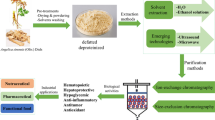
Abstract
Momordica charantia (M. charantia), as a common edible vegetable and herb, is mainly distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. M. charantia polysaccharides (MCPs), as the main pharmacologically active component in M. charantia, are water-soluble polysaccharides with an average molecular weight of 4–900 kDa. The extraction methods of MCPs mainly include hot water extraction, acid extraction, alkali extraction, ultrasonic extraction, enzyme extraction and three-phase partitioning extraction, and different extraction methods will affect the yield of MCPs. MCPs possess a variety of bioactivities, including antidiabetic, antiaging, antioxidant, antiviral, immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects. The purpose of this review is to systematically summarize the latest research progress of MCPs in extraction, purification, structural characterization, and biological activity. In addition, the structure–activity relationship will be further discussed. We believe that this review will provide a useful reference for the investigation, production, and application of MCPs in functional foods and therapeutic agents.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Momordica charantia (M. charantia, Fig. 1), also known as bitter gourd, bitter melon, kugua, balsam pear or karela, is a plant that belongs to the family Cucurbitaceae, is native to East India, and has been widely cultivated in tropical to temperate regions of the world (such as Asia, East Africa, and South America) for thousands of years [1, 2]. M. charantia is a common edible vegetable and is traditionally used to treat diarrhoea, dysentery, jaundice, scabies, haemorrhoids, and diabetes in traditional Chinese medicine [3]. The compendium of Materia Medica records that M. charantia is bitter, cold and nontoxic and has the effect of clearing the heart and improving eyesight, relieving fatigue and removing heat [4, 5]. With the deepening of chemical and pharmacological research on M. charantia, it has been found that it contains rich biological activities, such as antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, antiulcer, antiosteoporosis and antiobesity activities [6,7,8]. These pharmacological effects are attributed to its various bioactive components, including polysaccharides, proteins, saponins, triterpenes, Momordica alkaloids, flavonoids, phenolic compounds, sterols, etc. [9, 10].
Plant polysaccharides (such as pumpkin polysaccharides [11], Bletilla striata polysaccharides [12] and Lycium barbarum polysaccharides [13]) have become a new research hotpot in recent years due to their high biological activity and low toxicity. With the development of modern technology, the structural analysis, biological activity and metabolomic studies of plant polysaccharides have been further studied [14, 15]. As the main active components of M. charantia, M. charantia polysaccharides (MCPs) have been gradually noticed by scientists because of their wide range of biological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antidiabetes, lipid-lowering, neuroprotection, immune regulation and gastrointestinal protection activities [16,17,18]. However, different extraction and purification methods have obtained MCPs with different structures and bioactivities, and there are few systematic introductions on the relationship between their structures and bioactivities.
To comprehensively and systematically understand MCPs, this paper collected and summarized the related research findings of MCPs in previous reports and summarized the extraction methods, purification, structural characteristics and biological activities, providing a scientific reference for further study of MCPs.
Extraction and purification of MCPs
MCP is a natural macromolecular carbohydrate soluble in water. Different parameters, such as extraction temperature, extraction time, pH value, and the ratio of raw materials and solutions, will affect the yield of MCP. A schematic representation of the extraction, purification, structural features and biological activities of MCP is shown in Fig. 2.
Extraction of MCPs
There are many kinds of extraction methods for polysaccharides. Different extraction methods can be selected according to the different properties of polysaccharides, and the commonly used extraction methods of polysaccharides include hot water extraction, acid extraction, alkali extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, enzyme-assisted extraction and microwave-assisted extraction [19, 20]. The advantages and disadvantages of these common extraction methods are shown in Table 1.
