Abstract
This Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 7) analysis addresses critical challenges through three questions, backed by literature and evidence. Environmental, social, and governance concerns were discussed. A notable SDG target shortfall was observed from International Renewable Energy Agency, International Energy Agency, and United Nation’s publications. Urgent actions include refining greenhouse gas emission equivalent estimations and establishing unified life cycle assessment standards. While prioritizing renewables, minimizing dependence on non-renewables for a lower carbon footprint is vital. Balancing energy production with per capita consumption reduction, especially with a growing population, is key to achieving net-zero emissions. This solution demands a thoughtful evaluation of challenges tied to specific renewable technologies and their socio-economic impact. Balancing economic growth, crisis response, and resource management is crucial for acheiving SDG 7 targets.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Fossil fuels (GT), actuating the progress of human civilization from the industrial age (1800) to current era of economic growth (2023), provides the essentials in the form of electricity for various aspects of modern life, including transportation, thermal comfort, industrial processes, refrigeration, medical care, agriculture (food), electronics, and beyond [1,2,3,4,5,6]. However, burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, primarily accounts for the escalating greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) (Major: CO2, CH4 Minor: N2O, H2O, O3, CFCs) driven by the seven largest emitters (China, India, USA, EU, Indonesia, Russia, Brazil), which has contributed to ~ 50% of the climate change (GT) in 2023, (Floods in Libya, North Africa, 2023 [7]) [8, 9]. To combat these climate challenges and to improve the quality of human’s life, the United Nations (UN) has set SDGs (GT) encompassing 17 goals, 169 objectives, and 231 indicators [10]. SDG7 (GT) emphasis on providing affordable and sustainable energy (GT) to aid in achieving netzero (GT) emissions by 2050 (Paris Agreement, SDG 13) (GT) and has interrelations between other SDGs (Fig. 1). Without reliable access to energy, it becomes challenging to eradicate poverty (SDG 1) as it limits opportunities for income generation and hinders access to essential services. Moreover, quality education (SDG 4) is compromised without reliable energy for schools, and good health (SDG 3) is jeopardized without power for healthcare facilities. The objectives of SDG7 involves increasing the adoption of renewables (GT), achieving a twofold enhancement in energy efficiency, fostering stronger international cooperation, technological and infrastructural progress, which are accessed by metrics including accessibility to electricity (%), adoption of clean cooking technologies, utilization of renewable energy (GT), improved energy efficiency (J or kWh), investments in clean energy (USD or EUR), and carbon emissions per unit of electricity generated (gCO2/kWh) [9, 10]. Figure 2a depicts the energy market evolution from 1900 to 2023. Wind and solar energy costs dropped significantly, from 100 USD/MWh in 2014 to 30 USD/MWh in 2022. This signals a strong global push to phase out fossil fuels by 2030. The globe requires > 50% of reduction in GHG emissions by 2030 to limit warming to 1.5 °C, which is globally supported by shifting to renewables. According to [11] and Fig. 2a SDG7 targets energy poverty and vulnerability, particularly affecting specific social groups, but lacks emphasis on absolute dematerialization (GT). Further, the shift to renewables may inadvertently increase production sites in rural areas with lower land values and formalized land rights [11]. Previous reports suggest that the SDG framework broadly focusses on Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and decarbonization, accentuating less on technology and socioeconomic scenarios [10, 12,13,14,15].
Interrelations between other SDGs and SDG 7 (SDG 7, centred on affordable and clean energy, directly, curtails reliance on costly and polluting fuels, thereby addressing poverty (SDG 1) while facilitating clean energy for healthcare services (SDG 3) and sustainable urbanization (SDG 11) through reliable infrastructure and power. It also aligns with responsible consumption and production (SDG 12), with lesser consumption of resources and reduced negative effects on ecosystem. Indirectly, SDG 7 supports all kinds of agricultural practices that promotes sustainability (SDG 2), elevates educational quality (SDG 4), empowers women by creating Jobs (SDG 5), facilitates clean water access (SDG 6), drives economic expansion (SDG 8), spurs technological innovation (SDG 9), advances social equality (SDG 10), aids climate change mitigation (SDG 13), safeguards biodiversity (SDG 14, SDG 15), and fosters peace, justice, and collaborative partnerships (SDG 16, SDG 17). This interconnectedness underscores the importance of SDG 7
a Schematic timeline of energy transition and global initiatives from 1990 to 2023, here NDC means Nationally Determined Contributions (b) Consumption of fossil fuels from 1800 to 2023 and their projected depletion in years (data used under CC license from [16]and [17] Energy Institute Statistical Review of World Energy (2023); Vaclav Smil (2017)) (c) Global warming anomaly (data obtained from [16] and [18, 19]) (d) % share of renewables equivalent installed in major marketable countries. (All data used and analyzed were obtained from [20] and Ember's European Electricity Review; Energy Institute Statistical Review of World Energy [21], curated and filtered) (e) % of electricity contributed from renewables in Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Africa, Asia, Australia, China, Europe, India, UK and Us (Note: Europe includes majorly Germany, Spain, UK and Finland)
In this analysis, we focus on addressing three primary challenges associated with transition to renewables, considering their environmental (E), social (S) and Governance (G) impact in compliance with SDG7: Target 7.1 (Ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services). The 'Just Transition' [22] to renewables involves broader assessment and has complexities related to long-term productions, job security, financial hurdles, which are yet to be clearly addressed.
Challenge 1 (E): The emissions stemming from equipment production, infrastructure development, transportation, and eventual decommissioning and end-of-life waste management (GT) of renewable energy sources necessitate a deeper understanding on how it balances the long-term emissions from fossil fuels. Is the transition to renewable energy truly sustainable?
Challenge 2 (S): Gap exists between fair employment opportunities for workers affected by job displacement from Oil & Gas to renewable energy. Additionally, measures are still needed to bridge the energy efficiency gap between affluent and resource-constrained communities, preventing the potential augmentation of socio-economic disparities.
Challenge 3 (G): While developed nations extend support, the high initial costs of renewable technologies (hydropower and concentrated solar power) hinder the progress in low-income countries. however, acknowledging this trade-off may temporarily benefit low-income households and may develop affordability gaps across income groups. How can governments implement measures to alleviate these upfront expenses ?
Before addressing the challenges, three key questions assisted by literature [8, 11,12,13,14,15, 23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] and factual evidence from International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), International Energy Agency (IEA), Energy Information Administration (EIA), The World Bank Group, British Petroleum (BP), World Resources Institute (WRI), Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) | https://www.iea.org/ | https://www.eia.gov/ | https://www.irena.org/ | https://www.seia.org/ | https://gwec.net/ | https://www.wri.org/ | https://www.bp.com/ | https://www.worldbank.org/en/home are introduced to analyse the listed challenges, accompanied by the constructive suggestions of the authors.
