Abstract
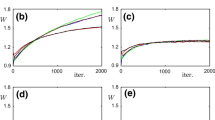
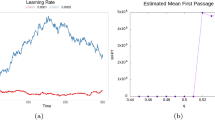
The Feynman machine is a neural network model in which the spike-timing-dependent firing process is described through a path integral formulation. In addition, the gradient descent in the free energy is proposed as an ideal learning rule of the model system. The unique formulation of the Feynman machine is useful for studying the substance of the firing and the learning process in a spiking neural network; however, the implementation of the Feynman machine is not a plan problem because of the difficulty in calculating the free energy. We here introduce how to perform the simulation of both the firing and the learning processes in the Feynman machine through the Monte Carlo or the numerical integral method. We demonstrate the adequacy of the methods by applying them to the firing and the learning processes in some neural systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Dayan and L. F. Abbott, Theoretical Neuroscience (MIT Press, London, 2001).
W. Gerstner, R. Kempter, J. L. van Hemmen and H. Wagner, Nature 383, 761 (1996).
H. Markram, J. Lübke, M. Frotscher and B. Sakamann, Science 275, 213 (1997).
G-Q. Bi and M-M. Poo, J. Neurosci. 18, 10464 (1998).
L. F. Abbott and S. B. Nelson, Nature Neurosci. 3, 1178 (2000).
S. Song, K. D. Miller and L. F. Abbott, Nat. Neurosci. 3, 919 (2000).
S. Song, S. and L. F. Abbott, Neuron 32, 339 (2001).
M. W. Cho, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 64, 1213 (2014).
W. Gerstner and W. M. Kistler, Spiking Neuron Models (Cambridge Universe Press, Cambridge, 2002).
M. W. Cho and M. Y. Choi, Europhys. Lett. 115, 38001 (2016).
M. W. Cho, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 71, 222 (2017).
M. W. Cho, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 74, 63 (2019).
M. W. Cho, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 73, 1385 (2018).
R. B. Stein, Biophys. J. 7, 37 (1967).
M. W. Cho, New Phys.: Sae Mulli 67, 862 (2017).
G. M. Torrie and J. P. Valeau, J. Comput. Phys. 23, 187 (1977).
D. P. Landau and K. Binder, A Guide to Monte Carlo Simulations in Statistical Physics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000).
E. J. Chichilnisky, Network Comp. Neural. 12, 199 (2000).
O. Schwartz, J. W. Pillow, N. C. Rust and E. P. Simoncelli, J. Vision 6, 484 (2006).
M.-H. Park and S. Kim, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 29, 9 (1996).
M. W. Cho and M. Y. Choi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 208102 (2007).
M. W. Cho, New Phys.: Sae Mulli 66, 786 (2016).
M. W. Cho and M. Y. Choi, Neural Networks 49, 51 (2014).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sungshin Women’s University Research Grant of 2017-1-21-007/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, M.W. Simulations in a Spiking Neural Network Model Based on the Free Energy Principle. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 75, 261–270 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.261
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.261