Considering the good water solubility of polysaccharides, solvent extraction is the most common method, including hot water extraction, alkali extraction and acid extraction. The hot water extraction method is the most common method to extract MCPs [21]. The process is mainly by mixing M. charantia with hot water, stirring and filtering, and then using ethanol precipitation and centrifugation to obtain crude polysaccharide MCPs [22]. Chen et al. [23] dried fresh M. charantia at 50 °C for 12 h, ground it into powder, added 1000 mL of distilled water to the M. charantia powder and heated it at 90 °C for 2 h. The solution was collected by centrifugation, and ethanol was added to obtain MCP. In another study [24], 1 g of lyophilized bitter melon powder was added to 40 mL of 0.1 M citrate–phosphate buffer and incubated with continuous shaking on a shaker at 250 rpm, and it was found that a 36% (w/w) MCP yield was obtained under the conditions of pH 2, 80 °C, and an extraction temperature of 2 h. Meanwhile, it was found that MCP is an acidic heteropolysaccharide that contains a large amount of monosaccharides, mainly glucose, galactose and amino acids. The solvent extraction method has certain disadvantages, such as low extraction efficiency, high energy consumption, and long extraction time [25]. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction, enzymatic-assisted extraction, and microwave extraction were used as alternative methods for polysaccharide extraction.
Ultrasonic-assisted extraction is a green nonthermal treatment technology that has attracted attention for the extraction of polysaccharides because of its enhanced mass transfer and destruction of cell walls through acoustic cavitation [26]. The dried M. charantia powder was removed from lipids and pigments, and the residue was immersed in distilled water and ultrasonically extracted at 350 W and 55 °C for 30 min. The solution was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 20 min to obtain the supernatant. MCP was obtained by adding four volumes of ethanol to the supernatant and then centrifuging [27]. One-step aqueous two-phase extraction (ATPE)-assisted ultrasonic microwave extraction based on an isopropano1/(NH4)2SO4 aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) was used to extract MCP. When the extraction temperature was 70 °C, the solid–liquid ratio was 1:70, and the extraction time was 15 min, the yield of MCP was 24.67% [28]. Ultrasonic extraction for too long may destroy the MCP structure. Meanwhile, ultrasonic extraction cannot be widely used because of the limitations of instruments and equipment in the industrial field [29].
The enzyme-assisted extraction method allows the release of polysaccharides within plant cells by catalyzing the explanation of cell walls. This method has the advantages of high efficiency, convenient operation and environmental friendliness [30]. However, as the enzyme is a bioactive substance, its activity is based on the pH value of the enzyme solution, and a suitable pH value is selected to ensure the optimal activity of the enzyme [31]. Fan et al. [32] established an efficient enzymolysis-ultrasonic assisted extraction (EUAE) and further optimized the extraction conditions of MCP using response surface methodology (RSM) and Box-Behnken design (BBD). The extraction rate of MCP reached 29.75 ± 0.48% when the optimal conditions were as follows: pH value of 4.38, extraction temperature of 52.02 °C, complex enzyme solution (2:2:1 ratio of cellulose:pectinase:trypsin) concentration of 2.5%, and extraction time of 36.87 min.
Three-phase partitioning (TPP) is used to efficiently extract bioactive compounds from natural resources, such as proteins, polysaccharides, enzymes, lipids, and carbohydrates [33, 34]. After fresh bitter melon was washed and sliced, the juice and residue of bitter melon were extracted by a juicer, and water-soluble BPS was extracted from the juice by the TPP method, which was named BPS-J, and the extraction rate was 14.36%. In addition, the residue of bitter melon was divided into three equal parts, and distilled water, citric acid (pH 3.0) and 1.25 M NaOH/0.05% NaBH4 aqueous solution were added. An ultrasonic homogenizer was used at 25 °C for 30 min at 350 W and then centrifuged, evaporated and concentrated to collect the supernatant, which was precipitated by ethanol overnight. Then, the precipitate was collected by centrifugation, and three partially purified water-soluble BPSs were obtained through deproteinization, dialysis and drying, which were expressed as BPS-W, BPS-C and BPS-A. The extraction rates were 3.09%, 3.82% and 4.18%, respectively. The results showed that different solvents had a great influence on the extraction rate of BPS, and acidic and alkaline media were more likely to destroy the cell wall than distilled water to improve the extraction rate of BPSs [35]. The extraction methods of MCPs are summarized in Table 2.
