Abstract
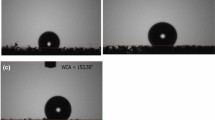
In the present work, we intend to focus on the synthesis, characterization, and application of a high-performing hydrophobic and oleophilic polyurethane foam functionalized with diatomaceous earth and fluorosilane, which are eco-friendly and low-cost materials for their potential use as absorbents for hydrophobic materials. The scanning electron microscopic studies and thermogravimetric analysis showed that the surface-modified polyurethane has a significant micro–nano-structure and surface functionalization, and the water contact angle measurement showed an increase in hydrophobicity due to the fluorosilane-functionalized diatomaceous earth particles anchoring onto the polyurethane foam. Also, the thermogravimetric analysis revealed an increased thermal stability due to the surface functionalization. The novel fluorosilane—diatomaceous earth—polyurethane foam exhibited a silver mirror-like effect when immersed into water due to inherent hydrophobicity and had an enhanced absorption of oil and organic solvents compared to the unmodified polyurethane. This research presents the successful synthesis of surface-modified polyurethane for its suitability for oil absorption capacity for cleaning the oil pollutants from water and for organic solvents clean-up purposes.
Graphical abstract
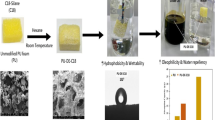
Overview of the research approach, which represents stepwise synthesis of the polyurethane (PU) foam surface modified with diatomaceous earth (DE) and fluorosilane (FS) to form low-density and high-absorbing surface-functionalized PU foam exhibiting enhanced oil absorption making this novel composite as a potential candidate for crude oil clean-up and recovery process.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.R. Joshi, N. Adhikari, An overview on common organic solvents and their toxicity. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 28(3), 1–18 (2019)
M. Adebajo, R. Frost, J. Kloprogge et al., Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: a review of synthesis and absorbing properties. J. Porous Mater. 10, 159–170 (2003)
A. Varela, G. Oliveira, F.G. Souza Jr., C.H.M. Rodrigues, M.A.S. Costa, New petroleum absorbers based on cardanolfurfuraldehyde magnetic nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 53(1), 44–51 (2013)
A.A. Elhakeem, W. Elshorbagy, R. Chebbi, Oil spill simulation and validation in the Arabian (Persian) Gulf with special reference to the UAE coast. Water Air Soil Pollut. 184(1–4), 243–254 (2007)
N. Issa, S. Vempatti, Oil spills in the Arabian Gulf: a case study and environmental review. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res. 8(2), 144 (2018)
H.A. Harahsheha, Oil Spill Detection and Monitoring of Abu Dhabi Coastal Zone Using KOMPSAT-5 SAR Imagery. Int Arch Photogrammetry Remote Sens Spatial Inf Sci 8, 1–7 (2016)
M.M. Shriadah, Impacts of an oil spill on the marine environment of the United Arab Emirates along the Gulf of Oman. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 36(11), 876–879 (1998)
M. Bourgeois, K. Guth, R.D. Harbison. Information Resources in Toxicology (Fifth Edition), Chapter 21 - Chemicals: solvents, Academic Press, 2020, 221–228, ISBN 9780128137246.
B. Doshi, M. Sillanpää, S. Kalliola, A review of bio-based materials for oil spill treatment. Water Res. 135, 262–277 (2018)
A. Cybulski, J. Trawczyński, Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol over platinum and ruthenium catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 47(1), 1–13 (2004)
A. Cambiella, E. Ortea, G. Rios, J.M. Benito, C. Pazos, J. Coca, Treatment of oil-in-water emulsions: performance of a sawdust bed filter. J. Hazard. Mater. 131(1–3), 195–199 (2006)
P.C. Brandão, T.C. Souza, C.A. Ferreira, C.E. Hori, L.L. Romanielo, Removal of petroleum hydrocarbons from aqueous solution using sugarcane bagasse as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 175(1–3), 1106–1112 (2010)
T. Viraraghavan, G.N. Mathavan, Treatment of oil-in-water emulsions using peat. Oil Chem. Pollut. 4(4), 261–280 (1988)
A.L. Ahmad, S. Sumathi, B.H. Hameed, Residual oil and suspended solid removal using natural adsorbents chitosan, bentonite and activated carbon: a comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 108(1–2), 179–185 (2005)
Y. Hozumi, T. Inaoka, T. Gomi, T. Goto, T. Uno, K. Rakutani. U.S. Patent No. 5,374,600. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (1994).
