Abstract
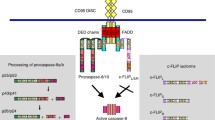
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a genetically regulated mechanism with a central role in both metazoan development and homeostasis. Death receptors (Fas, TNFR-2, DR3, and TRAIL receptors) induce apoptosis upon ligation to cognate ligands or ectopic expression. The assembly of a death-inducing signalling complex occurs in a hierarchical manner upon receptor activation. The death domain of the receptor binds to the corresponding domain of the adapter molecule FADD, which in turn recruits the zymogen form of the death protease FLICE (MACH/caspase-8). Upon approximation, FLICE “zymogens” attain a sufficient concentration to self-activate and to trigger the apoptotic pathway. For the first time, a transmembrane receptor directly engaging a protease at the signalling complex and subsequently triggering a proteolytic signalling cascade is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raff MC. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature 1992; 356: 397.
Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 1995; 267: 1445.
Vaux, DL, Haecker G, Strasser A. An evolutionary perspective on apoptosis. Cell 1994; 76: 777.
Chinnaiyan AM, Dixit VM. The cell-death machine. Curr Biol 1996; 6: 555
Baglioni C. Mechanisms of cytotoxicity, cytolysis, and growth stimulation by TNF. In: Beutler B, ed. Tumor necrosis factors. The molecules and their emerging role in medicine. New York: Raven; 1992: 425–438.
Itoh N, Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M, Mizushima S-I, Sameshima M, Hase A, Seto Y, Nagata S. The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell 1991; 66: 233.
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AMJ, Matzku S, Moller P, Falk W, Debatin K-M, Krammer PH. Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 1989; 245: 301.
Smith CA, Davis T, Anderson D, Solam L, Beckmann MP, Jerzy R, Dower SK, Cosman D, Goodwin RG. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science 1990; 248: 1019.
Tewari M, Dixit VM. Signalling through members of the tumor necrosis receptor family. In: Purton M, Heldin C, eds. Modular texts in molecular and cell biology. London: Chapman and Hall, 1995.
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Yu G-L, Lyons RH, Garg M, Duan R, Xing L, Gentz R, Ni J, Dixit VM. Signal transduction by DR3, a death domain-containing receptor related to TNFR-1 and CD95. Science 1996; 274: 990.
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Sholak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Raich C, Smith CA, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 1995; 3:673.
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the TNF cytokine family. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 12687.
Marsters SA, Pitti RM, Donhaue CJ, Ruppert S, Bauer RD, Ashkenazi A. Activation of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand is independent of FADD but blocked by CrmA. Curr Biol 1996; 6: 750.
Pan G, O’Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R, Ebner R, Ni J, Dixit VM. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science 1997; 276: 111.
Pan G, Ni J, Wei Y-F, Yu G-L, Gentz R, Dixit VM. An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science 1997; 277: 815.
Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM, Gurney A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Ramakrishnan L, Gray CL, Baker K, Wood WL, Goddard AD, Godowski P, Ashkenazi A. Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 1997; 277: 818.
Itoh N, Nagata S. A novel protein domain required for apoptosis. Mutational analysis of human Fas antigen. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 10932.
Tartaglia LA, Ayres TM, Wong GHW, Goeddel DV. A novel domain within the 55 kd TNF receptor signals cell death. Cell 1993; 74: 845.
Boldin MP Varfolomeev EE, Pancer Z, Mett IL, Camonis JH, Wallach D. A novel protein that interacts with the death domain of Fas/APO1 contains a sequence motif related to the death domain. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 7795.
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM. FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 1995; 81: 505.
Cleveland JL, Ihle JN. Contenders in FasL/TNF signaling. Cell 1995; 81: 479.
Hsu H, Xiong J, Goeddel DV. The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell 1995; 81:495.
Stanger BZ, Leder P, Lee TH, Kim E, Seed B. RIP: a novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell 1995; 81: 513.
Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Behrmann I, Germer M, Pawlita M, Krammer PH, Peter ME. Cytoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins (CAP) form a death-inducing signalling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J 1995; 14:5579.
Hsu H, Shu H-B, Pan M-P, Goeddel DV. TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor-1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 1996; 84: 299.
Hsu H, Huang J, Shu H-B, Baichwal V, Goeddel DV. TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity 1996; 4: 387.
Chinnaiyan AM, Tepper CG, Seldin MF, O’Rourke K, Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Krammer PH, Peter ME, Dixit VM. FADD/MORT1 is a common mediator of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 4961.
Chaudhary PM, Eby M, Jasmin A, Bookwalter A, Merray J, Hood L. Death receptor 5, a new member of the TNFR family, and DR4 induce FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate the NF-kB pathway. Immunity 1997; 7:821.
Schneider P, Thome M, Burns K, Bodmer J-L, Hofman K, Kataoka T, Holler N, Tschopp J. TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kB. Immunity 1997; 7: 831.
Hengartner MO. Programmed cell death in invertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1996; 6: 34.