Purification of MCP
MCP obtained by solvent extraction, ultrasonic extraction and other methods is usually crude polysaccharides containing proteins, pigments and other impurities, which need to be further removed to obtain purified MCP. Purification of MCP is an indispensable step for further analysis of its structure and biological activity. For example, proteins can be removed by the Sevage method and trichloroacetic acid [36], small molecules can be removed by dialysis, ultrafiltration, and ethanol extraction [37], and pigments can be removed by DEAE cellulose adsorption and activated carbon adsorption [38].
Sevage is a main method to remove proteins from polysaccharides [39, 40]. Papain was also used to remove proteins from MCP. Guan used the Sevage method combined with papain to remove free protein to obtain purified MCP [41]. To obtain purified MCP, DEAE cellulose and column chromatography were used. The polysaccharide was deproteinized by the Sevage method and lyophilized to obtain crude polysaccharide. The crude polysaccharide was purified with DEAE-52 cellulose and Sephadex G-100, and the main polysaccharide fraction was collected, lyophilized and named MCPIIa [42]. Crude MCP was purified by AB-8 macroporous resin, and purified MCP was obtained by alcohol precipitation, acetone washing and dialysis with a purity of 97.84% [28]. Deng et al. [43] purified MCP by DEAE-52 cellulose anion exchange chromatography to obtain two purified MCPs, named MCP1 and MCP2, with yields of 48.74% and 15.16%, respectively.
Physiochemical and structural features of MCP
The chemical structure of polysaccharides includes molecular weight, monosaccharide composition, type and configuration of glycosidic linkages, and other characteristics [44]. The structures of MCPs are diverse and complex, and the differences in these structures may be related to the differences in raw materials, extraction methods and purification methods [45]. While different structures of MCPs lead to differences in biological activity, it is of great significance to study the structure–activity relationship of MCPs. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), mass spectrometry (MS), high-performance gel permeation chromatography (HPGPC), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS) are commonly used methods to analyze the composition and structure of MCP. The monosaccharide composition, molecular weight, structural characteristics and biological activity are summarized in Table 3.
Monosaccharide compositions
The monosaccharide composition of polysaccharides is usually detected and quantified by complete acid hydrolysis, derivatization, GC and HPLC [46, 47]. The basic units of monosaccharides determine the structure and properties of polysaccharides. Research data on MCPs indicate that MCPs are classified as heteropolysaccharides and that most MCPs are composed of galactose, rhamnose, glucose, arabinose and mannose at different ratios.
The water-soluble polysaccharide MCP was detected by HPLC to contain arabinose, xylose, galactose and rhamnose in a ratio of 1.00:1.12:4.07:1.79 [39]. Another study [24] also used HPLC to detect the monosaccharide composition of MCP and found that MCP was mainly composed of glucose, galactose and galactic acid, and the molar ratios were 0.38:0.31:0.15. MCP was also found to contain other monosaccharides, including mannose, rhamnose, xylose, and arabinose. These results suggested that MCP was a heteropolysaccharide. Yan et al. [27] showed that different conditions may affect the monosaccharide composition and content of polysaccharides. Three drying methods, namely, hot air drying, freeze drying and infrared radiation drying, were used to dry M. charantia. Furthermore, three water-soluble M. charantia polysaccharides, named BPS-H, BPS-F and BPS-I, were obtained through separation and purification. The monosaccharide composition of the three polysaccharides was detected by ion chromatography (IC), and the contents of neutral sugar (73.09%) and uronic acid (17.09%) of BPS-I were higher than those of BPS-F (63.86%, 15.97%) and BPS-H (61.70%, 10.10%). Meanwhile, the galactose content of BPS-F (1.6%) was lower than that of BPS-H (5.7%) and BPS-I (6.1%).