-
1.
Does relying solely on renewables offer an affordable, reliable, and sustainable energy solution?
Transitioning to renewables by 2050 could save up to $12tn globally but requires a drastic reduction in fossil fuel production and consumption [33]. Figure 2b illustrates the consumption trend of fossil fuels from 1800 to 2023, along with the projected years remaining until their depletion: Coal (140), Oil (57), and Gas (49). With energy demand spiking 2.3% in 2018, and a projected 3.4% Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth by 2040, thus the priority should be improving the energy efficiency of existing systems. In 2022, oil demand increased by 2.3 mb/d, and projections for 2023 indicated a growth of 1.7 mb/d (IEA 2023) [34]. Roughly 83% of oil reserves, primarily in Canada, should remain untapped (~ > 3% decline in oil consumption is required each year till 2050). Thus, shifting to natural gas is the next priority, given its abundant reserves (7,124 trillion cubic feet, 2018) [35]. Figure 2c underscores the urgency of this transition, with sea temperatures surging from -0.4℃ in 1990 to 0.9℃ in 2023. This alarming trend poses a threat to aquatic habitats [34, 36]. Rising sea temperatures threaten marine ecosystems, causing disruptions in species life cycles, coral bleaching, and biodiversity loss. This underscores the urgency of mitigating human activities linked to climate change to protect marine environments.
The literature reviewed in this study were chosen from Scopus, based on the selection criteria, mentioned in appendix. Based on [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46], we agree that primary challenges include time and financial constraints. These are exacerbated by the intermittent nature of renewables, requiring auxiliary energy storage and grid upgrades for integration. However, considering long-term viability, we assert the obligation of deep analysis on (i) technological maturity (given the continuous innovation in renewables, standardization remains as a challenge), (ii) economic viability (return on investments, resource availability, market competition & impact, access to capital among other externalities), (iii) subsidy dependence (with implications for market distortion and inequalities), (iv) Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) (should include life cycle assessments and extended producer responsibilities) [47], and (v) regional needs (not an exhaustive list). Thus, a broader assessment is required for this paradigm shift.
-
2.
What is the current level of accessibility to renewable energy, and how swiftly are we progressing towards broader availability? Additionally, what are the projected trends?
Renewable energy comes from naturally replenishing sources, offering lasting potential but limited short-term outputs (EIA 2020). Figure 2c, d shows the 50% of renewables contributions in major marketable countries (Germany, US, Brazil, and China have highest contributions). The per capita installed capacity for renewable energy generation in > 230 developing nations excluding pumped hydrogen increased overall from 104 W in 2013 to 241 W in 2022, with this trend the projections are ~ 630 W in 2050, which means additional ~ 30% increase in production or decrease in consumption is needed to meet the targets [16]. In 2013, the installed solar energy capacity was 141417 MW, which grew to 1061630 MW in 2022. However, concentrated solar power's installed capacity is less (6602 MW) due to its high initial investment. Bioenergy, derived mainly from organic waste, constitutes over ~ 40% of total renewables, followed by wind, hydro, and geothermal energy [48]. Wind energy, harnessed from both onshore and offshore turbines, has seen remarkable growth in the past two decades. Overall, major contributors to renewables include China, India, Brazil, Germany, the UK, and the USA, Australia, Japan, etc., while regions in Asia (Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Vietnam, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, etc.), Africa (Congo, Liberia, Angola, etc.), and Europe (Denmark, Norway, Netherlands, Romania, etc.), Middle east could benefit from increased contributions [16, 49].
-
3.
Are the current levels of financial investment in renewables adequate to progress in this transition?
In 2022, global renewable energy investment reached $0.5 trillion, marking a 19% increase from 2021 and a 70% surge from pre-pandemic 2019 levels. In 2020, solar photovoltaic received 43% of total renewables investment, followed by onshore and offshore wind at 35% and 12% respectively [25]. However, this falls short of the annual average needed from 2023 to 2030, underscoring the urgency to boost investments in off-grid (G) renewables, especially in solar. Regional disparities persist, with over half of the global population in developing nations (Sub-Saharan Africa, Middle East) receives only 15% of global investments, whereas Europe and US leads by ~ 40% in 2020 [16]. Redirecting $1 trillion annually from fossil fuels to energy-transition-related technologies in developing countries is needed [25].
Sustainability of the renewable energy
The transition to renewables is paradoxically reliant on non-renewable resources, particularly mined metals. In 2020, mining operations for materials essential to renewable energy production was ~ 16% of wilderness areas and the production of a single ton of rare-earth and toxic elements (La, Nd, Sr, Te, Cd of ~ 5 to 10 g/m2 for PV [50] etc.) generates ~ 2,000 tons of waste. Life cycle assessment (LCA) (G) studies are necessary for addressing the environmental concerns of major marketable renewables (solar, wind, hydro, geothermal and others). The methodology of LCA analysis for solar PV and wind is stated elsewhere [51,52,53] The installed capacities of renewables as per IRENA is shown in Table 1.
Coal emissions increased ~ 1.6% (243 Mt), while oil emissions rose by 2.5% partly due to increased aviation in 2022 compared to 2021. The biggest spike in emissions (1.8% or 261 Mt) occurred in electricity and heat generation, predominantly from coal sources, particularly in emerging ASEAN economies [54,55,56,57]. The US saw a 0.8% increase (36 Mt) in emissions, largely due to peak electricity demand during summer heat waves. The analysis in Table 2 and Fig. 3 reveals that biomass and nuclear energy production result in higher CO2-e emissions compared to solar and wind energy. Hydroelectric energy falls in the mid-range in terms of emissions. Moreover, solar and biomass energy have lower initial installation costs, and the payback period is shorter for solar, wind, and geothermal energy. When considering sustainability, renewables can be ranked from highest to lowest as follows: solar, hydroelectric, wind, biomass, geothermal, and nuclear.
Major stages of carbon emissions in renewables (a) CO2 emissions from Commercial PV modules (adapted from IEA, 2021) (b) Emissions (CO2-e) from wind energy harvesting (data adapted from [77,78,79,80,81,82,83] (c) Emissions from hydro compared with other renewables (data adapted from [84]) (d) GHG emissions tracking from biomass such as soybean, canola, carinata and tallow (reused with permission from [85])
However, the concept of CO2-e emissions indeed poses several challenges in the context of GHG reduction efforts. Firstly, it fails to distinguish between specific greenhouse gases like CO2, N2O, CH4 as well as other less prevalent but potent gases. This lack of specificity can be problematic because different gases have varying levels of global warming potential (GWP) and different lifetimes in the atmosphere. For instance, while CO2 is the most prevalent GHG, its long-term impact is more enduring than shorter-lived but highly potent gases like CH4. Consequently, a reduction in CH4 emissions might have a more immediate and significant impact on mitigating global warming. Furthermore, CO2-e labelling may not accurately reflect the true environmental and economic costs associated with each greenhouse gas. Calculating GWP involves a degree of ambiguity, as it depends on complicated models and discrepancies in published literatures [18, 21]. This ambiguity can make it challenging to accurately price GHG emissions, potentially leading to misallocations of resources in mitigation efforts.
