Abstract
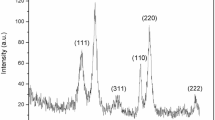
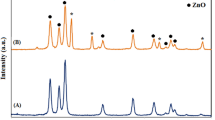
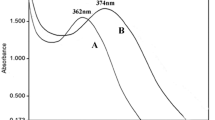
Objectives of the present study were to evaluate the antibacterial activity of the two types of inorganic magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2] and calcium carbonate [CaCO3] nanoparticles (NPs) on the growth of three Gram-negative bacteria, e.g., Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens and three Gram-positive bacteria, e.g., Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus bovis. The synthesis of these NPs was done by a microwave hydrothermal method. The structures and sizes of synthesized nanoparticles were investigated using X-ray diffractometer. Antimicrobial susceptibility of different NPs was determined at 20, 50 and 100 mg/mL by the agar-well diffusion method, growth reduction at the aqueous solution and time-kill assay. The antimicrobial effects across NPs and bacterial species were shown to be dose-dependent. The results of the different experiments indicated that smaller NP sizes have higher antibacterial effects. M29 [Mg(OH)2-29] nanoparticles followed by silver (Ag) and C1 (CaCO3-1) showed the highest influence on bacterial growth rates, while similar ability to kill bacteria across treatment time. In addition, Gram-negative bacteria were more affected in terms of the inhibition zone and reduction of growth rates after 24 h as well as in terms of the prolonged treatment of NPs up to 36 h due to the influence of different nanoparticles. We recommend to search the chance of further using M29 and C1 in medicine and industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ataee, R.A., Derakhshanpour, J., Mehrabi Tavana, A., and Eydi, A., Antibacterial effect of calcium carbonate nanoparticles on Agrobacterium tumefaciens,Iran. J. Mil. Med., 2011, vol. 13, pp. 65–70.
Creighton, J.A., Blatchford, C.G., and Albrecht, M.G., Plasma resonance enhancement of Raman scattering by pyridine adsorbed on silver or gold sol particles of size comparable to the excitation wavelength, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 2, 1979, vol. 75, pp. 790–798.
Di, D.R., He, Z.Z., Sun, Z.Q., and Liu, J., A new nano-cryosurgical modality for tumor treatment using biodegradable MgO nanoparticles, Nanomedicine, 2012, vol. 8, pp. 1233–1241.
Dizaj, S.M., Barzegar-Jalali, M., Zarrintan, M.H., Adibkia, K., and Lotfipour, F., Calcium carbonate nanoparticles; potential in bone and tooth disorders, Pharm. Sci., 2015, vol. 20, pp. 175–182.
Dong, C., Cairney, J., Sun, Q., Maddan, O.L., He, G., and Deng, Y., Investigation of Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles as an antibacterial agent, J. Nanopart. Res., 2010, vol. 12, pp. 2101–2109.
Dong, C., He, G., Li, H., Zhao, R., Han, Y., et al., Antifouling enhancement of poly (vinylidene fluoride) microfiltration membrane by adding Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles, J. Membr. Sci., 2012, vols. 387–388, pp. 40–47.
Dong, C., He, G., Zheng, W., Bian, T., Li, M., et al., Study on antibacterial mechanism of Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles, Mater. Lett., 2014, vol. 134, pp. 286–289.
Dong, C., Song, D., Cairney, J., Maddan, O.L., He, G., et al., Antibacterial study of Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles, Mater. Res. Bull., 2011, vol. 46, pp. 576–582.
Fang, M., Chen, J.H., Xu, X.L., Yang, P.H., and Hildebrand, H.F., Antibacterial activities of inorganic agents on six bacteria associated with oral infections by two susceptibility tests, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, 2006, vol. 27, pp. 513–517.
Feng, Q.L., Wu, J., Chen, G.Q., Cui, F.Z., Kim, T.N., and Kim, J.O., A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A, 2000, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 662–668.
Greulich, C., Kittler, S., Epple, M., Muhr, G., and Koller, M., Studies on the biocompatibility and the interaction of silver nanoparticles with human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), Langenbecks Arch. Surg., 2009, vol. 394, pp. 495–502.
Jeon, H.J., Yi, S.C., and Oh, S.G., Preparation and antibacterial effects of Ag-SiO2 thin films by sol–gel method, Biomaterials, 2003, vol. 24, pp. 4921–4928.
Jiao, C.M., Wang, Z.Z., Ye, Z., Hu, Y., and Fan, W.C., Flame retardation of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer using nano magnesium hydroxide and nano hydrotalcite, J. Fire Sci., 2006, vol. 24, pp. 47–64.