Molecular weights
The average molecular weight of polysaccharides is usually determined by HPLC and HPGPC methods [48, 49]. Based on these techniques, the various MCPs mentioned and discussed in this article have an average molecular weight of 4–900 kDa (Table 3). However, the molecular weights of the obtained MCPs were significantly different due to the different extraction methods and sources of M. charantia.
In one study [43], two polysaccharides, MCP1 and MCP2, were obtained from M. charantia by hot water extraction. The average molecular weights measured by HPGPC were 85.5 kDa and 441 kDa, respectively. Tan et al. [24] used acid extraction to obtain MCP. The average molecular weight of MCP was 91,919 Da. MCP can be modified by different means to obtain compounds with different molecular weights and more diverse uses. For example, Ru et al. [50] obtained MCP by water extraction and alcohol precipitation, further deproteinized it by the Sevage method, and purified it by DEAE-52 cellulose and Sephadex G-100 to obtain a polysaccharide, named MCPIIa, with a molecular weight of 13,029 Da. MCPIIa was selenized by the ascorbic acid-sodium selenite method to obtain a new selenium-containing polysaccharide, named Se-MCPIIa-1, and the average molecular weight was significantly increased to 4.0038 × 104 Da, as determined by HPGPC. Meanwhile, Se-MCPIIa-1 showed a certain preventive effect on pancreatic, liver and kidney damage caused by diabetes.
Chemical structures
Apart from the composition and average molecular weight of polysaccharides, the chemical structure of MCPs is also important for understanding their biological activity.
The structural features of MCPs were analyzed by methylation, periodate oxidation, Smith degradation, NMR, 13C and 1H [51, 52]. Some information about the possible structure of MCPs has been published, and Fig. 3 summarizes some of the backbone and branches of MCPs.
The structure of a specific polysaccharide (PS) isolated from M. charantia was determined by NMR, period oxidation and methylation analysis. This result showed that the repeat unit of PS contains a backbone of four (1→4)-linked d-methyl galacturonic acid residues, one of which was branched at the O-2 position and had a β-d-galactopyranosyl residue. The backbone was mainly composed of [→4)-α-d-GalpA6Me-(1]3→4)-α-d-GalpA6Me-(1→ [53]. MCP was isolated by hot water extraction and further purified by DEAE-52 cellulose anion exchange chromatography to obtain two main components, MCP1 and MCP2. FTIR analysis revealed that there were a pyran ring, β-d-glucopyranose and α-d-glucopyranose in MCP1 and MCP2, respectively. Although both α- and β-types are present in MCP1 and MCP2, they were both dominated by d-glucosyl residues in the pyranose form. These data indicated that both MCP1 and MCP2 were heteropolysaccharides based on the glucan backbone [43]. Zhang et al. [42] studied the structure of MCPIIa by FTIR, 13C NMR and 11H NMR and showed that it passed through β-glycosidic bonds linked to a large number of arabino furanose, glucuronic acid and xylopyranose residues.
Molecular morphology
The molecular morphology of polysaccharides is helpful to understand their pharmacological activity. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) are valuable techniques for analyzing the molecular morphology of polysaccharides [54,55,56]. The SEM image shows that the surface of the MCP11-a molecule is rough, showing an irregular fibrous network structure (50 μm), while the surface of the Se-MCP11-a molecule modified by selenization is smoother and more delicate, and some regular grids and small circles can be seen (50 μm), which confirms that selenization modification could change the rough and irregular surface morphology of polysaccharides. In addition, the AFM images show that the height of Se-MCP11-a is higher than that of MCP11-a, indicating that the aggregation effect of Se-MCP11-a is more obvious, and selenization could increase the molecular weight and even change the biological activity [50].