Equitable employment opportunities
Increasing Human development Index (HDI) and higher degree holders imply progress in education and socio-economic status (Fig. 4a) [86]. However, there is a potential downside. Individuals may find themselves accepting jobs with lower pay and positions in energy sector that do not align with their educational qualifications. Additionally, employment in coal industries has drastically reduced (Fig. 4b). The shift to net-zero emissions could create 9 million new energy sector jobs by 2030, despite an estimated loss of 5 million in fossil fuel production. Additionally, clean energy sectors, encompassing efficiency, automotive [87,88,89,90,91,92,93], and construction, could generate over 30 million jobs by 2030, offering new opportunities in emissions-reducing technologies (Fig. 4c) [94, 95]. However, the transition has led to job displacement in fossil fuel-reliant communities, particularly in coal. This shift from Oil & Gas to solar and wind energy has resulted in fewer job opportunities compared to the offset in oil and gas as of 2023. Both industries rely on imports, potentially limiting local job growth in countries like US, Singapore, and Australia (Fig. 4d). Transitioning to renewables demands workforce retraining, and encounters resistance from fossil fuel interests, potentially causing social disruptions in communities heavily reliant on fossil fuels [96, 97]. For instance, petroleum related jobs are localized but crucial for many local economies. While the energy sector constitutes a small portion of global employment (1.2%), in places like Saudi Arabia, it significantly contributes to GDP (50%) despite employing a smaller percentage (4.8%) [94, 98].
a Evolution of human development index (HDI), which is proportional to employment (data adapted from Our world in data [86, 99] [99]) (b) Total employment in coal industries in UK from 1890 to 2022 (data adapted from Our world in data [86, 99]) (c) Global employment in terms of number of Jobs as per 2022 (World Bank, IEA, Our World in Data [100]) (d) Job shift towards renewables marked by individual countries 2022 (World Bank, IEA, Our World in Data [99]) (e) Top companies in O &G, renewables and NOE – Number of Employees (World Economic Forum, Thomson Reuters, Wikipedia) (f) Comparison of wages in fossil fuels and renewables sector (data adapted from [101] and [102])
The top companies in Oil & Gas, renewables, and their number of employees as per 2022 is listed in Fig. 4e. The Oil & Gas, industries, including Saudi Aramco, Chevron, ExxonMobil, British Petroleum (BP) and Royal Dutch Shell currently have more employees than renewable industries (NextEra Energy, Vestas Wind Systems, Siemens Gamesa, and Enel Green Power); however, the recruiting counts of Oil & Gas, have slightly reduced in 2022. Former coal workers often find replacement jobs with lower pay and skill gaps (Fig. 4f). Fossil fuel workers also tend to earn more and have higher health insurance coverage compared to solar and wind workers. Coal-linked pension funds suffer due to economic decline, impacting communities. Areas with power plants and mines experience lower education rates and income instability. Coal closures lead to reduced local tax revenue, resulting in budget cuts, school closures, and job losses [103]. The transition can increase energy insecurity, disproportionately affecting low-income individuals. In 2018, United Steelworkers represented 18% of petroleum workers, while solar and wind workers had lower unionization rates (4% and 6% respectively) [94, 98].
While the shift towards renewable energy is crucial for environmental sustainability, these economic and social consequences highlight the need for comprehensive support measures for affected communities and workers. Existing energy workers possess skills transferable to clean roles, such as in wind, carbon capture, and low-carbon gas. Restoring closed mines can maintain post-closure jobs [49]. Focusing on qualified workers and inclusive support is vital for clean energy jobs, ensuring safety, equity, and inclusion in affected communities. Government support with inclusive criteria drives economic development and public acceptance. The Global Commission is shaping principles for diverse transitions, guiding IEA's efforts and COP26 input. The overall progress in SDG 7 is shown in Fig. 5a-f. Access to investments in green energy was identified as unstable (7.A.1), indicating a need for increased attention and focus.
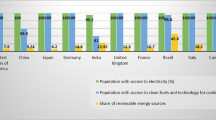
Mapping the progress in SDG 7 individual goals (a) 7.1.1 Proportion of population with accessibility to electricity (b) 7.1.2 Access to green fuels for cooking (c) 7.2.1 Renewable energy share in total energy consumption (d) 7.3.1 Energy Intensity measured in GDP and primary energy consumption (e) 7.A.1 Investments in clean energy (f) 7.B.1 Energy services for developing countries. (Data adapted from Our World in Data, World Economic Forum [104,105,106,107,108,109])
Affordability gaps in renewable adoption
Affordability gaps in renewable adoption stem from high initial costs, rapid tech evolution, and economies of high-income favouring larger projects (Fig. 5e, f). This could particularly affect low-income households, who already allocate a significant portion of their income to energy expenses [110]. In 2022, energy investment is set to surge by 8%, but almost half of this increase is due to rising costs rather than expanding capacity or savings. These cost hikes are driven by supply chain strains, labour shortages, and increased prices for materials like steel and cement. However, higher prices alone can't ensure sustainable choices, especially in less affluent nations with inadequate policies [110,111,112].
Power generation projects in renewables and grids often rely on debt, while smaller ventures or areas with limited credit use equity more. Although advanced economies have easier access to debt, equity remains crucial for emerging sectors. Power generation costs range from 3–7% depending on the region [113, 114]. It's unfair for developing economies to bear the full cost of the transition. Currently, increasing fossil fuel prices disproportionately affect Asia and Africa, with an estimated 90 million struggling to afford energy. This raises concerns about possible energy poverty, affecting nearly 90 million people in Asia and Africa struggling to meet basic energy needs [111, 115].
In the solar sector of Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDE), institutional investors grapple with hurdles. A key obstacle is the limited availability of instruments tailored for solar ventures. Additionally, institutional investors in EMDE prioritize liquid assets like equity, bonds, and structured finance, discouraging solar investments. Low credit ratings of solar corporate bonds in EMDE further dissuades participation. To navigate complexities and mitigate risks, investors often rely on intermediaries like debt funds. Unfortunately, a shortage of specialized financial services exacerbates these challenges, hindering the realization of solar energy's potential in these economies [116, 117].
