.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janeisch R, Mintz B (1974) Simian virus 40 DNA sequences in DNA healthy adult mice derived from preimplantation blastocysts injected with viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71(4):1250–1254
Gordon JW, Scangos GA, Plotkin DJ, Barbosa JA, Ruddle FH (1980) Genetic transformation of mouse embryos by microinjection of purified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7380–7384
Gordon JW, Ruddle FH (1981) Integration and stable germ line transmission of genes injected into mouse pronuclei. Science 214:1244–1246
Lavitrano M, Camaioni A, Fazio VM, Dolci S, Farace MG, Spadafora C (1989) Sperm cells as vectors for introducing foreign DNA into eggs: genetic transformation of mice. Cell 57:717–723
Hirabayashi M, Hochi S (2010) Generation of transgenic rats by ooplasmic injection of sperm cells exposed to exogenous DNA. Methods Mol Biol 597:127–136
Perry AC, Wakayama T, Kishikawa H, Kasai T, Okabe M, Toyoda Y, Yanagimachi R (1999) Mammalian transgenesis by intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Science 284:1180–1183
Chan AWS, Chong KY, Martinovich C, Simerly C, Schatten G (2001) Transgenic monkeys produced by retroviral gene transfer into mature oocytes. Science 291(5502):309–312
García-Vázquez FA, Ruiz S, Matás C, Izquierdo-Rico MJ, Grullón LA, De Ondiz A, Vieira L, Avilés-López K, Gutiérrez-Adán A, Gadea J (2010) Production of transgenic piglets using ICSI-sperm-mediated gene transfer in combination with recombinase RecA. Reproduction 140(2):259–272
Brinster RL (2002) Germline stem cell transplantation and transgenesis. Science 296:2174–2176
Dhup S, Majumdar SS (2008) Transgenesis via permanent integration of genes in repopulating spermatogonial cells in vivo. Nat Methods 5:601–603
Zhang X, Miao XY, Yin XH, Ma YF, Qu ZJ, Zhang QT (2009) Study of transgenic efficiency in different spermatogenic stages in mice. Prog Biochem Biophys 36(8):1019–1024
Zou K, Yuan Z, Yang Z, Luo H, Sun K, Zhou L, Xiang J, Shi L, Yu Q, Zhang Y, Hou R, Wu J (2009) Production of offspring from a germline stem cell line derived from neonatal ovaries. Nat Cell Biol 11(5):631–636
Zhang Y, Yang Z, Yang Y, Wang S, Shi L, Xie W, Sun K, Zou K, Wang L, Xiong J, Xiang J, Wu J (2011) Production of transgenic mice by random recombination of targeted genes in female germline stem cells. J Mol Cell Biol 3(2):132–141
Cibelli JB, Stice SL, Golueke PJ, Kane JJ, Jerry J, Blackwell C, Ponce de Leon FA, Robl JM (1998) Cloned transgenic calves produced from nonquiescent fetal fibroblasts. Science 280:1256–1258
Park KW, Cheong HT, Lai L, Im GS, Kuhholzer B, Bonk A, Samuel M, Rieke A, Day BN, Murphy CN, Carter DB, Prather RS (2001) Production of nuclear transfer-derived swine that express the enhanced green fluorescent protein. Anim Biotechnol 12:173–181
McCreath KJ, Howcroft J, Campbell KH, Colman A, Schnieke AE, Kind AJ (2000) Production of gene-targeted sheep by nuclear transfer from cultured somatic cells. Nature 405:1066–1069
Lois C, Hong EJ, Pease S, Brown EJ, Baltimore D (2002) Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science 295:868–872
Hofmann A, Kessler B, Ewerling S, Weppert M, Vogg B, Ludwig H, Stojkovic M, Boelhauve M, Brem G, Wolf E, Pfeifer A (2003) Efficient transgenesis in farm animals by lentiviral vectors. EMBO Rep 4(11):1054–1060