Different extraction methods could change the surface structure of MCP. The SEM images showed that the BPS-J obtained by the TPP technique exhibits a large bulk structure with a relatively dense and rough surface. However, the BPS-W extracted by ultrasound extraction showed a sheet-like structure with a relatively smooth surface. In contrast, BPS-C extracted by ultrasound extraction in citric acid showed irregular, dense and relatively small structures. The BPS-A extracted by ultrasonic treatment of alkaline aqueous solution showed the appearance of small and loose block-like structures, accompanied by some cracks and holes [35]. In addition, different drying methods also have a significant effect on the MCP microstructure. SEM observation shows that the BPS-H obtained by hot air drying has many pores and a honeycomb-like ultrastructure and shows severe shrinkage. The BPS-F obtained by cold air drying has a clear porous structure and a uniform structure, which indicates that it has a positive effect on maintaining the porous cell structure. Compared with BPS-H and BPS-F, the structure of BPS-I obtained by drying by infrared radiation is dense and has no obvious porous structure [27].
Biological activities of MCPs
MCPs have rich and diverse biological activities and have been widely studied in various fields. The biological activities of MCPs include antioxidant, antidiabetes, anti-inflammatory, gastrointestinal protection, immune regulation, antiaging and neuroprotection effects.
Gastrointestinal tract protection activity
Chinese herbal medicines have been used for thousands of years in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases with remarkable curative effects [57]. Plant polysaccharides (such as Atractylodes polysaccharides, Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer polysaccharides and jujube polysaccharides), as one of the main extracts of Chinese herbal medicines, have shown extensive gastrointestinal protective effects in recent years [58, 59]. MCP also showed protective function of the gastrointestinal tract. Prophylactic administration of MCP (300 mg/kg orally) could alleviate ethanol-induced gastric ulcer injury in rats, mainly by lowering the level of inflammatory factors (MPO, TNF-α and IL-6), inhibiting oxidative stress and reducing apoptosis [60]. Ji et al. [61] found that MCP could reduce colonic edema, improve the expression of intestinal barrier proteins [occludin and zona occludens protein-1 (ZO-1)] and inhibit the intestinal inflammatory response (up-regulation of IL-10, down-regulation of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6) in mice with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D), which could provide a new strategy for the treatment of IBS-D.
Antioxidant activity
Oxidative stress is involved in the occurrence and development of many diseases, including diabetes, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease [62, 63]. Therefore, it is of great significance to find safe and effective antioxidants. MCP has obvious antioxidant properties [40, 64]. Panda et al. [53] found that MCP had an obvious effect on scavenging free radicals (EC50 = 2.22 mg/mL) and exhibited 50% lipid inhibition at a concentration of 2.05 mg/mL. In in vivo experiments, MCP at doses of 150 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg significantly increased the contents of SOD and CAT in the serum, liver and brain of mice while reducing the content of MDA in the liver and brain. MCP scavenges peroxide free radicals produced in the body and has certain antiaging and antioxidant effects [65]. Chemical modification could significantly improve the acid-pyridine method, and the P-polysaccharide was prepared by the phosphorus oxychloride-pyridine method. It was found that the anti-lipid peroxidation and superoxide anion scavenging ability of chemically modified S-MCP and P-MCP were significantly stronger than that of MCP, which provided a theoretical basis for Momordica charantia polysaccharide as a functional antioxidant food [23]. Another study [66] prepared MCP by water extraction and alcohol precipitation and obtained carboxymethylated bitter gourd polysaccharide (CM-P) and acetylated bitter gourd polysaccharide (Ac-P) through carboxymethylation and acetylation modification, respectively. It was also found that different chemical modifications could improve the antioxidant capacity of MCP to different degrees by detecting the antioxidant activity, including scavenging hydroxyl radicals, scavenging DPPH radicals and anti-lipid peroxidation.
Immunomodulatory activity
Immune regulation is the physiological function of the body to recognize and eliminate antigenic foreign bodies and maintain its own physiological stability [67]. Polysaccharides isolated from plants (such as Lentinula edodes polysaccharides and Schisandra polysaccharides) have good immunomodulatory functions [68, 69]. A study found that Astragalus polysaccharide could improve the phagocytosis of macrophages and upregulate the expression of IL-2 and IFN-γ in dendritic cells [70]. The polysaccharide of Auranthus aurantiae could stimulate the proliferation of splenocytes, enhance the phagocytosis of peritoneal macrophages, and show strong immunostimulatory activity [71].