Closing the investment gap in emerging economies is crucial for equitable climate action and sustainable development. Additional financial and technical support, including concessional and private sector capital, are pivotal. Without a substantial increase in clean energy investment, global efforts to combat climate change and achieve sustainability goals will face significant challenges. Geopolitical events are prompting investments in various fuels, including coal in emerging Asian markets [111, 116]. Additionally, rising prices of critical minerals are emphasizing the importance of mining, refining, and processing in the transition to more sustainable energy systems. Institutional investment in renewable projects can be facilitated with essential risk-mitigating tools such as guarantees and insurance. Partial credit guarantees from international development institutions bolster bond ratings, and solar debt funds with public first-loss protection appeal to low-risk investors. The International Solar Alliance (ISA), Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), Alliance for Rural Electrification (ARE), Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) (GBA- led by India as the G20 Chair, to accelerates global biofuel adoption) and IEA are actively working on solutions to enhance capital accessibility. Coordinated efforts and innovative strategies are imperative to close the renewable energy investment gap and align with Paris Agreement, SDG objectives [111, 115,116,117].
Summary and outlook
Conclusion
This article compiles data and information regarding the current progress in renewable energy development. The speed of this transition is lagging and uncertain, contingent on various factors including policy support, technological advancements, and economic considerations. We have underscored three challenges, the need for more comprehensive and standardized reporting standards for GHG emissions from renewables, the trade-offs in job opportunities, and affordability gaps for low-income communities in adopting renewable technologies. The following analysis were made,
-
The United States witnessed a 0.8% CO2 emission increase (36 Mt), primarily due to increased electricity demand during summer heat waves. Solar and biomass energy showed promise with lower installation costs and shorter payback periods. When assessing the sustainability of renewables, solar, hydroelectric, wind, biomass, geothermal, and nuclear energy were ranked from highest to lowest sustainable. Immediate challenges to address are the issues associated with the credibility of CO2-equivalent emissions. The method lacks specificity in distinguishing between different gases, such as CO2 and CH4, each with unique global warming potentials and atmospheric lifetimes. Focusing on methane emissions reduction may offer more immediate global warming mitigation.
-
The shift toward achieving net-zero emissions by 2030 has the capacity to generate 9 million new jobs in the energy sector, counterbalancing the anticipated loss of 5 million jobs in fossil fuel production. In the realm of clean energy, encompassing efficiency, automotive, and construction, there is a potential for over 30 million jobs, underscoring the opportunities in emissions-reducing technologies. However, such a transition necessitates workforce retraining and may encounter resistance from fossil fuel interests, posing the risk of social disruptions in affected communities. It is imperative for government support, characterized by inclusive criteria, to play a vital role in facilitating economic development and securing public acceptance.
-
Closing the investment gap in emerging economies is crucial for equitable climate action and sustainable development. Increased financial and technical support, involving concessional and private sector capital, is essential. Without a substantial rise in clean energy investment, global efforts to combat climate change and achieve sustainability goals will face significant challenges.
Prospects
-
1.
If renewables are harnessed with a concerted effort to minimize GHG emissions, the prospects are promising. A substantial reduction in carbon footprint would be achieved, significantly contributing to global climate goals.
-
2.
While the renewable energy sector holds great potential for innovation and job creation, it requires efforts to retrain and upskill the workforce from traditional energy industries. Adapting to this shift will be crucial in maximizing the economic benefits and ensuring a sustainable transition for all stakeholders involved.
-
3.
Implementing targeted subsidies and financial incentives to reduce the upfront costs of renewable technologies for consumers and businesses could also support the global climatic initiatives.
Authors viewpoint
The transition from petroleum to electrification and the fight against climate change present a multifaceted challenge that demands a debatable approach. There is no one-size-fits-all solution; instead, a careful evaluation of interconnected processes in energy extraction is required until renewable technologies can independently lead the way. While fossil fuels are currently necessary for decarbonization, powering EVs, and supporting renewable energy production, it is crucial to ensure their use aligns with UN sustainability goals. Despite notable progress, achieving the SDG7 goals demands ongoing efforts, including the establishment of comprehensive and unified GHG reduction standards, optimized resource allocation, micro-assessment of GHG emissions, mandatory sustainable reporting, and the introduction of Green Scores. Developing economies face an inequitable burden in the transition, experiencing the impact of rising fossil fuel prices, particularly in Asia and Africa where 90 million people struggle with energy poverty. This situation adversely affects education and income stability. There is an urgent call for investments in off-grid renewables, especially solar. Ongoing regional disparities show that Europe and the US lead in investments, making up 40%, while developing nations receive only 15%. Innovation, market-driven strategies, data transparency, fact verifiability, global collaboration, and increased public awareness about climate change are critical components of this clean energy transition.
Appendix
Methodology
This article was drafted by reviewing 67 primary research articles from the Scopus database from 2014 to 2023 based on PRISMA approach [118] and [119]. These articles were curated through targeted searches using specific keywords combinations, "SDG7 AND Efficiency," "SDG7 AND Challenges," "SDG7 AND Africa," "SDG7 AND China," "SDG7 AND India," "SDG7 AND Europe," "SDG7 AND Indonesia," "SDG7 AND Trade-offs," 7 AND Renewable Energy", "SDG7 AND Sustainable Development", "SDG7 AND Energy Access", "SDG7 AND Clean Energy", "SDG7 AND Rural Electrification", "SDG7 AND Energy Transition", "SDG7 AND Policy Implementation", "SDG7 AND Technology Innovation", "SDG7 AND Energy Security", "SDG7 AND Carbon Emissions", "SDG7 AND Green Economy","SDG7 AND Climate Resilience", "SDG7 AND Power Generation", "SDG7 AND Energy Poverty", "SDG7 AND Sustainable Practices", "SDG7 AND Access to Electricity", "SDG7 AND Energy Affordability", "SDG7 AND Decentralized Energy", "SDG7 AND Urban Energy", "SDG7 AND Energy Efficiency Measures" and "SDG7 AND Case Study." The initial pool of identified articles across all searches ranged from 150 to 170.
The final selection was refined based on relevance, and alignment with the theme, culminating in a set of 67 research articles. The article also has used data from sources including the IEA, IRENA, World Economic Forum, EIA, and Our World in Data. The data for this study was gathered from various sources, curated, and subsequently visualized using Microsoft Excel and Origin 3.2. Additionally, the study delves into the authors' perspectives on potential future developments in this context. For the convenience of researchers and stakeholders interested in further scrutinizing or replicating our work, all the datasets employed in this study have been available for access in the 'Datasets.zip' archive, provided the original source solely owns the rights for the datasets and must be cited. Furthermore, to uphold transparency and acknowledge the contributions of the original data sources, we have documented the copyrights and sources in the accompanying 'copyrights and sources.docx' file.
