Abstract
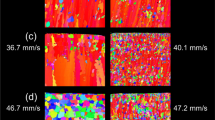
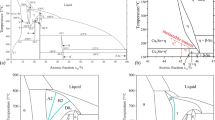
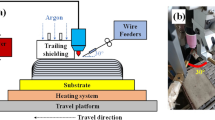
Elevated temperature co-sputtering of immiscible elements results in a variety of self-organized morphologies due to phase separation. Cu–Ta is used as a model system to understand the evolution of phase-separated microstructural morphologies by co-sputtering thin films with nominal 50–50 at.% composition at four temperatures: 25, 400, 600, and 800 °C. Scanning/transmission electron microscopy of the film cross sections showed the microstructure morphology varied from nanocrystalline Cu–Ta at 25 °C to a wavy ribbon-like structure at 400 °C, to Cu-rich agglomerates surrounded by Ta-rich veins at 600 and 800 °C. In the agglomerate-vein morphology, microstructural features were present on two length scales, from a few nanometers to a few tens of nanometers, thus making the structures hierarchical. On the nanoscale, the Cu-rich agglomerates contained Ta precipitates, whereas the Ta-rich veins had embedded Cu nanocrystals. The various microstructures can be attributed to the highly disparate constituent element interdiffusion at the deposition temperatures with the Cu having orders of magnitude higher mobility than Ta at the deposition temperatures. This study of processing–microstructure relationship will be useful in guiding the design of hierarchical multiphase microstructures in binary or multicomponent thin films with tailored mechanical properties.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Avallone, T. Nizolek, T. Pollock, and M. Begley: A model for high temperature deformation of nanolaminate Cu–Nb composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A761, 138016 (2019).
K. Wu, J. Zhang, J. Li, Y. Wang, G. Liu, and J. Sun: Length-scale-dependent cracking and buckling behaviors of nanostructured Cu/ Cr multilayer films on compliant substrates. Acta Mater.100, 344–358 (2015).
Y. Cui, B. Derby, N. Li, and A. Misra: Design of bicontinuous metallic nanocomposites for high-strength and plasticity. Mater. Des.166, 107602 (2019).
F.T.N. Vullers and R. Spolenak: From solid solutions to fully phase separated interpenetrating networks in sputter deposited “immiscible” W–Cu thin films. Acta Mater.99, 213–227 (2015).
Y. Cui, N. Li, and A. Misra: An overview of interface-dominated deformation mechanisms in metallic nanocomposites elucidates using in situ straining in a TEM. J. Mater. Res.34, 1470–1478 (2019).
N. Mara and I. Beyerlin: Interface-dominant multilayers fabricated by severe plastic deformation: Stability under extreme conditions. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci.19, 265–276 (2015).
A. Misra, M. Demkowicz, X. Zhang, and R. Hoagland: The radiation damage tolerance of ultra-high strength nanolayered composites. JOM59, 62–65 (2007).
Y.C. Wang, A. Misra, and R. Hoagland: Fatigue properties of nanoscale Cu/Nb multilayers. Scripta Mater.54, 1593–1598 (2006).
I. Beyerlin and J. Wang: Interface-drive mechanisms in cubic/noncubic nanolaminates at different scales. MRS Bull.44, 31–39 (2019).
J. Thornton: Influence of apparatus geometry and deposition conditions on the structure and topography of thick sputtered coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Tech.11, 666–670 (1974).
B. Derby, Y. Cui, J.K. Baldwin, and A. Misra: Effects of substrate temperature and deposition rate on the phase separated morphology of co-sputtered Cu–Mo thin films. Thin Solid Films647, 50–56 (2018).
B. Derby, Y. Cui, J.K. Baldwin, R. Arroyave, M. Demkowicz, and A. Misra: Processing of novel psuedomorphic Cu–Mo hierarchies in thin films. Mater. Res. Lett.7, 1–11 (2019).
Y. Lu, C. Wang, Y. Gao, R. Shi, X. Liu, and Y. Wang: Microstructure map for self-organized phase separation during film deposition. Phys. Rev. Lett.109, 086101 (2012).
A. Kumar, B. Derby, R. Raghavan, A. Misra, and M. Demkowicz: 3-D phase-field simulations of self-organized composite morphologies in physical vapor deposited phase-separating binary alloys. J. Appl. Phys126, 075306 (2019).
K. Holloway, P. Fryer, C. Cabral, J.M.E. Harper, P.J. Bailer, and K.H. Kelleher: Tantalum as a diffusion barrier between copper and silicon: Failure mechanism and effect of nitrogen additions. J. Appl. Phys71, 5433 (1992).
A. Jain, S.P. Ong, G. Hautier, W. Chen, W.D. Richards, S. Dacek, S. Cholia, D. Gunter, D. Skinner, G. Ceder, and K.A. Persson: The materials project: A materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation. APL Mater.1, 011002 (2013).
M. Buehler and A. Misra: Mechanical behavior of nanocomposites. MRS Bull.44, 19–24 (2019).
C.M. Muller, S. Parviainen, F. Djurabekova, K. Nordlund, and R. Spolenak The as-deposited structure of co-sputtered Cu–Ta alloys, studied by X-ray diffraction and molecular dynamics simulations. Acta Mater.82, 51–63 (2015).
C.M. Muller, A. Sologubenko, S. Gerstl, and R. Spolenak: On spinodal decomposition in Cu-34 at.% Ta thin films—An atom probe tomography and transmission electron microscopy study. Acta Mater.89, 181–192 (2015).
