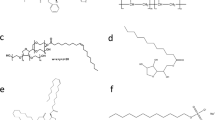
Abstract
Solvents, accounting the majority of the organogel system, have a tremendous impact on the characteristics of gels. To date, there is a large variety of organogel systems; relatively few have been investigated in the field of structure-solvent correlation. Here, a series of solvent parameters were applied to explore the role of solvent effect on network forming and gel property, intending to build the connection between the precise solvent parameter and gel property. Among the solvent parameters, Kamlet–Taft Parameters and Hansen solubility parameters can distinguish specific types of intermolecular interactions, which could correlate solvent parameter with the gel property. From an analysis of the morphologies obtained from POM and SEM, the gelator structure has an impact on its self-assembly. For possible conformations, the gelators were investigated through XRD. The investigation of solvent-property relationship will provide a theoretical basis for controllable drug delivery implants.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loh XJ, Nam Nguyen VP, Kuo N, Li J. Encapsulation of basic fibroblast growth factor in thermogelling copolymers preserves its bioactivity. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(7):2246.
Kharkar PM, Kiick KL, Kloxin AM. Designing degradable hydrogels for orthogonal control of cell microenvironments. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42(17):7335–72.
Han L, Xu J, Lu X, Gan D, Wang Z, Wang K, et al. Biohybrid methacrylated gelatin/polyacrylamide hydrogels for cartilage repair. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(4):731–41.
Deng J, Cheng C, Teng Y, Nie C, Zhao C. Mussel-inspired post-heparinization of a stretchable hollow hydrogel tube and its potential application as an artificial blood vessel. Polym Chem. 2017;8(14):2266–75.
Liu Y, Yang F, Feng L, Yang L, Chen L, Wei G, et al. In vivo retention of poloxamer-based in situ hydrogels for vaginal application in mouse and rat models. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2017;7(4):502–9.
Vintiloiu A, Leroux JC. Organogels and their use in drug delivery—a review. J Control Release. 2008;125(3):179–92.
Sangeetha NM, Maitra U. Supramolecular gels: functions and uses. Chem Soc Rev. 2005;34(10):821–36.
Ye F, Chen S, Tang G, Ma M, Wang X. Self-assembled nanofibrillar gel network toughened PMMA nanocomposite by in situ thermal polymerization of MMA gel. Colloid Surface A. 2015;480:1–10.
Liow SS, Karim AA, Loh XJ. Biodegradable thermogelling polymers for biomedical applications. MRS Bull. 2016;41(07):557–66.
Lupi FR, Greco V, Baldino N, de Cindio B, Fischer P, Gabriele D. The effects of intermolecular interactions on the physical properties of organogels in edible oils. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016;483:154–64.
Huang C-B, Chen L-J, Huang J, Xu L. A novel pyrene-containing fluorescent organogel derived from a quinoline-based fluorescent porbe: synthesis, sensing properties, and its aggregation behavior. RSC Adv. 2014;4(37):19538.
Pirner D, Dulle M, Mauer MEJ, Förster S. Reinforcement of nanostructured organogels by hydrogen bonds. RSC Adv. 2016;6(48):42730–8.
Simsolo EE, Eroglu I, Tanriverdi ST, Ozer O. Formulation and evaluation of organogels containing hyaluronan microparticles for topical delivery of caffeine. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018;19(3):1367–76.
Uzan S, Barış D, Çolak M, Aydın H, Hoşgören H. Organogels as novel carriers for dermal and topical drug delivery vehicles. Tetrahedron. 2016;72(47):7517–25.
Mandal D, Mandal SK, Ghosh M, Das PK. Phenylboronic acid appended pyrene-based low-molecular-weight injectable hydrogel: glucose-stimulated insulin release. Chem Eur J. 2015;21(34):12042–52.
Zhao Y, Zhou L, Liu J, Chen Z, Yang L, Shi H. Preparation and investigation of a novel levobupivacaine in situ implant gel for prolonged local anesthetics. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017;45(3):404–8.
Li Z, Cao J, Li H, Liu H, Han F, Liu Z, et al. Self-assembled drug delivery system based on low-molecular-weight bis-amide organogelator: synthesis, properties and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(8):3168–78.
Hu B, Wang W, Wang Y, Yang Y, Xu L, Li S. Degradation of glutamate-based organogels for biodegradable implants: in vitro study and in vivo observation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;82:80–90.
Long D, Gong T, Zhang Z, Ding R, Fu Y. Preparation and evaluation of a phospholipid-based injectable gel for the long term delivery of leuprolide acetaterrh. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016;6(4):329–35.