Availability of data and materials
The data used in this study were discussed in the manuscript. Datasets can be provided upon reasonable request to the authors.
Abbreviations
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide gas
- CH4 :
-
Methane gas
- O3 :
-
Ozone gas
- N2O:
-
Nitrous oxide
- H2O:
-
Water
- ASEAN:
-
Association of Southeast Asian Nations
- BP:
-
British Petroleum
- CO2-e:
-
CO2 equivalent
- CFCs:
-
Chlorofluorocarbon
- EIA:
-
U.S. Energy Information Administration
- EMDE:
-
Emerging Market and Developing Economies
- EROEI:
-
Energy Return on Investment
- GDP:
-
Gross Domestic Product
- GWEC:
-
Global Wind Energy Council
- GWP:
-
Global Warming Potential
- IEA:
-
International Energy Agency
- IRENA:
-
International Renewable Energy Agency
- SEIA:
-
Solar Energy Industries Association
- SDG:
-
Sustainable Development Goals
- WRI:
-
World Resources Institute
References
Jakob M, Hilaire J. Unburnable fossil-fuel reserves. Nature. 2015;517(7533):150–1. https://doi.org/10.1038/517150a.
Ramasubramanian B, Subramanian S, Prasada Rayavarapu PR, et al. Novel low-carbon energy solutions for powering emerging wearables, smart textiles, and medical devices. Energy Environ Sci. 2022;15:4928. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EE02695C.
Rajagopalan K, Ramasubramanian B, Manojkumar K, et al. Organo-metallic electrolyte additive for regulating hydrogen evolution and self-discharge in Mg–air aqueous battery. New J Chem. 2022;46:19950–62. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NJ04488A.
Rajagopalan K, Ramasubramanian B, Velusamy S, et al. (2022) Examining the economic and energy aspects of manganese oxide in li-ion batteries. Mat Circ Eco. 2022;4(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42824-022-00064-4.
Ramasubramanian B, Chinglenthoiba C, Huiqing X, et al. Sustainable Fe-MOF@carbon nanocomposite electrode for supercapacitor. Surfaces Interfaces. 2022;34: 102397. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SURFIN.2022.102397.
Krishna AMS, Ramasubramanian B, Haseena S, et al. Functionalized Graphene-incorporated cupric oxide charge-transport layer for enhanced Photoelectrochemical performance and hydrogen evolution. Catalysts. 2023;13:785. https://doi.org/10.3390/CATAL13040785.
Libya floods: Why damage to Derna was so catastrophic - BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-66799518. Accessed 14 Sep 2023.
Fuso Nerini F, Sovacool B, Hughes N, et al. Connecting climate action with other sustainable development goals. Nat Sustainabil. 2019;2(8):674–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0334-y.
What Is Climate Change? | United Nations. https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-climate-change.
Kates RW, Parris TM, Leiserowitz AA. What is sustainable development? Goals Indicators Values Pract. 2012;47:8–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/00139157.2005.10524444.
Menton M, Larrea C, Latorre S, et al. Environmental justice and the SDGs: from synergies to gaps and contradictions. Sustain Sci. 2020;15:1621–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11625-020-00789-8/TABLES/1.
Pradhan P, Costa L, Rybski D, et al. A systematic study of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interactions. Earths Future. 2017;5:1169–79. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017EF000632.
Diaz-Sarachaga JM, Jato-Espino D, Castro-Fresno D. Is the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) index an adequate framework to measure the progress of the 2030 Agenda? Sustain Dev. 2018;26:663–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/SD.1735.
Zakari A, Khan I, Tan D, et al. Energy efficiency and sustainable development goals (SDGs). Energy. 2022;239:122365. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2021.122365.
Griggs D, Stafford-Smith M, Gaffney O, et al. (2013) Sustainable development goals for people and planet. Nature. 2013;495(7441):305–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/495305a.
Renewable energy statistics 2023. https://www.irena.org/Publications/2023/Jul/Renewable-energy-statistics-2023. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
GOAL 7: Affordable and clean energy | UNEP - UN Environment Programme. https://www.unep.org/explore-topics/sustainable-development-goals/why-do-sustainable-development-goals-matter/goal-7. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
Morice CP, Kennedy JJ, Rayner NA, et al. An updated assessment of near-surface temperature change from 1850: the hadCRUT5 data set. J Geophys Res: Atmospheres. 2021;126:e2019JD032361. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD032361.
Morice CP, Kennedy JJ, Rayner NA, et al. An updated assessment of near-surface temperature change from 1850: the HadCRUT5 dataset. J Geophys Res. 2021;126:e2019JD032361. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD032361.
Hannah Ritchie, Max Roser and Pablo Rosado (2020) - “Renewable Energy” Published online at OurWorldInData.org. Retrieved from: 'https://ourworldindata.org/renewable-energy' [Online Resource]
Open Data | Electricity & Climate | Ember. https://ember-climate.org/data/. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
Guidelines for a just transition towards environmentally sustainable economies and societies for all (2015), International Labour Organization, https://www.ilo.org/global/topics/green-jobs/publications/WCMS_432859/lang--en/index.htm.
Pailman W, de Groot J. Rethinking education for SDG 7: A framework for embedding gender and critical skills in energy access masters programmes in Africa. Energy Res Soc Sci. 2022;90:102615. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ERSS.2022.102615.
Santika WG, Urmee T, Simsek Y, et al. An assessment of energy policy impacts on achieving Sustainable Development Goal 7 in Indonesia. Energy Sustain Dev. 2020;59:33–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESD.2020.08.011.
Li D, Bae JH, Rishi M. Sustainable Development and SDG-7 in Sub-Saharan Africa: balancing energy access, economic growth, and carbon emissions. Eur J Dev Res. 2023;35:112–37. https://doi.org/10.1057/S41287-021-00502-0/TABLES/7.
Madurai Elavarasan R, Pugazhendhi R, Irfan M, et al. A novel Sustainable Development Goal 7 composite index as the paradigm for energy sustainability assessment: a case study from Europe. Appl Energy. 2022;307:118173. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2021.118173.
He J, Yang Y, Liao Z, et al. Linking SDG 7 to assess the renewable energy footprint of nations by 2030. Appl Energy. 2022;317:119167. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2022.119167.
Madurai Elavarasan R, Pugazhendhi R, Jamal T, et al. Envisioning the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through the lens of energy sustainability (SDG 7) in the post-COVID-19 world. Appl Energy. 2021;292:116665. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2021.116665.
Chirambo D. Towards the achievement of SDG 7 in sub-Saharan Africa: creating synergies between power Africa, sustainable energy for all and climate finance in-order to achieve universal energy access before 2030. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;94:600–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2018.06.025.