Yuan J, Shaham S, Ledoux S, Ellis HM, Horvitz HR. TheC. elegans cell death geneced-3 encodes a protein similar to Mammalian interleukin-1β-converting enzyme. Cell 1993; 75:641.
Miura M, Zhu H, Rotello R, Hartwieg EA, Yuan J. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by IL-1β converting enzyme, a mammalian homolog of theC. elegans cell death geneced-3. Cell 1993; 75:653.
Williams MS, Henkart PA. Apoptotic cell death induced by intracellular proteolysis. J Immunol 1994; 50:4247.
Kuida K, Lippke JA, Ku G, Harding MW, Livingston DJ, Su M S-S, Flavell RA. Altered cytokine export and apoptosis in mice deficient in interleukin-1β converting enzyme. Science 1995; 267: 2000.
Li P, Allen H, Banerjee S, Franklin S, Herzog L, Johnston C, McDowell J, Paskind M, Rodman L, Salfeld J, Towne E, Tracey D, Wardwell S, Wei F-Y, Wong W, Kamen R, Seshadri T. Mice deficient in IL-1β-converting enzyme are defective in production of mature IL-1β and resistant to endotoxic shock. Cell 1995; 80: 401.
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC. Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 1994; 371: 346.
Tewari M, Quan LT, O’Rourke K, Desnoyers S, Zeng Z, Beidler DR, Poirier GG, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM. Yama/CPP32β, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell 1995; 81: 801.
Gu Y, Kuida K, Tsitsui H, Ku G, Hsiao K, Fleming MA, Hayashi N, Higashino K, Okamura H, Nakanishi K, Kurimoto M, Tanimoto T, Flavell RA, Sato V, Harding MW, Livingston DJ, Sums S. Activation of interferon-gamma inducing factor mediated by interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Science 1997; 275: 206.
Alnemri EA, Livingston DJ, Nicholson DW, Salvesen G, Thornberry NA, Wong WW, Yuan J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 1996; 87: 171.
Martin SJ, Green DR. Protease activation during apoptosis; death by a thousand cuts? Cell 1995; 82: 349.
Casciola-Rosen L, Anhalt GJ, Rosen A. DNA-dependent protein kinase is one of a subset of autoantigens specifically cleaved early during apoptosis. J Exp Med 1995; 182: 1625.
Takahashi A, Alnemri ES, Lazabnik YA, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G, Moir RD, Goldman RD, Poirier GG, Kaufmann SH, Earnshaw WC. Multiple interleukin-1β-converting enzyme-related proteases with distinct substrate recognition properties are active in apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93:8395.
Kothakota S, Azuma T, Reinhard C, Klippel A, Tang J, Chu K, McGarry TJ, Kirschiner MW, Koths K, Kwiatkowski DJ, Williams LT. Caspase-3-generated fragment of gelsolin: effector of morphological change in apoptosis. Science 1997; 278:294.
Caulin C, Salvesen GS, Oshima RG. Caspase cleavage of keratin 18 and reorganization of intermediate filaments during epithelial cell apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1997; 138: 1379.
Na S, Chuang TH, Cunningham A, Turi TG, Hanre JH, Bokoch GM, Danley DE. D4-GDI, a substrate of CPP32, is proteolyzed during Fas-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1996; 271:11209.
Enari M, Sakahira H, Hyokoyama H, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Nagata S. A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor, ICAD. Nature 1997; 391:43.
Sakahira H, Enari M, Nagata S. Cleavage of CAD inhibitor in CAD activation and DNA degradation during apoptosis. Nature 1997; 391:96.
Boldin MP, Goncharov TM, Goltsev YV, Wallach D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in FAS/Apo-1 and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell 1996; 85:803.
Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kirschkel FC, O’Rourke K, Shevchenko A, Scaffidi C, Bretz JD, Zhang M, Ni J, Gentz R, Mann M, Krammer PH, Peter ME, Dixit VM. Flice, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). Cell 1996; 85:817.
Srinivasula S, Ahmad M, Fernandes-Alnemri G, Litwack E, Alnemri E. Molecular ordering of the Fas-apoptotic pathway: the Fas/Apo-1 protease MCH5 is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that activates multiple CED-3/ICE-like cysteine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93:14486.
Los M, Van de Craen M, Penning LC, Schenk H, Westendorp M, Baeuerle PA, Droge W, Drammer PH, Fiers W, Schulze-Osthoff K. Requirement of an ICE/CED-3 protease for Fas/APO-1-mediated apoptosis. Nature 1995; 375:81.
Muzio M, Salvesen G, Dixit VM. FLICE induced apoptosis in a cell free system: cleavage of caspase zymogens. J Biol Chem 1997; 272:2552.
Muzio M, Stockwell BR, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM. An induced proximity model for FLICE (caspase-8) activation. J Biol Chem 1998; 273:2926.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muzio, M. Signalling by proteolysis: death receptors induce apoptosis. Int J Clin Lab Res 28, 141–147 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005990050035
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005990050035