Martin B, Brouillet F, Franceschi S, Perez E. Evaluation of organogel nanoparticles as drug delivery system for lipophilic compounds. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017;18(4):1261–9.
Gravelle AJ, Davidovich-Pinhas M, Zetzl AK, Barbut S, Marangoni AG. Influence of solvent quality on the mechanical strength of ethylcellulose oleogels. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;135:169–79.
Liu C, Corradini M, Rogers MA. Self-assembly of 12-hydroxystearic acid molecular gels in mixed solvent systems rationalized using Hansen solubility parameters. Colloid Polym Sci. 2015;293(3):975–83.
Lan Y, Corradini MG, Weiss RG, Raghavan SR, Rogers MA. To gel or not to gel: correlating molecular gelation with solvent parameters. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(17):6035–58.
Haldar S, Karmakar K. A systematic understanding of gelation self-assembly: solvophobically assisted supramolecular gelation via conformational reorientation across amide functionality on a hydrophobically modulated dipeptide based ambidextrous gelator, N-n-acyl-(l)Val-X(OBn), (X = 1,ω-amino acid). RSC Adv. 2015;5(81):66339–54.
Zhao C, Wang H, Bai B, Qu S, Song J, Ran X, et al. Organogels from unsymmetrical [small pi]-conjugated 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. New J Chem. 2013;37(5):1454–60.
Edwards W, Smith DK. Dynamic evolving two-component supramolecular gels—hierarchical control over component selection in complex mixtures. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(15):5911–20.
Bustamante P, Navarro-Lupión J, Peña MA, Escalera B. Hildebrand solubility parameter to predict drug release from hydroxypropyl methylcellulose gels. Int J Pharm. 2011;414(1):125–30.
Bonnet J, Suissa G, Raynal M, Bouteiller L. Organogel formation rationalized by Hansen solubility parameters: dos and don’ts. Soft Matter. 2014;10(18):3154–60.
Bonnet J, Suissa G, Raynal M, Bouteiller L. Organogel formation rationalized by Hansen solubility parameters: influence of gelator structure. Soft Matter. 2015;11(11):2308–12.
Diehn KK, Oh H, Hashemipour R, Weiss RG, Raghavan SR. Insights into organogelation and its kinetics from Hansen solubility parameters. Toward a priori predictions of molecular gelation. Soft Matter. 2014;10(15):2632–40.
Chen S, Tang G, Wu B, Ma M, Wang X. The key effect of the self-assembly mechanism of dendritic gelators: solubility parameters, generations and terminal effects. RSC Adv. 2015;5(44):35282–90.
Vay K, Scheler S, Frieß W. Application of Hansen solubility parameters for understanding and prediction of drug distribution in microspheres. Int J Pharm. 2011;416(1):202–9.
Gårdebjer S, Andersson M, Engström J, Restorp P, Persson M, Larsson A. Using Hansen solubility parameters to predict the dispersion of nano-particles in polymeric films. Polym Chem. 2016;7(9):1756–64.
Wang K, Jia Q, Han F, Liu H, Li S. Self-assembled L-alanine derivative organogel as in situ drug delivery implant: characterization, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2010;36(12):1511–21.
Wang K, Jia Q, Yuan J, Li S. A novel, simple method to simulate gelling process of injectable biodegradable in situ forming drug delivery system based on determination of electrical conductivity. Int J Pharm. 2011;404(1–2):176–9.
Li Z, Cao J, Hu B, Li H, Liu H, Han F, et al. Studies on the in vitro and in vivo degradation behavior of amino acid derivative-based organogels. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42(11):1732–41.
Bielejewski M, Kowalczuk J, Kaszynska J, Lapinski A, Luboradzki R, Demchuk O, et al. Novel supramolecular organogels based on a hydrazide derivative: non-polar solvent-assisted self-assembly, selective gelation properties, nanostructure, solvent dynamics. Soft Matter. 2013;9(31):7501–14.
Edwards W, Lagadec CA, Smith DK. Solvent–gelator interactions—using empirical solvent parameters to better understand the self-assembly of gel-phase materials. Soft Matter. 2011;7(1):110–7.
Hansen CM. Hansen solubility parameters: a user’s handbook. Milton Park: Taylor & Francis Group; 2007.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 81273445.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 973 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, B., Sun, W., Yang, B. et al. Application of Solvent Parameters for Predicting Organogel Formation. AAPS PharmSciTech 19, 2288–2300 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1074-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1074-4