Gebara CH, Laurent A. National SDG-7 performance assessment to support achieving sustainable energy for all within planetary limits. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2023;173:112934. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2022.112934.
Salvia AL, Brandli LL (2020) Energy Sustainability at Universities and Its Contribution to SDG 7: A Systematic Literature Review. World Sustainability Series 29–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15604-6_3/COVER.
Trinh VL, Chung CK. Renewable energy for SDG-7 and sustainable electrical production, integration, industrial application, and globalization: review. Clean Eng Technol. 2023;15:100657. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLET.2023.100657.
Way R, Ives MC, Mealy P, Farmer JD. Empirically grounded technology forecasts and the energy transition. Joule. 2022;6:2057–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2022.08.009.
Oil Market Report - August 2023 – Analysis - IEA. https://www.iea.org/reports/oil-market-report-august-2023. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
Kulandaivalu T, Mohamed AR, Ali KA, Mohammadi M. Photocatalytic carbon dioxide reforming of methane as an alternative approach for solar fuel production-a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2020;134:110363. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2020.110363.
Renewables Data Explorer – Data Tools - IEA. https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-tools/renewables-data-explorer. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
White LV. Sintov ND (2019) Health and financial impacts of demand-side response measures differ across sociodemographic groups. Nature Energy. 2019;5(1):50–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-019-0507-y.
Hain M, Schermeyer H, Uhrig-Homburg M, Fichtner W. Managing renewable energy production risk. J Bank Financ. 2018;97:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JBANKFIN.2018.09.001.
Tu T, Rajarathnam GP, Vassallo AM. Optimization of a stand-alone photovoltaic–wind–diesel–battery system with multi-layered demand scheduling. Renew Energy. 2019;131:333–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2018.07.029.
Hussain MT, Bin SDN, Hussain MS, Jabir M. Optimal Management strategies to solve issues of grid having Electric Vehicles (EV): a review. J Energy Storage. 2021;33: 102114. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EST.2020.102114.
Verzijlbergh RA, De Vries LJ, Dijkema GPJ, Herder PM. Institutional challenges caused by the integration of renewable energy sources in the European electricity sector. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;75:660–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2016.11.039.
Antonelli M, Desideri U, Franco A. Effects of large scale penetration of renewables: the Italian case in the years 2008–2015. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;81:3090–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2017.08.081.
Headley AJ, Copp DA. Energy storage sizing for grid compatibility of intermittent renewable resources: a California case study. Energy. 2020;198: 117310. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2020.117310.
Simshauser P. On intermittent renewable generation & the stability of Australia’s national electricity market. Energy Econ. 2018;72:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2018.02.006.
Oree V, Sayed Hassen SZ, Fleming PJ. Generation expansion planning optimisation with renewable energy integration: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;69:790–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2016.11.120.
Babatunde OM, Munda JL, Hamam Y. A comprehensive state-of-the-art survey on power generation expansion planning with intermittent renewable energy source and energy storage. Int J Energy Res. 2019;43:6078–107. https://doi.org/10.1002/ER.4388.
Ramasubramanian B, Tan J, Chellappan V, Ramakrishna S. Recent advances in extended producer responsibility initiatives for plastic waste management in Germany and UK. Mat Circ Eco. 2023;5(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42824-023-00076-8.
Ramasubramanian B, Rao RP, Chellappan V, Ramakrishna S. Towards sustainable fuel cells and batteries with an AI perspective. Sustainability. 2022;14:16001. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU142316001.
IEA – International Energy Agency - IEA. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-employment/execu. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
ECN Publicaties. https://publicaties.ecn.nl/ECN-RX--06-016. Accessed 13 Sep 2023.
Fthenakis V (2020) Comparative Life Cycle Analysis of Scalable Single-Junction and Tandem Perovskite Solar Cell (PSC) Systems. https://doi.org/10.2172/1691513.
Naves AX, Barreneche C, Fernández AI, et al. Life cycle costing as a bottom line for the life cycle sustainability assessment in the solar energy sector: a review. Sol Energy. 2019;192:238–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLENER.2018.04.011.
Kaldellis JK, Apostolou D. Life cycle energy and carbon footprint of offshore wind energy. Comparison with onshore counterpart. Renew Energy. 2017;108:72–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2017.02.039.
Li G, Hu R, Hao Y, et al. CO2 and air pollutant emissions from bio-coal briquettes. Environ Technol Innov. 2023;29: 102975. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ETI.2022.102975.
Jonek-Kowalska I. Towards the reduction of CO2 emissions. Paths of pro-ecological transformation of energy mixes in European countries with an above-average share of coal in energy consumption. Resourc Pol. 2022;77:102701. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RESOURPOL.2022.102701.
Coal 2022 – Analysis - IEA. https://www.iea.org/reports/coal-2022. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
Kumar Dalapati G, Ghosh S, Sherin PAT, et al. Maximizing solar energy production in ASEAN region: opportunity and challenges. Results Eng. 2023;20:101525. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RINENG.2023.101525.
Ludin NA, Mustafa NI, Hanafiah MM, et al. Prospects of life cycle assessment of renewable energy from solar photovoltaic technologies: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;96:11–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2018.07.048.
Hou G, Sun H, Jiang Z, et al. Life cycle assessment of grid-connected photovoltaic power generation from crystalline silicon solar modules in China. Appl Energy. 2016;164:882–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2015.11.023.
Kim BJ, Lee JY, Kim KH, Hur T. Evaluation of the environmental performance of sc-Si and mc-Si PV systems in Korea. Solar Energy. 2014;99:100–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLENER.2013.10.038.
Ludin, N. A., Mustafa, N. I., Hanafiah, M. M., Ibrahim, M. A., Teridi, M. A. M., Sepeai, S.,& Sopian, K. Prospects of life cycle assessment of renewable energy from solar photovoltaic technologies: A review. Renew. sustain. energy rev. 2018;96;11–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.07.048.
Lu L, Yang HX. Environmental payback time analysis of a roof-mounted building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) system in Hong Kong. Appl Energy. 2010;87:3625–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2010.06.011.
Perry AM, Devine Jr, WD, Cameron AE, Marland G, Plaza H, Reister DB, Treat NL, Whittle CE. Net energy analysis of five energy systems. United States: N. p., 1977. https://www.osti.gov/biblio/5261809.
Kato K, Murata A, Sakuta K. Energy pay-back time and life-cycle CO 2 emission of residential PV power system with silicon PV module. Progr Photovoltaics: Res Appl. 1998;6:105. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-159X(199803/04)6:2.
Kim HC, Fthenakis V, Choi JK, Turney DE. Life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of thin-film photovoltaic electricity generation. J Ind Ecol. 2012;16:S110–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1530-9290.2011.00423.X.
