Abstract
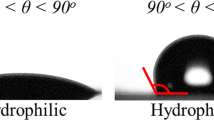
Superhydrophobic surfaces are widely used in various fields because of their excellent properties and are currently an important research hotspot. Here, we developed a simple method and successfully prepared a functional surface with superhydrophobic properties. The relationship between laser process parameters on the surface morphology and wettability properties of stainless steel mesh was systematically investigated, and the surface corrosion resistance, mechanical stability, and self-cleaning properties of superhydrophobic stainless steel mesh were explored. The results show that under laser ablation with optimal process parameters, the surface of the superhydrophobic SSM has a large number of laser-induced periodic micro-nano corrugated structures, which store a large amount of air in the structure to form a layer of air cushion, reducing the contact between the surface and the corrosion solution, improving the corrosion resistance of the SSM, and also showing excellent performance characteristics in terms of mechanical stability, time-sensitive, and self-cleaning performance.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
X. Zheng, Q. Zhang, J. Wang, Fabrication of super-hydrophobic magnetic Fe/SiO2 surface with tunable adhesion inspired by lotus leaf[J]. Micro & Nano Lett. 7(6), 561–563 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2012.0335
G. Xuefeng, J. Lei, Water-repellent legs of water striders. Nature 432, 36 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/432036a
S. Pan, M. Chen, L. Wu, Smart superhydrophobic surface with restorable microstructure and self-healable surface chemistry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(4), 5157–5165 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b22693
H. Ye, L. Zhu, W. Li et al., Constructing fluorine-free and cost-effective superhydrophobic surface with normal-alcohol-modified hydrophobic SiO2 nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(1), 858–867 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12820
J. Li, D. Li, Y. Yang et al., A prewetting induced underwater superoleophobic or underoil (super) hydrophobic waste potato residue-coated mesh for selective efficient oil/water separation [J]. Green Chem. 18(2), 541–549 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5gc01818h
Y. Li, B. Li, X. Zhao et al., Totally waterborne, nonfluorinated, mechanically robust, and self-healing superhydrophobic coatings for actual anti-icing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(45), 39391–39399 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b15061
T. Yu, F. Halouane, D. Mathias et al., Preparation of magnetic, superhydrophobic / superoleophilic polyurethane sponge: separation of oil/water mixture and demulsification. Chem. Eng. J. 384, 123339–123347 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123339
H.R. Gao, R.Y. Wang, H.J. Sun et al., Preparations and characterizations of super-hydrophobic surfaces on Al alloys and their anti-icing properties. Materiali in tehnologije 52, 299–306 (2018). https://doi.org/10.17222/mit.2017.125
Y. Zhu, A. Feng, C. Zhang et al., Research on preparation and water collection characteristics of bionic pattern surface for multi-order combination-multi-segment transport. Opt. Laser Technol. 156, 108482 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.108482
X.N. Zhang, L. Gan, B. Sun et al., Bio-inspired manufacturing of superwetting surfaces for fog collection and anti-icing applications. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 65(9), 1975–1994 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-022-2101-9
V.S. Saji, Superhydrophobic surfaces and coatings by electrochemical methods–a review. J. Adhesion Sci. Technol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2022.2031462
Q. Liu, Y. Tang, W. Luo et al., Fabrication of superhydrophilic surface on copper substrate by electrochemical deposition and sintering process. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 23(7), 1200–1205 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.11.034
Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, J. Yang et al., Fabrication of superhydrophobic surface on stainless steel by two-step chemical etching. Chem. Phys. Lett. 797, 139567 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.11.034
S. Ge-Zhang, H. Yang, H. Ni et al., Biomimetic superhydrophobic metal/nonmetal surface manufactured by etching methods: a mini review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.958095
Z. Buczko, K. Olkowicz, J. Krasucki et al., Superhydrophobic properties of aluminium produced by surface abrasive blasting, anodic oxidation and fatty acid impregnation. Trans IMF 99(2), 73–79 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/00202967.2021.1877473
S.F. Ou, K.K. Wang, Y.C. Hsu, Superhydrophobic NiTi shape memory alloy surfaces fabricated by anodization and surface mechanical attrition treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 425, 594–602 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.038
Y. Li, X. Zhu, X. Zhou et al., A facile way to fabricate a superamphiphobic surface. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process 115(3), 765–770 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8438-8
L.S. Solaree, A. Monshi, H. Ghayour, A new approach for the fabrication of hydrophobic silica coatings on glass using sol–gel Method. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org., Nano-Met. Chem. 45(12), 1769–1772 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2013.872132
W. Li, X. Tan, J. Zhu et al., Broadband antireflective and superhydrophobic coatings for solar cells[J]. Mater. Today Energy 12, 348–355 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2019.03.006
Y. Song, C. Wang, X. Dong et al., Controllable superhydrophobic aluminum surfaces with tunable adhesion fabricated by femtosecond laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 102, 25–31 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.12.024
X. Bai, F. Chen, Recent advances in femtosecond laser-induced superhydrophobic surfaces. Acta. Optica Sinica 41(1), 0114003 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3788/AOS202141.0114003
X. Li, Y. Jiang, Z. Zhang et al., Facile and environmentally-friendly fabrication of underwater superaerophobic and superaerophilic metallic surfaces through laser ablation and heat treatment. Coll. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 621, 126547 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126547
J. Huo, Q. Yang, J. Yong et al., Underwater Superaerophobicity/Superaerophilicity and unidirectional bubble passage based on the femtosecond laser-structured stainless steel mesh. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 7(14), 1902128 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201902128