L. Han, J. Zhu, J. Kang, Y. Liang, Y. Sun, Catalytic wet air oxidation of high-strength organic coking wastewater. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 4(5), 624–627 (2009)
S. Keav, A. Martin, J. Barbier Jr., D. Duprez, Deactivation and reactivation of noble metal catalysts tested in the catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol. Catal. Today 151(1–2), 143–147 (2010)
M. Fingas, Oil Spill Science & Technology, 1st edn. (Elsevier, New Yok, 2011), pp. 303–337
A. Das, P. Mahanwar, A brief discussion on advances in polyurethane applications. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 3, 93–101 (2020)
E.K. Sam, J. Liu, X. Lv, Surface engineering materials of superhydrophobic sponges for oil/water separation: a review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 60(6), 2353–2364 (2021)
H. Li, L. Liu, F. Yang, Oleophilic polyurethane foams for oil spill cleanup. Procedia Environ. Sci. 18, 528–533 (2013)
N.V. Gama, A. Ferreira, A. Barros-Timmons, Polyurethane foams: past, present, and future. Materials 11(10), 1841 (2018)
K. Sklenickova, S. Abbrent, M. Halecky et al., Biodegradability and ecotoxicity of polyurethane foams: a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1, 1–46 (2020)
A. Kemona, M. Piotrowska, polyurethane recycling and disposal: methods and prospects. Polymers (Basel) 12(8), 1752 (2020)
S. Singh, R. Jelinek, Solar-mediated oil-spill cleanup by a carbon dot-polyurethane sponge. Carbon 160, 196–203 (2020)
O. Guselnikova, A. Barras, A. Addad, E. Sviridova, S. Szunerits, P. Postnikov, R. Boukherroub, Magnetic polyurethane sponge for efficient oil adsorption and separation of oil from oil-in-water emulsions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 240, 116627 (2020)
T. Zhang, L. Kong, Y. Dai, X. Yue, J. Rong, F. Qiu, J. Pan, Enhanced oils and organic solvents absorption by polyurethane foams composites modified with MnO2 nanowires. Chem. Eng. J. 309, 7–14 (2017)
S. Mallakpour, V. Behranvand, Modification of polyurethane sponge with waste compact disc-derived activated carbon and its application in organic solvents/oil sorption. N. J. Chem. 44, 15609–15616 (2020)
H. Li, L. Liu, F. Yang, Hydrophobic modification of polyurethane foam for oil spill cleanup. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 64(8), 1648–1653 (2012)
S. Qiu, Y. Li, G. Li, Z. Zhang, Y. Li, T. Wu, Robust superhydrophobic sepiolite-coated polyurethane sponge for highly efficient and recyclable oil absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 5560–5567 (2019)
H.J. Perera, H. Mortazavian, F.D. Blum, Surface properties of silane-treated diatomaceous earth coatings: effect of alkyl chain length. Langmuir 33(11), 2799–2809 (2017)
H.J. Perera, F.D. Blum. Alkyl chain modified diatomaceous earth superhydrophobic coatings. In 2018 Advances in science and engineering technology international conferences (ASET) (1–4). IEEE.
H.J. Perera, F.D. Blum. Competitive adsorption on diatomaceous earth particles. In 2019 Advances in science and engineering technology international conferences (ASET) (1–4). IEEE (2019, March).
H.J. Perera, B.K. Khatiwada, A. Paul, H. Mortazavian, F.D. Blum, Superhydrophobic surfaces with silane-treated diatomaceous earth/resin systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44072
F. Kucuk, S. Sismanoglu, Y. Kanbur, U. Tayfun, Optimization of mechanical, thermo-mechanical, melt-flow and thermal performance of TPU green composites by diatomaceous earth content. Clean. Eng. Technol. 4, 100251 (2021)
S. Ye, B. Wang, Y. Shi, B. Wang, Y. Zhang et al., Superhydrophobic and superelastic thermoplastic polyurethane/multiwalled carbon nanotubes porous monolith for durable oil/water separation. Compos. Commun. 21, 100378 (2020)
S. Pashaei, X.X.X. Siddaramaiah, A.A. Syed, Thermal degradation kinetics of polyurethane/organically modified montmorillonite clay nanocomposites by TGA. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 47(8), 777–783 (2010)
B.R. Sedai, S.H. Alavi, S.P. Harimkar, M. McCollum, J.F. Donoghue, F.D. Blum, Particle morphology dependent superhydrophobicity in treated diatomaceous earth/polystyrene coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 416, 947–956 (2017)
F. Kucuk, S. Sismanoglu, Y. Kanbur, U. Tayfun, Effect of silane-modification of diatomite on its composites with thermoplastic polyurethane. Mater. Chem. Phys. 256, 123683 (2020)
S. Davoudizadeh, M. Ghasemi, K. Khezrollah, S. Bahadorikhalil, Poly(styrene-co-butyl acrylate)/mesoporous diatomaceous earth mineral nanocomposites by in situ AGET ATRP. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 131, 2513–2521 (2018)
O. Oribayo, X. Feng, G.L. Rempel, Q. Pan, Synthesis of lignin-based polyurethane/graphene oxide foam and its application as an absorbent for oil spill clean-ups and recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 323, 191–202 (2017)