Nugent D, Sovacool BK. Assessing the lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions from solar PV and wind energy: a critical meta-survey. Energy Policy. 2014;65:229–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2013.10.048.
Comparison of the emissions intensity of different hydrogen production routes, 2021 – Charts – Data & Statistics - IEA. https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/comparison-of-the-emissions-intensity-of-different-hydrogen-production-routes-2021. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
Dolan SL, Heath GA. Life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of utility-scale wind power: systematic review and harmonization. J Ind Ecol. 2012;16:S136. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1530-9290.2012.00464.X.
Bhandari R, Kumar B, Mayer F. Life cycle greenhouse gas emission from wind farms in reference to turbine sizes and capacity factors. J Clean Prod. 2020;277:123385. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2020.123385.
Li S, Zhang Q. Carbon emission from global hydroelectric reservoirs revisited. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2014;21:13636–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-014-3165-4/METRICS.
Pehl M, Arvesen A, Humpenöder F, et al. (2017) Understanding future emissions from low-carbon power systems by integration of life-cycle assessment and integrated energy modelling. Nature Energy. 2017;2(12):939–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-017-0032-9.
Rüdisüli M, Romano E, Eggimann S, Patel MK. Decarbonization strategies for Switzerland considering embedded greenhouse gas emissions in electricity imports. Energy Policy. 2022;162:112794. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2022.112794.
A Eberle GA Heath AC Carpenter Petri SR Nicholson 2017 Systematic Review of Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Geothermal Electricity https://doi.org/10.2172/1398245.
O’Sullivan M, Gravatt M, Popineau J, et al. Carbon dioxide emissions from geothermal power plants. Renew Energy. 2021;175:990–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2021.05.021.
Warner ES, Heath GA. Life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of nuclear electricity generation. J Ind Ecol. 2012;16:S73–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1530-9290.2012.00472.X.
Nuclear and wind power estimated to have lowest levelized CO2 emissions | Energy Institute. https://energy.utexas.edu/news/nuclear-and-wind-power-estimated-have-lowest-levelized-co2-emissions. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
Guezuraga B, Zauner R, Pölz W. Life cycle assessment of two different 2 MW class wind turbines. Renew Energy. 2012;37:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2011.05.008.
Garrett P, Rønde K. Life cycle assessment of wind power: Comprehensive results from a state-of-the-art approach. Int J Life Cycle Assess. 2013;18:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11367-012-0445-4/METRICS.
Bonou A, Laurent A, Olsen SI. Life cycle assessment of onshore and offshore wind energy-from theory to application. Appl Energy. 2016;180:327–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2016.07.058.
Xu L, Pang M, Zhang L, et al. Life cycle assessment of onshore wind power systems in China. Resour Conserv Recycl. 2018;132:361–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RESCONREC.2017.06.014.
Yang J, Chang Y, Zhang L, et al. The life-cycle energy and environmental emissions of a typical offshore wind farm in China. J Clean Prod. 2018;180:316–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.01.082.
Ozoemena M, Cheung WM, Hasan R. Comparative LCA of technology improvement opportunities for a 1.5-MW wind turbine in the context of an onshore wind farm. Clean Technol Environ Policy. 2018;20:173–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10098-017-1466-2/TABLES/9.
Alsaleh A, Sattler M. Comprehensive life cycle assessment of large wind turbines in the US. Clean Technol Environ Policy. 2019;21:887–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10098-019-01678-0/METRICS.
Ubierna M, Santos CD, Mercier-Blais S (2022) Water security and climate change: hydropower reservoir greenhouse gas emissions. Water Resources Development and Management 69–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5493-0_5/COVER.
Xu H, Ou L, Li Y, et al. Life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of biodiesel and renewable diesel production in the United States. Environ Sci Technol. 2022;56:7512–21. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.2C00289/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/ES2C00289_0003.JPEG.
Bastian Herre and Pablo Arriagada. “The Human Development Index and related indices: what they are and what we can learn from them” Published online at OurWorldInData.org. 2023. Retrieved from: 'https://ourworldindata.org/human-development-index'.
Brindha R, Mohanraj R, Manojkumar P, et al. Hybrid electrochemical behaviour of La1-xCaxMnO3 Nano Perovskites and recycled polar interspersed graphene for metal-air battery system. J Electrochem Soc. 2020;167:120539. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ABB34F.
Ramasubramanian B, Reddy VS, Zhen Y, et al. Metal organic framework derived Zirconia-Carbon Nanoporous Mat for integrated strain sensor powered by solid-state supercapacitor. Adv Fiber Mat. 2023;5:1404–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42765-023-00283-7/METRICS.
Ramasubramanian B, Reddy MV, Zaghib K, et al. Growth mechanism of micro/Nano metal dendrites and cumulative strategies for countering its impacts in metal ion batteries: a review. Nanomaterials. 2021;11:2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO11102476.
Senthilkumar SH, Ramasubramanian B, Rao RP, et al. Advances in Electrospun materials and methods for Li-Ion batteries. Polymers. 2023;15:1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM15071622.
Mohanraj R, Brindha R, Kandeeban R, et al. Electrochemical detection of 5-hydroxytryptamine using sustainable SnO2-Graphite nanocomposite modified electrode. Mater Lett. 2021;305:130796. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2021.130796.
Kumar KK, Brindha R, Nandhini M, et al. Water-suspended graphene as electrolyte additive in zinc-air alkaline battery system. Ionics (Kiel). 2019;25:1699–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11581-019-02924-7/METRICS.
Ramasubramanian B, Sundarrajan S, Chellappan V, et al. Recent development in carbon-LiFePO4 cathodes for Lithium-Ion batteries: a mini review. Batteries. 2022;8:133. https://doi.org/10.3390/BATTERIES8100133.
Overview – World Energy Employment – Analysis - IEA. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-employment/overview. Accessed 18 Sep 2023
Gender and Energy Data Explorer – Data Tools - IEA. https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-tools/gender-and-energy-data-explorer?Topic=Employment&Indicator=Gender+wage+gap+conditional+on+skills. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
Ramasubramanian B, Reddy VS, Chellappan V, Ramakrishna S. Emerging materials, wearables, and diagnostic advancements in therapeutic treatment of brain diseases. Biosensors. 2022;12:1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOS12121176.
Zhen Y, Reddy VS, Ramasubramanian B, Ramakrishna S. Three-dimensional AgNps@Mxene@PEDOT:PSS composite hybrid foam as a piezoresistive pressure sensor with ultra-broad working range. J Mater Sci. 2022;57:21960–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10853-022-08012-Y/FIGURES/6.