K.W. Kwon, C. Ryu, R. Sinclair, and S.S. Wong: Evidence of heteroepitaxial growth of copper on beta-tantalum. Appl. Phys. Lett.71, 3069 (1997).
H.J. Lee, K.W. Kwon, C. Ryu, and R. Sinclair: Thermal stability of a Cu/Ta multilayer: An intriguing interfacial reaction. Acta Mater.47, 3965–3975 (1999).
M. Jackson and C. Li: Stress relaxation and hillock growth in thin films. Acta Metall.30, 1993–2000 (1982).
A Segmuller and M Murakami: X-ray diffraction analysis of strains and stresses in thin films. Treatise Mater. Sci. Technol27, 143–200 (1988).
A. Jiang, T.A. Tyson, L. Axe, L. Gladczuk, M. Sosnowski, and P. Cote: The structure and stability of β-Ta thin films. Thin Solid Films479, 166–173 (2005).
J.J. Colin, G. Abadias, A. Michel, and C. Jaouen: On the origin of the metastable β-Ta phase stabilization in sputtered thin films. Acta Mater.126, 481–93 (2017).
M. Read and C. Altaian: A new structure in tantalum thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett.7, 51 (1965).
A. Jiang, A. Yohannan, N. Nnolim, T.A. Tyson, L. Axe, S. Lee, and P. Cote: Investigation of the structure of β-Ta. Thin Solid Films437, 116–122 (2003).
S.L. Lee, M. Doxbeck, J. Mueller, M. Cipollo, and P. Cote: Texture, structure, and phase transformation in sputter beta tantalum coating. Surf. Coating. Technol.177–178, 44–51 (2004).
L.A. Clevenger, A. Mutscheller, J.M.E. Harper, C. Cabral, and K. Barmak: The relationship between deposition conditions, the beta to alpha phase transformation, and stress relaxation in tantalum thin films. J. Appl. Phys.72, 4918 (1992).
J. Wang and X. Zhang: Twinning effects on strength and plasticity of metallic materials. MRS Bull.41, 274–281 (2016).
A. Puthucode, A. Devaraj, S. Nag, S. Bose, P. Ayyub, M.J. Kaufman, and R. Banerjee: De-vitrification of nanoscale phase-separated amorphous thin films in the immiscible copperniobium system. Phil. Mag.94, 1622–1641 (2014).
M. Rajagopalan, K. Darling, S. Turnage, R.K. Koju, B. Hornbuckle, Y. Mishin, and K.N. Solanki: Microstructural evolution in a nanocrystalline Cu–Ta alloy: A combined in situ TEM and atomistic study. Mater. Des.113, 178–185 (2017).
M. Powers, B. Derby, E. Raeker, N. Champion, and A. Misra: Hillock formation in co-deposited thin films of immiscible metal alloy systems. Thin Solid Films693, 137692 (2020).
M. Nastasi, F.W. Saris, L.S. Hung, and J.W. Mayer: Stability of amorphous Cu/Ta and Cu/W alloys. J. Appl. Phys.58, 3052–3058 (1985).
J. Xue, Y. Li, L. Hao, L. Gao, D. Qian, Z. Song, and J. Chen: Investigation on the interfacial stability of multilayered Cu–W films at elevated deposition temperatures during co-sputtering. Vacuum166, 162–169 (2019).
H.P. Bonzel: Surface diffusion tables. In Diffusion in Solid Metals and Alloys, 1st ed., H. Mehrer, ed. (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, 1990); pp. 728–744.
C.D. Adams, M. Atzmon, Y.T. Cheng, and D.J. Srolovitz: Phase separation during co-deposition of Al-Ge thin films. J. Mater. Res.7, 653–666 (1991).
K. Fukutani, K. Tanji, T. Saito, and T. Den: Fabrication of well-aligned Al nanowire array embedded in Si matrix using limited spinodal decomposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.47, 1140–1146 (2008).
M. Ohring:Materials Science of Thin Films: Deposition and Structure, 2nd ed. (Academic Press, San Diego, 2002); p. 495.
J. Stewart and R. Dingreville: Microstructure morphology and concentration modulation of nanocomposite thin-films during simulation physical vapor deposition. Acta Mater.188, 181–191 (2020).
R. Banerjee, A. Puthucode, S. Bose, and P. Ayyub: Nanoscale phase separation in amorphous immiscible copper-niobium alloy thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett.90, 021904 (2007).
Acknowledgements
This research was performed under the Center for Research Excellence on Dynamically Deformed Solids (CREDDS) sponsored by the Department of Energy—National Nuclear Security Administration (DOE-NNSA), Stewardship Science Academic Program under the Award No. DE-NA0003857.
Microscopy was performed at the Michigan Center for Materials Characterization at the University of Michigan (JEOL 2010F AEM and JEOL 2100F STEM). Some of the high-resolution S/TEM characterization (JEOL 200 C-ARM) was performed at Northwestern University under the Northwestern University Atomic and Nanoscale Characterization Experimental Center in the Electron Probe Instrumentation Center assisted by Dr. Xiaobing Hu and Dr. Kun He.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Powers, M., Derby, B., Shaw, A. et al. Microstructural characterization of phase-separated co-deposited Cu–Ta immiscible alloy thin films. Journal of Materials Research 35, 1531–1542 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.100
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.100