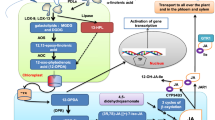
Abstract
Induction of defense response against Karnal bunt (KB) by suppressing the pathogenesis was observed upon exogenous application of jasmonic acid (JA) as evident from decrease in the coefficient of infection and overall response value in both susceptible and resistant varieties of wheat. The ultra-structural changes during disease progression showed the signs of programmed cell death (PCD). However, JA strengthened the defense barrier by enhancing the lignifications of cell walls as observed in spikes of both varieties by histochemical analysis. Compared to the plants inoculated with pathogen alone, plants of resistant line (RJP) first treated with JA followed by inoculation with pathogen showed more lignifications and extracellular deposition of other metabolites on cells, which is supposed to prevent mycelial invasions. Contrary to this, susceptible (SJP) lines also showed lignifications but the invasion was more compared to resistant line. Induction of protease activity was higher in resistant variety than its corresponding susceptible variety. The protease activity induced during the colonization of the pathogen and its proliferation inside the host system gets inhibited by JA treatment as demonstrated by the quantitative and in-gel protease assay. The results indicate the role of JA signalling in inhibiting the proteases due to expression of certain protease inhibitor genes. SDS-PAGE analysis shows differential gene expression through induction and/or suppression of different proteins in wheat spikes of resistant and susceptible varieties under the influence of JA. Thus, exogenously applied JA provides the conditioning effect prior to the challenge of infection and induces defense against KB probably by maintaining a critical balance between proteases and protease inhibitors and/or coordinating induction of different families of new proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- KB:
-
Karnal bunt
- MeJA:
-
methyl jasmonate
- SA:
-
salicylic acid
References
Aujla S S, Grewal A S, Gill K S and Sharma I 1980 A screening technique for Karnal bunt disease of wheat;Crop Improv. 7 145–146
Bradford M M 1976 A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram qualities of proteins utilizing the principle of dye binding;Anal. Bochem. 72 248–254
Brady A V and Zimmerman D C 1989 Metabolism of Fatty acid hydroperoxides byChlorella pyrenoldosa;Plant Physiol. 90 125–132
Carr J P and Klessig D F 1989 The pathogenesis related proteins of plants; inGenetic engineering. Principles and methods (eds) R A Setlow and A Hofleander (New York: Plenum Press) vol. 11, pp 65–109
Chona B L, Munjal R L and Adlakha K L 1961 A method for screening wheat plants for resistance toNeovossia indica;Indian Phytopathol.14 99–101
Coego A, Ramirez V, Flors V, Mauch-Mani B and Vera P 2005 An Arabidopsis homeodomain transcription factor, OVEREXPRESSOR OF CATIONIC PEROXIDASE 3, mediates resistance to infection by necrotrophic pathogens;Plant Cell. 17 2123–2137
Delaney T P, Uknes S, Vernoij B, Friendrich L, Weymann K, Negrotto D, Gaffney T, Gut-Rella M, Kessmann H, Ward E and Ryals J A 1994 Central role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance;Science 266 1247–1250
Diaz J, ten Have A and van Kan J A 2002 The role of ethylene and wound signalling in resistance of tomato toBotrytis cinerea;Plant Physiol. 29 1341–1351
Doke N, Sanchez L M, Yoshioka H, Kawakita K, Mura Y and Ark H J 1998Molecular genetics of host-specific toxin in plant diseases (Neatherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers) pp 331–341
Duran R and Cromarty R 1977Tilletia indica a heterothallic wheat bunt fungus with multiple alleles controlling incompatibility;Phytopathology 76 812–815
Howe G A, Lightner J, Browse J and Ryan C A 1996 An octadecanoid pathway mutant (JL5) of tomato is compromised in signaling for defense against insect attack;Plant Cell 8 2067–2077
Knoester M L C, Vanloon J, Vander Heurel J F, Bol H U M and Linthorst 1998 Ethylene insensitive tobacco lacks no host resistance against Soil, borne fungi;Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 1933–1937