The importance of focusing on jobs and fairness in clean energy transitions – Analysis - IEA. https://www.iea.org/commentaries/the-importance-of-focusing-on-jobs-and-fairness-in-clean-energy-transitions. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
UNDP (United Nations Development Programme). Human Development Report 2021-22: Uncertain Times, Unsettled Lives: Shaping our Future in a Transforming World. New York. 2022. https://hdr.undp.org/content/human-development-report-2021-22.
Employment by sector (%) - World Bank Gender Data Portal. https://genderdata.worldbank.org/indicators/sl-empl-zs/. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
How much do energy industry jobs pay? A look at the data » Yale Climate Connections. https://yaleclimateconnections.org/2021/09/how-much-do-energy-industry-jobs-pay-a-look-at-the-data/. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
National Minimum Wage and National Living Wage rates - GOV.UK. https://www.gov.uk/national-minimum-wage-rates. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
IEA – International Energy Agency - IEA. https://www.iea.org/commentaries/the-importance-of-focusing-on-jobs-and-fairness-in-clean-energy-transitionstive-summary. Accessed 15 Nov 2023.
Tracking SDG7: The Energy Progress Report, 2021 – Analysis - IEA. https://www.iea.org/reports/tracking-sdg7-the-energy-progress-report-2021. Accessed 11 Oct 2023.
Energy intensity – SDG7: Data and Projections – Analysis - IEA. https://www.iea.org/reports/sdg7-data-and-projections/energy-intensity. Accessed 11 Oct 2023.
Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption - Sustainable Development Goals - United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. https://w3.unece.org/SDG/en/Indicator?id=23. Accessed 11 Oct 2023.
Stoner O, Gavin G, Economou T, et al. Global household energy model: a multivariate hierarchical approach to estimating trends in the use of polluting and clean fuels for cooking. J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat. 2020;69:815–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/RSSC.12428.
Access to electricity (% of population) | Data. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EG.ELC.ACCS.ZS. Accessed 11 Oct 2023.
The Sustainable Development Goals Report Extended Report-Goal 7, United Nations, 2021. unstats.un.org.
Challenges and opportunities beyond 2021 – Renewable energy market update – Analysis - IEA. https://www.iea.org/reports/renewable-energy-market-update/challenges-and-opportunities-beyond-2021. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
Renewable Energy Agency I. Off-grid renewable energy solutions to expand electricity access: An opportunity not to be missed, IRENA, 2019. https://www.irena.org/publications/2019/Jan/Off-grid-renewable-energy-solutions-to-expand-electricity-to-access-An-opportunity-not-to-be-missed.
How to End Energy Poverty And Reach Net-Zero Emissions | World Economic Forum. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/07/how-to-end-energy-poverty-net-zero-emissions/. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
Tucho GT, Kumsa DM. Challenges of achieving sustainable development goal 7 from the perspectives of access to modern cooking energy in developing countries. Front Energy Res. 2020;8:564104. https://doi.org/10.3389/FENRG.2020.564104/BIBTEX.
Qadir SA, Al-Motairi H, Tahir F, Al-Fagih L. Incentives and strategies for financing the renewable energy transition: a review. Energy Rep. 2021;7:3590–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EGYR.2021.06.041.
Karekezi S. Renewable Energy in Africa: Prospects and Limits Republic of Senegal United Nations Renewable energy development Waeni Kithyoma, AFREPREN for The Workshop for African Energy Experts on Operationalizing the NEPAD Energy Initiative Operationalizing the NEPAD Energy Initiative, 2019. https://un-energy.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/nepadkarekezi.pdf.
Della Valle N, Bertoldi P. Promoting energy efficiency: barriers, societal needs and policies. Front Energy Res. 2022;9:804091. https://doi.org/10.3389/FENRG.2021.804091/BIBTEX.
Renewables Are the Solutions to Malaysia’s Sustainable Future and Renewed Climate Ambition. https://www.irena.org/News/pressreleases/2023/Mar/Renewables-Are-the-Solution-to-Malaysias-Sustainable-Future-and-Renewed-Climate-Ambition. Accessed 18 Sep 2023.
Malički M, Jerončić A, Aalbersberg IjJ, et al (2021) Systematic review and meta-analyses of studies analysing instructions to authors from 1987 to 2017. Nature Communications 2021 12:1 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26027-y.
Helton E. Guides: Conducting a Literature Review (PGBS): Scopus, 2018. https://infoguides.pepperdine.edu/litreview/scopustips.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank National University of Singapore for supporting with in-house facilities and access to literatures. Authors acknowledge NUS Hybrid-Integrated Flexible (Stretchable) Electronic Systems (HiFES) Program Seed Fund (Grant No. R265000628133), NUS Resilience and Growth fund for Development of Li-ion rechargeable batteries (A-0000065-54-00).
Funding
No funding was received or used for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BR and SR did formal analysis, collected, and curated the data, BR wrote the original draft, SR reviewed, edited, supervised, and validated the original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study does not require ethical approval from Institutions or Organizations. The data utilization adheres to all relevant national and international ethical guidelines, ensuring the rights, safety, involved in the study.
Consent for publication
Authors involved in this study have provided Informed consent for publishing the work in Sustainable Earth Reviews.
Competing interests
There are no conflicts to disclose among the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Glossary
- Climate change
-
Long-term alterations in temperature, weather patterns, and sea levels due to human activities, primarily the release of greenhouse gases
- Decommissioning
-
Reducing material usage and waste generation by employing efficient technologies and sustainable practices
- Dematerialization
-
Reducing material usage and waste generation by employing efficient technologies and sustainable practices
- Fossil fuels
-
Non-renewable natural resources like coal, oil, and natural gas used for generation of energy (electrical)
- LCA
-
Method to evaluate environmental impacts of a product or process over its entire life cycle, from production to disposal
- Netzero
-
Achieving a balance between the greenhouse gases emitted and those removed from the atmosphere
- Off-grid
-
Energy systems or communities independent of the main electrical grid, often relying on localized renewable sources
- Paris Agreement
-
Global treaty adopted in 2015, aiming to limit global warming and promote climate resilience
- Renewable energy
-
Power generated from sources that naturally replenish, minimizing environmental impact
- Renewables
-
Energy derived from naturally replenished resources like sunlight, wind, and water
- SDG 13
-
Focuses on climate action, urging immediate steps to combat climate change and its impacts
- SDG7
-
Targets universal access to affordable, reliable, sustainable energy by 2030
- SDGs
-
United Nations' set of 17 global goals to address social, economic, and environmental challenges by 2030
- Sustainable energy
-
Power sources with minimal environmental impact, ensuring long-term availability and reducing harmful emissions
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramasubramanian, B., Ramakrishna, S. What's next for the Sustainable Development Goals? Synergy and trade-offs in affordable and clean energy (SDG 7). Sustain Earth Reviews 6, 17 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42055-023-00069-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42055-023-00069-0