Sasaki E, Suemizu H, Shimada A, Hanazawa K, Oiwa R, Kamioka M, Tomioka I, Sotomaru Y, Hirakawa R, Eto T, Shiozawa S, Maeda T, Ito M, Ito R, Kito C, Yagihashi C, Kawai K, Miyoshi H, Tanioka Y, Tamaoki N, Habu S, Okano H, Nomura T (2009) Generation of transgenic non-human primates with germline transmission. Nature 459:523–527
Motono M, Yamada Y, Hattori Y, Nakagawa R, Nishijima K, Iijima S (2010) Production of transgenic chickens from purified primordial germ cells infected with a lentiviral vector. J Biosci Bioeng 109(4):315–321
Kim JN, Park TS, Park SH, Park KJ, Kim TM, Lee SK, Lim JM, Han JY (2010) Migration and proliferation of intact and genetically modified primordial germ cells and the generation of a transgenic chicken. Biol Reprod 82(2):257–262
Beard C, Hochedlinger K, Plath K, Wutz A, Jaenisch R (2006) Efficient method to generate single-copy transgenic mice by site-specific integration in embryonic stem cells. Genesis 44:23–28
Bu L, Gao XL, Jiang X, Chien KR, Wang Z (2010) Targeted conditional gene knockout in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Res 20:379–382
Toledo F, Liu CW, Lee CJ, Wahl GM (2006) RMCE-ASAP: a gene targeting method for ES and somatic cells to accelerate phenotype analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 34(13):e92
Hasuwa H, Kaseda K, Einarsdottir T, Okabe M (2002) Small interfering RNA and gene silencing in transgenic mice and rats. FEBS Lett 532:227–230
Seibler J, Schwenk F (2010) Transgenic RNAi applications in the mouse. Methods Enzymol 477:367–386
Miao XY, Zhang RJ (2011) Production of transgenic sheep by inhibin α shRNA. Transgenic Res 20(5):1185
Porteus MH (2006) Mammalian gene targeting with designed zinc-finger nucleases. Mol Ther 13(2):438–446
Zhao XY, Li W, Lv Z, Liu L, Tong M, Hai T, Hao J, Wang X, Wang L, Zeng F, Zhou Q (2010) Viable fertile mice generated from fully pluripotent iPS cells derived from adult somatic cells. Stem Cell Rev 6(3):390–397
Lee AY, Lloyd KC (2011) Rederivation of transgenic mice from iPS cells derived from frozen tissue. Transgenic Res 20(1):167–175
Miao XY (2011) Production of transgenic animals using spermatogonial stem cells. Agri Sci China 10(5):101–105
Brinster RL, Avarbock MR (1994) Germline transmission of donor haplotype following spermatogonial transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(24):11303–11307
Nagano M, Brinster CJ, Orwig KE, Ryu BY, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL (2001) Transgenic mice produced by retroviral transduction of male germ-line stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(23):13090–13095
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Ikawa M, Takehashi M, Ogonuki N, Miki H, Inoue K, Kazuki Y, Lee J, Toyokuni S, Oshimura M, Ogura A, Shinohara T (2006) Production of knockout mice by random or targeted mutagenesis in spermatogonial stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(21):8018–8023
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Kato M, Takehashi M, Morimoto H, Takashima S, Chuma S, Nakatsuji N, Hirabayashi M, Shinohara T (2008) Production of transgenic rats via lentiviral transduction and xenogeneic transplantation of spermatogonial stem cells. Biol Reprod 79(6):1121–1128
Honaramooz A, Megee S, Zeng W, Destrempes MM, Overton SA, Luo J, Galantino-Homer H, Modelski M, Chen F, Blash S, Melican DT, Gavin WG, Avres S, Yang F, Wang PJ, Echelard Y, Dobrinski I (2008) Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated transduction of male germ line stem cells results in transgene transmission after germ cell transplantation. FASEB J 22(2):374–382