Z.C. Ng, R.A. Roslan, W.J. Lau, M. Gürsoy, M. Karaman, N. Jullok, A. Ismail, A green approach to modify surface properties of polyurethane foam for enhanced oil absorption. Polymers 12, 1883 (2020)
M. Farid, A. Purniawan, A. Rasyida, M. Ramadhani, S. Komariyah, Improvement of acoustical characteristics: wideband bamboo based polymer composite. IOP Conf Ser 223, 012021 (2017)
R. Dias, S. Rogéria, A. Eliane, O. Rodrigo, Porous biodegradable polyurethane nanocomposites: preparation, characterization, and biocompatibility tests. Mater. Res. 13(2), 211–218 (2010)
A. Azadeh, M.T. Khorasani, A. Behnamghader, B. Farsad, B. Shahin, Manufacturing of biodegradable polyurethane scaffolds based on polycaprolactone using a phase separation method: physical properties and in vitro assay. Int. J. Nanomed. 6, 2375–2384 (2011)
I. Hamadneh, A. Alatawi, R. Zalloum, R. Albuqain, S. Alsotari, F.I. Khalili, A.H. Al-Dujaili, Comparison of Jordanian and standard diatomaceous earth as an adsorbent for removal of Sm (III) and Nd (III) from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 26, 20969–20980 (2019)
B.R. Sedai, B.K. Khatiwada, H. Mortazavian, F.D. Blum, Development of superhydrophobicity in fluorosilane-treated diatomaceous earth polymer coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 386, 178–186 (2016)
A.R. Arianit, B. Pavlovski, P. Makreski, New optimized method for low-temperature hydrothermal production of porous ceramics using diatomaceous earth. Ceram. Int. 43(15), 12572–12578 (2017)
M. Judith, S. Silvana, O. Hugo, K. László, H. László, F. Éva, M. János, FTIR and FT-Raman spectroscopic study on polymer based high pressure digestion vessels. Croat. Chem. Acta 79, 497–501 (2006)
S. Pazokifard, S.M. Mirabedini, M. Esfandeh, S. Farrokhpay, Fluoroalkylsilane treatment of TiO2 nanoparticles in difference pH values: Characterization and mechanism. Adv. Powder Technol. 23(4), 428–436 (2012)
P.S. Brown, B. Bhushan, Bioinspired, roughness-induced, water and oil superphilic and super-phobic coatings prepared by adaptable layer-by-layer technique. Sci. Rep. 5, 14030 (2015)
V.T. Ambegoda, S.M. Egodage, F.D. Blum, M. Maddumaarachchi, Enhancement of hydrophobicity of natural rubber latex films using diatomaceous earth. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 138, 50047 (2021)
K.Y. Law, Definitions for hydrophilicity, hydrophobicity and superhydrophobicity: getting the basics right. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5(4), 686–688 (2014)
Y. Zhu, D. Wang, L. Jiang, J. Jin, Recent progress in developing advanced membranes for emulsified oil/water separation. Asia Mater 6, e101 (2014)
R.N. Wenzel, Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. In. Eng. Chem. 28, 988–994 (1936)
A. Martínez-Gómez, L. Silvia, G. Fernández, M. Teresa, F. Raquel, T. Pilar, G. Nuria, Long-term underwater hydrophobicity: exploring topographic and chemical requirements. ACS Omega 2(12), 8928–8939 (2017)
M. Lei, S. Yang, B. Hao, P.C. Ma, Ternary silicone sponge with enhanced mechanical properties for oil-water separation. Polym. Chem. 6, 5869 (2015)
T. Iline-Vul, S. Bretler, S. Cohen, I. Perelshtein, N. Perkas, A. Gedanken, S. Margel, Engineering of superhydrophobic silica microparticles and thin coatings on polymeric films by ultrasound irradiation. Mater Today Chem 21, 100520 (2021)
X. Li, J. Yang, J. Wang et al., A stable super-amphiphilic surface created from superhydrophobic silica/epoxy coating by low-temperature plasma-treatment. Surf. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/02670844.2021.1888214
X. Gong, S. He, Highly durable superhydrophobic polydimethyl siloxane/ silica nanocomposite surfaces with food self-cleaning ability. ACS Omega 5, 4100–4108 (2020)
S.J. Farrokhi, H. Pakzad, M. Fakhri, A. Moosavi, Superhydrophobic home-made polyurethane sponges for versatile and cost-effective oil and water separation. Sep Pnurif Technol 276, 119240 (2021)
Z. Guo, B. Long, S. Gao, J. Luo, L. Wang, X. Huang, D. Wang, H. Xue, J. Gao, Carbon nanofiber based superhydrophobic foam composite for high performance oil/water separation. J Hazard Mater. 402, 123838 (2021)
N. Xiao, Y. Zhou, Z. Ling, J. Qiu, Synthesis of a carbon nanofiber/carbon foam composite from coal liquefaction residue for the separation of oil and water. Carbon 59, 530–536 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Abu Dhabi Department of Education and Knowledge (ADEK) and the authors would like to acknowledge ADEK for their financial support and thank Higher Colleges of Technology, Abu Dhabi Women’s Campus and Khalifa University, for extending their cooperation and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perera, H.J., Goyal, A., Banu, H. et al. Low-cost fluorinated diatomaceous earth polyurethane foam for the absorption of oil. MRS Energy & Sustainability 9, 94–104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43581-022-00022-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43581-022-00022-2