Kruger J, Thomas C M, Golstein C, Dixon C M, Smoker M, Tang S, Mulder L and Jones J D 2002 A tomato cysteine protease required for Cf-2 dependent disease resistance and suppression of autonecrosis;Science 296 744–747
Mani S, Yadav M K, Khan G T, Singh U S and Kumar A 2005 Enhanced proteolysis leads to pre-mature cell death under the influence of elicitor like mycelial components from Karnal bunt (Tilletia indica) pathogen in wheat callus cultures;Indian J. Exp. Biol. 43 671–678
Mur A J M, Kenton P, Atzorn R, Miersch O and Wasternack C 2006 The outcomes of concentration-specific interactions between salicylate and jasmonate signaling include synergy, antagonism, and oxidative stress leading to cell death;Plant Physiol. 140 249–262
Muzio M 1998 Signalling by proteolysis: death receptors induce apoptosis;Int. J. Clin.Lan. Res. 28 141–147
Numberger T, Brunner F, Kemmerling B and Piater L 2004 Innate immunity in plants and animals: striking similarities and obvious differences;Immunol. Rev. 198 256–266
Penninckx I A, Thomma B P, Buchala A, Metraux J P and Brockaert W F 1998 Concomitant activation of jasmonate and ethylene response pathways is required for induction of a plant defensin gene in Arabidopsis;Plant Cell. 10 2103–2113
Pieterse C M J, Van Wees S C M, Hoffland Evan Pelt J A and van Loon L C 1996 Systemic resistance in Arabidopsis induced by biocontrol. Bacteria is independent of salicylic acid accumulation and pathogenesis related gene expression;Plant Cell. 8 1225–1237.1998
Schaller F, Schallar A. and Stintz A 2005 Biosynthesis and metabolism of jasmonates;J. Plant Growth Regul. 23 179–199
Sethy N K, Pandey D, Singh U S and Kumar A 2003 Caspase-3 like protein inWheat-Tilletia indica dual Culture system as potential biomarker for host resistance to Karnal bunt;Indian J. Biotechnol. 2 596–602
Shao F, Merritt P M, Bao Z, Innes R W and Dixon J E 2002 A Yersinia effector and aPseudomonas avirulence protein define a family of cysteine proteases functioning in bacterial pathogenesis;Cell 109 575–588
Singh R A and Krishna A 1982 Susceptible stage for inoculation and effect of Karnal bunt on viability of wheat seed;Indian Phytopathol. 35 54–56
Solomon M, Belienghi B, Delledonne M, Menachem E and Levine A 1999 The involvement of cysteine proteases and protease inhibitors genes in the regulation of programmed cell death in plants;Plant Cell,11 431–443
Sticher L 1997 Systemic acquired resistance;Annu.Rev Phytopathol. 35 235–270
Thomma B P H T, Eggermont K, Penninokx I A M A, Mauch-Mani B, Cammue B P A and Broekaert W F 1998 Separate Jasmonate dependent and salicylic acid dependent defense suspense pathway in Arabidopsis are essential for resistance to distinct Microbial pathogens;Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 15107–15111
Tifarenko E, Rojo E, Leon J and Sanchez-Serrano J J 1997 Jasmonic acid dependent and independent signalling pathways control wound induced gene activation inArabidopsis thaliana;Plant Physiol. 115 817–826
Ueda J. and Kato J 1980 Isolation and identification of senescence promoting substance from worn woodAterneria absinthium;Plant Physiol. 66 246–249
Veronese P, Nakagami H, Bluhm B, AbuQamar S, Chen X, Salmeron J, Dietrich R A, Hirt H and Mengiste T 2006 The membrane anchored BOTRYTIS-INDUCED KINASE1 plays distinct roles inArabidopsis resistance to necrotrophic and biotrophic pathogens;Plant Cell. 18 276–273
Vick B A and Zimmerman D C 1989 Biosynthesis of JA by several plant spp.;Plant Physiol. 75 458–471
Wasternack C and Parthier B 1997 Jasmonate-signalled plant gene expression;Trends Plant Sci. 2 302–307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, M.K., Pandey, D., Purwar, S. et al. Influence of jasmonic acid as potential activator of induced resistance against Karnal bunt in developing spikes of wheat. J. Biosci. 31, 607–616 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708413
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708413