Miao XY, Zhang X (2011) Production of transgenic mice carrying the Thanatin gene by intratesticular injection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 415(3):429–433
Izsvák Z, Fröhlich J, Grabundzija I, Shirley JR, Powell HM, Chapman KM, Ivics Z, Hamra FK (2010) Generating knockout rats by transposon mutagenesis in spermatogonial stem cells. Nat Methods 7:443–445
Ivics Z, Izsvák Z, Medrano G, Chapman KM, Hamra FK (2011) Sleeping Beauty transposon mutagenesis in rat spermatogonial stem cells. Nat Protoc 6(10):1521–1535
Honaramooz A, Yang Y (2011) Recent advances in application of male germ cell transplantation in farm animals. Vet Med Int 2011:657860. doi:10.4061/2011/657860
Naito M, Matsubara Y, Harumi T, Tagami T, Sakurai M, Kuwana T (2000) Foreign gene expression in the gonads of chimaeric chicken embryos by transfer of primordial germ cells transfected in vitro by lipofection for 24 hours. Anim Sci J 71(3):308–311
Van de Lavoir MC, Diamond JH, Leighton PA, Mather-Love C, Heyer BS, Bradshaw R, Kerchner A, Hooi LT, Gessaro TM, Swanberg SE, Delany ME, Etches RJ (2006) Germline transmission of genetically modified primordial germ cells. Nature 441(7094):766–769
Motono M, Yamada Y, Hattori Y, Nakagawa R, Nishijima K, Iijima S (2010) Production of transgenic chickens from purified primordial germ cells infected with a lentiviral vector. J Biosci Bioeng 109(4):315–321
Mueller S, Prelle K, Rieger N, Petznek H, Lassnig C, Luksch U, Aigner B, Baetscher M, Wolf E, Mueller M, Brem G (1999) Chimeric pigs following blastocyst injection of transgenic porcine primordial germ cells. Mol Reprod Dev 54(3):244–254
Nowak-Imialek M, Kues W, Carnwath JW, Niemann H (2011) Pluripotent stem cells and reprogrammed cells in farm animals. Microsc Microanal 17(4):474–497
Leighton PA, van de Lavoir MC, Diamond JH, Xia C, Etches RJ (2008) Genetic modification of primordial germ cells by gene trapping, gene targeting, and phiC31 integrase. Mol Reprod Dev 75(7):1163–1175
Suraeva NM, Baryshnikov AIu, Fisinin VI, Prokofev MI (2008) Efficacy of various methods of a reporter gene transfer to chicken embryonic cells. Izv Akad Nauk Ser Biol 1:18–23
Shin SS, Kim TM, Kim SY, Kim TW, Seo HW, Lee SK, Kwon SC, Lee GS, Kim H, Lim JM, Han JY (2008) Generation of transgenic quail through germ cell-mediated germline transmission. FASEB J 22(7):2435–2444
Li MA, Bradley A (2011) Crafting rat genomes with zinc fingers. Nat Biotechnol 29:39–41
Thomas KR, Capecchi MR (1987) Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell 51(3):503–512
Okada Y, Ueshin Y, Hasuwa H, Takumi K, Okabe M, Ikawa M (2009) Targeted gene modification in mouse ES cells using integrase-defective lentiviral vectors. Genesis 47(4):217–223
Kawamata M, Ochiya T (2011) Gene-manipulated embryonic stem cells for rat transgenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(11):1911–1915
Yamamoto S, Nakata M, Sasada R, Ooshima Y, Yano T, Shinozawa T, Tsukimi Y, Takeyama M, Matsumoto Y, Hashimoto T (2011) Derivation of rat embryonic stem cells and generation of protease-activated receptor-2 knockout rats. Transgenic Res. doi:10.1007/s11248-011-9564-0
Dong Z, Ge J, Li K, Xu Z, Liang D, Li J, Li J, Jia W, Li Y, Dong X, Cao S, Wang X, Pan J, Zhao Q (2011) Heritable targeted inactivation of myostatin gene in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. PLoS One 6(12):e28897
Tong C, Li P, Wu NL, Yan Y, Ying QL (2010) Production of p53 gene knockout rats by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature 467(7312):211–213