Numerous studies have shown that MCP has immunomodulatory activity. The proliferation of splenocytes and thymocytes is a hallmark of immune activation. When the dose of MCP was 200 μg/mL, the proliferation index of splenocytes was significantly higher than that of the PBS group. Meanwhile, MCP at a dose of 25 μg/mL had the greatest activity on the proliferation of thymocytes [53]. Deng et al. [43] confirmed that M. charantia polysaccharides (MCP1 and MCP2) could effectively promote the proliferation of normal spleen lymphocytes and cona-induced spleen lymphocytes through in vitro experiments. In vivo experiments confirmed that MCP could significantly increase spleen index, thymus, NK cytotoxicity and serum hemolysin levels in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice.
Neuroprotective activity
Researchers have investigated the neuroprotective effects of MCP in different models. Gong et al. [72] first reported that MCP has neuroprotective effects in 2014, and the mechanism is to scavenge superoxide, nitric oxide, and peroxynitrite and inhibit the JNK3/c-Jun/Fas-L signaling pathway and cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Another study [73] found that MCP could protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion after stroke by increasing the activity of SIRT1, reducing the level of acetylated β-catenin, promoting the nuclear translocation of β-catenin and promoting an increase in endogenous neural stem cells. Similarly, Hu et al. [74] confirmed that MCP could promote the occurrence of neural stem cells after ischemic stroke, providing a possibility for the clinical treatment of postischemic stroke recovery. Studies have found that inflammation is involved in the development of depression, and the C-Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK) pathway is one of the inflammation-related signaling pathways involved in depression [75, 76]. In a chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) mouse model of depression, MCP could reduce the level of inflammatory factors (IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1β) in the mouse hippocampus and increase the expression of JNK-3, c-Jun, and P-110β protein expression, which indicates that MCP may improve depression-like behavior through the regulation of the JNK3/PI3K/AKT pathway [77].
Antimicrobial activity
With the continuous development of bacterial resistance, the search for greener and more efficient alternatives to antibiotics has become a new research hotspot. At present, antibiotic alternatives such as antimicrobial peptides, prebiotics, and plant extracts are emerging one after another [78, 79]. Studies have found that many plant-derived polysaccharides exhibit significant antibacterial effects. For example, some sulfated polysaccharides derived from algae showed significant antibacterial activity against dental plaque bacteria [80]. In vitro experiments showed that polysaccharides extracted from Salicornia arabica (SAPS) have a strong inhibitory effect on gram-positive bacilli [81].
MCP also showed antibacterial effects and inhibited the growth of bacteria when the concentration (MIC) was greater than 100 mg/mL but had no obvious inhibitory effect on mold and yeast [82]. It has been reported that MCP has higher antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria than gram-negative bacteria, and E. coli has a more negatively charged cell surface than Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. The balsam pear polysaccharide nanoparticles (MCP-NPs) prepared by the nanoprecipitation method exhibited stronger antibacterial activity, which prolonged the antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis [83]. Sun et al. [21] found that the EC50 values of carboxymethylated Momordica charantia polysaccharide (Yb-CMCP) were 5.35 mg/mL and 7.71 mg/mL, respectively, and the inhibition rates of Mali and C. gloeosporioides were 76.11% and 44.25%, respectively. However, Yb-CMCP had poor antifungal effects on G. graminis, F. oxysporum and A. brasicae.
Antidiabetic activity
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disease that causes elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin deficiency, insulin resistance or both [84]. With the improvement of people’s living standards and changes in lifestyle, the incidence of DM is on the rise. Studies show that 600 million people around the world will have DM by 2030 [85]. At present, the development of safe and effective drugs to treat DM has become an important research hotspot. M. charantia is well-received as a food and herbal remedy for diabetes in many regions, such as Asia, South America, and East Africa [86]. MCP, as the main component of M. charantia, exhibits a good antidiabetic effect and is a promising compound for treating DM [50, 87].