Jung, W.K., Koo, H.C., Kim, K.W., Sook, S., Kim, S.H., and Park, Y.H., Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli,Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 74, pp. 2171–2178.
Kim, J.S., Kuk, E., Yu, K.N., Kim, J.-H., Park, S.J., et al., Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles, Nanomed.: Nanotechnol., Biol. Med., 2007, vol. 3, pp. 95–101.
Kumar, A., Vemula, P.K., Ajayan, P.M., and John, G., Silver-nanoparticle-embedded antimicrobial paints based on vegetable oil, Nat. Mater., 2008, vol. 7, pp. 236–241.
Kvitek, L., Vanickova, M., Panacek, A., et al., Initial study on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles (NPs) against Paramecium caudatum, J. Phys. Chem., 2009, vol. 113, pp. 4296–4300.
Liu, X.F., Yang, D.Z., Guan, Y.L., Li, Z., and Yao, K.D., Antibacterial action of chitosan and carboxymethylated chitosan, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2001, vol. 79, pp. 1324–1335.
Makhluf, S., Dror, R., Nitzan, Y., Abramovich, Y., Jelinek, R., and Gedanken, A., Microwave-assisted synthesis of nanocrystalline MgO and its use as a bacteriocide, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2005, vol. 15, pp. 1708–1715.
Mendonca, A.F., Amoroso, T.L., and Knabel, S.J., Destruction of gram-negative food-borne pathogens by high pH involves disruption of the cytoplasmic membrane, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1994, vol. 60, pp. 4009–4014.
Nel, A., Xia, T., Madler, L., and Li, N., Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel, Science, 2006, vol. 311, pp. 622–627.
Pal, S., Tak, Y.K., and Song, J.M., Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticles? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli,Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 73, pp. 1712–1720.
Pan, X., Wang, Y., Chen, Z., Pan, D., Cheng, Y., et al., Investigation of antibacterial activity and related mechanism of a series of nano-Mg(OH)2, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, vol. 5, pp. 1137–1142.
Perez, C., Pauli, M., and Bazerque, P., An antibiotic assay by the agar well diffusion method, Acta Biol. Med. Exp., 1990, vol. 15, pp. 113–115.
Raghupati, R.K., Koodali, R.T., and Manna, A.C., Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2011, vol. 27, pp. 4020–4028.
Rai, M., Yadav, A., and Gade, A., Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials, Biotechnol. Adv., 2009, vol. 27, pp. 76–83.
Sawai, J., Kojima, H., Igarashi, H., Hashimoto, A., Shoji, S., et al., Antibacterial characteristics of magnesium oxide powder, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 187–194.
Stoimenov, P.K., Klinger, R.L., Marchin, G.L., and Klabunde, K.J., Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents, Langmuir, 2002, vol. 18, pp. 6679–6686.
Suh, J.S., DiLella, D.P., and Moskovits, M., Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of colloidal metal systems: a two-dimensional phase equilibrium in p-aminobenzoic acid adsorbed on silver, J. Phys. Chem., 1983, vol. 87, pp. 1540–1544.
Tang, Z.-X. and Lv, B.-F., MgO nanoparticles as antibacterial agent: Preparation and activity, Braz. J. Chem. Eng., 2014, vol. 31, pp. 591–601.
Wang, X.J., Qiao, X.L., Chen, J.G., Wang, H.S., and Ding, S.Y., Advancement in research on inorganic antibacterial material, J. Ceram., 2003, vol. 24, pp. 39–44.
Yoshinari, M., Oda, Y., Kato, T., and Okuda, K., Influence of surface modifications to titanium on antibacterial activity in vitro, Biomaterials, 2001, vol. 22, pp. 2043–2048.
Yu, J.C., Ho, W.K., Lin, J., Yip, H., and Wong, P.K., Photocatalytic activity, antibacterial effect, and photoinduced hydrophilicity of TiO2 films coated on a stainless steel substrate, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, vol. 37, pp. 2296–2301.
Zhang, L.L., Jiang, Y.H., Ding, Y.L., Povey, M., and York, D., Investigation into the antibacterial behavior of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO nanofluids), J. Nanopart. Res., 2007, vol. 9, pp. 479–489.
Zhao, Y.K., Sung, W.P., Tsai, T.T., and Wang, H.J., Application of nanoscale silver-doped titanium dioxide as photocatalyst for indoor airborne bacteria control: A feasibility study in medical nursing institutions, J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc., 2010, vol. 60, pp. 337–345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Sanaa G. Al Attas, Faten Al-Hazmi, Alwafi, R. et al. Bactericidal Efficacy of New Types of Magnesium Hydroxide and Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 34, 252–262 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416819040086
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416819040086