Tong C, Huang G, Ashton C, Li P, Ying QL (2011) Generating gene knockout rats by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nat Protoc 6(6):827–844
Kuroiwa Y, Kasinathan P, Matsushita H, Sathiyaselan J, Sullivan EJ, Kakitani M, Tomizuka K, Ishida I, Robl JM (2004) Sequential targeting of the genes encoding immunoglobulin-μ and prion protein in cattle. Nat Genet 36(7):775–780
Wall RJ, Powell AM, Paape MJ, Kerr DE, Bannerman DD, Pursel VG, Wells KD, Talbot N, Hawk HW (2005) Genetically enhanced cows resist intramammary Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat Biotechnol 23(4):445–451
Lai L, Kang JX, Li R, Wang J, Witt WT, Yong HY, Hao Y, Wax DM, Murphy CN, Rieke A, Samuel M, Linville ML, Korte SW, Evans RW, Starzl TE, Prather RS, Dai Y (2006) Generation of cloned transgenic pigs rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Nat Biotechnol 24(4):435–436
Baldassarre H, Hockley DK, Dore M, Brochu E, Hakier B, Zhao X, Bordiqnon V (2008) Lactation performance of transgenic goats expressing recombinant human butyryl-cholinesterase in the milk. Transgenic Res 17(1):73–84
Bertolini LR, Bertolini M, Maga EA, Madden KR, Murray JD (2009) Increased gene targeting in Ku70 and Xrcc4 transiently deficient human somatic cells. Mol Biotechnol 41(2):106–114
Wongsrikeao P, Sutou S, Kunishi M, Dong YJ, Bai X, Otoi T (2011) Combination of the somatic cell nuclear transfer method and RNAi technology for the production of a prion gene-knockdown calf using plasmid vectors harboring the U6 or tRNA promoter. Prion 5(1):39–46
Waghmare SK, Estrada J, Reyes L, Li P, Ivary B, Sidner RA, Burlak C, Tector AJ (2011) Gene targeting and cloning in pigs using fetal liver derived cells. J Surg Res 171(2):e223–e229
Sakahara M, Ohkawara H, Nakao K, Yokozaki H, Aiba A (2009) The simultaneous induction of tumorigenesis and Cre-loxP recombination in mice. Kobe J Med Sci 54(6):279–281
Kyoungmi K, Hwain K, Daekee L (2009) Site-specific modification of genome with cell-permeable Cre fusion protein in preimplantation mouse embryo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388(1):122–123
Bouvier J, Cheng JG (2009) Recombineering-based procedure for creating Cre/loxP conditional knockouts in the mouse. Curr Protoc Mol Biol Chapter 23: Unit 23.13
Friedel RH, Wurst W, Wefers B, Kühn R (2011) Generating conditional knockout mice. Methods Mol Biol 693:205–231
Yamamoto M, Takeda K (2012) A method for the generation of conditional gene-targeted mice. Methods Mol Biol 757:399–410
Wakita T, Taya C, Katsume A, Kato J, Yonekawa H, Kanegae Y, Saito I, Hayashi Y, Koike M, Kohara M (1998) Efficient conditional transgene expression in hepatitis C virus cDNA transgenic mice mediated by the Cre/loxP system. J Biol Chem 273(15):9001–9006
Metzger D, Chambon P (2001) Site- and time-specific gene targeting in the mouse. Methods 24(1):71–80
Rendahl KG, Ouiroz D, Ladner M, Covne M, Seltzer J, Manning WC, Escobedo JA (2002) Tightly regulated long-term erythropoietin expression in vivo using tet-inducible recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors. Hum Gene Ther 13(2):335–342
Chenuaud P, Larcher T, Rabinowitz JE, Provost N, Joussemet B, Bujard H, Samulski RJ, Favre D, Moullier P (2004) Optimal design of a single recombinant adeno-associated virus derived from serotypes 1 and 2 to achieve more tightly regulated transgene expression from nonhuman primate muscle. Mol Ther 9(3):410–418