J. Wang, J. Xu, Z. Lian et al., Facile and green fabrication of robust microstructured stainless steel mesh for efficient oil/water separation via waterjet-assisted laser ablation. Coll. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 643, 128703 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128703
J. Wang, J. Xu, G. Chen et al., Reversible wettability between underwater superoleophobicity and superhydrophobicity of stainless steel mesh for efficient oil–water separation[J]. ACS Omega 6(1), 77–84 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c03369
Y. Ge, J. Cheng, X. Wang et al., Formation and properties of superhydrophobic Al coatings on steel. ACS Omega 6(28), 18383–18394 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c02299
A. Gong, Y. Zheng, Z. Yang et al., Spray fabrication of superhydrophobic coating on aluminum alloy for corrosion mitigation. Mater. Today Commun. 26, 101828 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101828
J. Zheng, G. Qu, B. Yang et al., Facile preparation of robust superhydrophobic ceramic surfaces with mechanical stability, durability, and self-cleaning function. Appl. Surf. Sci. 576, 151875 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151875
W. Li, Y. Zhan, S. Yu, Applications of superhydrophobic coatings in anti-icing: theory, mechanisms, impact factors, challenges and perspectives. Prog. Org. Coat. 152, 106117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.106117
M. Yu, X. Li, X. Tan et al., Fluorine-free preparation of superhydrophobic coating with anti-icing property, mechanical durability and self-cleaning effect. Soft Matter (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2sm01265k
S. Li, M. Cai, Y. Liu et al., S-Scheme photocatalyst TaON/Bi2WO6 nanofibers with oxygen vacancies for efficient abatement of antibiotics and Cr (VI): intermediate eco-toxicity analysis and mechanistic insights. Chin. J. Catal. 43(10), 2652–2664 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(22)64106-8
M. Cai, Y. Liu, K. Dong et al., A novel S-scheme heterojunction of Cd0. 5Zn0. 5S/BiOCl with oxygen defects for antibiotic norfloxacin photodegradation: performance, mechanism, and intermediates toxicity evaluation. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 629, 276–286 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.136
C. Wang, R. Yan, M. Cai et al., A novel organic/inorganic S-scheme heterostructure of TCPP/Bi12O17Cl2 for boosting photodegradation of tetracycline hydrochloride: kinetic, degradation mechanism, and toxic assessment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 610, 155346 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155346
M. Cai, Y. Liu, C. Wang et al., Novel Cd0. 5Zn0. 5S/Bi2MoO6 S-scheme heterojunction for boosting the photodegradation of antibiotic enrofloxacin: degradation pathway, mechanism and toxicity assessment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 304, 122401 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122401
S. Li, C. Wang, Y. Liu et al., S-scheme MIL-101 (Fe) octahedrons modified Bi2WO6 microspheres for photocatalytic decontamination of Cr (VI) and tetracycline hydrochloride: synergistic insights, reaction pathways, and toxicity analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 455, 140943 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140943
S. Li, M. Cai, C. Wang et al., Ta3N5/CdS core-shell S-scheme heterojunction nanofibers for efficient photocatalytic removal of antibiotic tetracycline and Cr (VI): performance and mechanism insights. Adv. Fiber Mater. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00253-5
S. Li, M. Cai, Y. Liu et al., Constructing Cd0. 5Zn0. 5S/Bi2WO6 S-scheme heterojunction for boosted photocatalytic antibiotic oxidation and Cr (VI) reduction. Adv. Powder Mater. 2(1), 100073 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmate.2022.100073
M. Cai, C. Wang, Y. Liu et al., Boosted photocatalytic antibiotic degradation performance of Cd0. 5Zn0. 5S/carbon dots/Bi2WO6 S-scheme heterojunction with carbon dots as the electron bridge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 300, 121892 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121892
Y. Wu, X. Tan, Y. Wang et al., Nonfluorinated, transparent, and antireflective hydrophobic coating with self-cleaning function. Coll. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 634, 127919 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127919
R. Wu, S. Wu, H. Jiang et al., Study on corrosion resistance of superhydrophobic surface on aluminum alloy. Mater. Exp. 11(12), 2004–2009 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2021.2118
C. Hu, X. Xie, K. Ren, A facile method to prepare stearic acid-TiO2/zinc composite coating with multipronged robustness, self-cleaning property, and corrosion resistance. J. Alloys Compd. 882, 160636 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160636
J. Zhang, H. Xu, J. Guo et al., A superhydrophobic self-cleaning and anti-Icing aluminum sheet fabricated by alkaline solution. Adv. Eng. Mater. 23(10), 2100347 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202100347
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau Major Science and Technology Special Project Grant NO. ZG2019002, the Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau Major Science and Technology Special Project Grant NO. ZG2020029, and the Wenzhou University Rui’an Graduate College of Science and Technology Project No YC202212024.
Funding
The Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau Major Science and Technology Special Project, NO. ZG2019002, Aixin Feng, the Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau Major Science and Technology Special Project, NO. ZG2020029, Xiaoming Pan, and the Wenzhou University Rui’an Graduate College of Science and Technology Project, YC202212024, yunhu zhu
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ contributed to writing of the original draft, conceptualization, methodology, visualization, and investigation. YZ contributed to software and data curation. XP contributed to software and data curation. JY contributed to software and data curation. PZ contributed to software and data curation. AF contributed to supervision and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Feng, A., Pan, X. et al. Research on the preparation and property of superhydrophobic surface with micro-nano ripple structure. Journal of Materials Research 38, 3136–3150 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01038-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01038-1