Rettig GR, Rice KG (2009) Quantitative in vivo imaging of non-viral-mediated gene expression and RNAi-mediated knockdown. Methods Mol Biol 574:155–171
Hasuwa H, Kaseda K, Einarsdottir T, Okabe M (2002) Small interfering RNA and gene silencing in transgenic mice and rats. FEBS Lett 532(1–2):227–230
Kunath T, Gish G, Lickert H, Jones N, Pawson T, Rossant J (2003) Transgenic RNA interference in ES cell-derived embryos recapitulates a genetic null phenotype. Nat Biotechnol 21(5):559–561
Kleinhammer A, Deussing J, Wurst W, Kühn R (2011) Conditional RNAi in mice. Methods 53(2):142–150
Dickins RA, McJunkin K, Hernando E, Premsrirut PK, Krizhanovsky V, Burgess DJ, Kim DY, Cordon-Cardo C, Zender L, Hannon GJ, Lowe SW (2007) Tissue-specific and reversible RNA interference in transgenic mice. Nat Genet 39(7):914–921
Dieckhoff B, Petersen B, Kues WA, Kurth R, Niemann H, Denner J (2008) Knockdown of porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) expression by PERV-specific shRNA in transgenic pigs. Xenotransplantation 15(1):36–45
Tessanne K, Golding MC, Long CR, Peoples MD, Hannon G, Westhusin ME (2012) Production of transgenic calves expressing an shRNA targeting myostatin. Mol Reprod Dev 79(3):176–185
Luo QM, Miao XY, Zhang RJ (2011) An update on the development of transgenic animal technology. Yi Chuan (Hereditas) 33(5):449–458
Meng X, Noyes MB, Zhu LJ, Lawson ND, Wolfe SA (2008) Targeted gene inactivation in zebrafish using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 26(6):695–701
Maeder ML, Thibodeau-Beganny S, Osiak A, Wright DA, Anthony RM, Eichtinger M, Jiang T, Foley JE, Winfrey RJ, Townsend JA, Unger-Wallace E, Sander JD, Müller-Lerch F, Fi Fu, Pearlberg J, Göbel C, Dassie JP, Pruett-Miller SM, Porteus MH, Sgroi DC, Iafrate AJ, Dobbs D, McCray PB Jr, Cathomen T, Voytas DF, Joung JK (2008) Rapid “open-source” engineering of customized zinc-finger nucleases for highly efficient gene modification. Mol Cell 31(2):294–301
Geurts AM, Cost GJ, Freyvert Y, Zeitler B, Miller JC, Choi VM, Jenkins SS, Wood A, Cui X, Meng X, Vincent A, Lam S, Michalkiewicz M, Schilling R, Foeckler J, Kalloway S, Weiler H, Ménoret S, Anegon I, Davis GD, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Jacob HJ, Buelow R (2009) Knockout rats via embryo microinjection of zinc-finger nucleases. Science 325(5939):433
Mashimo T, Takizawa A, Voigt B, Yoshimi K, Hiai H, Kuramoto T, Serikawa T (2010) Generation of knockout rats with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency(X-SCID) using zinc-finger nucleases. PLOS One 5(1):e8870
Carbery ID, Ji D, Harrington A, Brown V, Weinstein EJ, Liaw L, Cui X (2010) Targeted genome modification in mice using zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 186:451–459
Cui X, Ji D, Fisher DA, Wu Y, Briner DM, Weinstein EJ (2011) Targeted integration in rat and mouse embryos with zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 29(1):64–67
Hauschild J, Petersen B, Santiago Y, Queisser AL, Carnwath JW, Lucas-Hahn A, Zhang L, Meng X, Gregory PD, Schwinzer R, Cost GJ, Niemann H (2011) Efficient generation of a biallelic knockout in pigs using zinc-finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(29):12013–12017
Gupta A, Meng X, Zhu L, Lawson ND (2011) Zinc-finger protein-dependent and -independent contributions to the in vivo off-target activity of zinc-finger nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res 39(1):381–392
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126(4):663–676
Yu JY, Hu KJ, Smuga-Otto K, Tian SL, Stewart R, Slukvin II, Thomson JA (2009) Human induced pluripotent stem cells free of vector and transgene sequences. Science 324(5928):797–801
Hiratsuka M, Uno N, Kurosaki H, Imaoka N, Kazuki K, Ueno E, Akakura Y, Katoh M, Osaki M, Kazuki Y, Nakagawa M, Yamanaka S, Oshimura M (2011) Integration-free iPS cells engineered using human artificial chromosome vectors. PLoS One 6(10):e25961
Warren L, Manos PD, Ahfeldt T, Loh YH, Li H, Lau F, Ebina W, Mandal PK, Smith ZD, Meissner A, Daley GQ, Brack AS, Collins JJ, Cowan C, Schlaeger TM, Rossi DJ (2010) Highly efficient reprogramming to pluripotency and directed differentiation of human cells with synthetic modified mRNA. Cell Stem Cell 7(5):618–630
Anokye-Danso F, Trivedi CM, Juhr D, Gupta M, Cui Z, Tian Y, Zhang Y, Yang W, Gruber PJ, Epstein JA, Morrisey EE (2011) Highly efficient miRNA-mediated reprogramming of mouse and human somatic cells to pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 8(4):376–388
Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Sepac A, Sedlic F, Bosnjak ZJ, Lough JW, Duncan SA (2010) Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells by simple transient transfection of plasmid DNA encoding reprogramming factors. BMC Dev Biol 10:81
Kim D, Kim CH, Moon JI, Chung YG, Chang MY, Han BS, Ko S, Yang E, Cha KY, Lanza R, Kim KS (2009) Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells by direct delivery of reprogramming proteins. Cell Stem Cell 4(6):472–476
Hockemeyer D, Wang H, Kiani S, Lai CS, Gao Q, Cassady JP, Cost GJ, Zhang L, Santiago Y, Miller JC, Zeitler B, Cherone JM, Meng X, Hinkley SJ, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Jaenisch R (2011) Genetic engineering of human pluripotent cells using TALE nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 29(8):731–734
Liu Y, Rao M (2011) Gene targeting in human pluripotent stem cells. Methods Mol Biol 767:355–367
West FD, Terlouw SL, Kwon DJ, Mumaw JL, Dhara SK, Hasneen K, Dobrinsky JR, Stice SL (2010) Porcine induced pluripotent stem cells produce chimeric offspring. Stem Cells Dev 19(8):1211–1220
West FD, Uhl EW, Liu Y, Stowe H, Lu Y, Yu P, Gallegos-Cardenas A, Pratt SL, Stice SL (2011) Brief report: chimeric pigs produced from induced pluripotent stem cells demonstrate germline transmission and no evidence of tumor formation in young pigs. Stem Cells 29(10):1640–1643
Qin T, Miao XY (2010) Current progress and application prospects of induced pluripotent stem cells. Yi Chuan (Hereditas) 32(12):1205–1214
Miao XY, Chen XY (2012) Study and application of induced pluripotent stem cells. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 45(2):369–375
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from The Major Science and Technology Project of New Variety Breeding of Genetically Modified Organisms (Nos. 2009ZX08008-004B and 2008ZX08008-003), the National High Technology Research Development Program of China (863 Program No. 2008AA10Z140), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30571339) and the Innovation Research Foundation of CAAS (No. 2004-CAAS-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, X. Recent advances in the development of new transgenic animal technology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 815–828 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1081-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1081-7