In the alloxan-induced diabetic mouse model, MCP was administered orally at doses of 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg, and 300 mg/kg. The results showed that the fasting blood glucose of the MCP group was significantly reduced, the glucose tolerance was significantly improved, and the weight was reduced when compared with the diabetic group [39]. Another animal experiment found that MCP could increase the level of SOD, reduce the level of MDA, significantly increase the antioxidant capacity of diabetic rats, and alleviate damage to the kidney and pancreas, which indicates that the hypoglycemic effect of MCP may occur through the repair of pancreatic β cells and promote antioxidant capacity [28].
As the main glucose tolerance molecule, chromium could enhance the sensitivity of pancreatic islets, accelerate the utilization of glucose, and play a role in lowering blood sugar [88]. Combining chromium and M. charantia polysaccharide MCPIIa to form a new compound, MCPII-aC, in vivo experiments confirmed that MCPII-aC could significantly reduce fasting blood sugar in diabetic mice and alleviate damage to the pancreas, liver and kidney tissue. At the same time, the effective dose of MCPIIaC is more than ten times lower than that of MCPIIa, and MCPIIaC has no toxic effect on normal mice [89]. Fermentation, as a new biogenic method, can improve the bioavailability and bioactivity of polysaccharides. Compared with nonfermented M. charantia polysaccharide (NFP), fermented M. charantia polysaccharide (FP) significantly improved hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia and oxidative stress in diabetic rats and significantly improved the diversity and abundance of the intestinal flora. This indicates that fermentation can improve the function of M. charantia polysaccharide and enhance its antidiabetic effect [90].
Anti-inflammatory activity
Polysaccharides exert anti-inflammatory effects through a variety of different mechanisms [91]. Studies have shown that MCP exerts cardioprotective effects by downregulating the expression of inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10), inflammatory markers (nitric oxide, myeloperoxidase, and inducible nitric oxide synthase) and apoptosis markers (caspase3 and BAX) [92]. Pectin polysaccharide (CCPS, pectic polysaccharide) was extracted from M. charantia to verify its effect on reproductive diseases and infertility. Studies have found that CCPS has anti-inflammatory properties and can reduce the levels of the inflammatory factors NF-κB, TNF-α and IL-6 and the expression of the apoptosis proteins Bcl-2, Caspase-3, poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) to improve the fertility of female arsenic-poisoned rats [22]. Prophylactic administration of MCP attenuates gastric injury in rats by reducing the levels of MPO, TNF-α, NF-κB, and IL-6 [61].
Other activities
In addition to the abovementioned biological activities, an increasing number of biological activities of MCP have been confirmed in recent years, including antitumor and renal protective activities, improving obesity and reducing blood lipids. Zhang et al. used transmission electron microscopy to show that MCP attenuated lesions in the pancreatic tissue of diabetic mice [42]. MCP is expected to be a drug for the treatment of diabetes by regulating β-cell regeneration [93]. MCP has an inhibitory function on HepG2 cells and HeLa cells, and the inhibitory effect of sulfated modified MCP is stronger, indicating that sulfated modification can enhance the antitumor activity of MCP [41]. Lipid lowering is another biological effect of MCP. As mentioned earlier, MCP protects against myocardial damage, and one of the mechanisms is to reduce the level of blood lipids and heart weight [92]. In addition, Lactobacillus plantarum-fermented M. charantia polysaccharide FP could improve obesity by reducing body weight and blood lipid levels and improving insulin resistance in obese rats [94]. Raish et al. [95] found that MCP could protect the kidney from hyperglycemia by inhibiting oxidative stress and improving the HO-1/Nrf2 pathway. Combining M. charantia polysaccharide (BGP) with k2PtCl4 to prepare BGP-stabilized platinum nanoclusters (Pt-BGP NCs) with good biocompatibility, further experiments found that it has peroxidase-like properties and can be used to detect ascorbic acid, which is an efficient, low-cost and reliable method for ascorbic acid detection [96]. In d-galactose-induced aging models, MCP plays an antiaging role by exerting antioxidant capacity and activating the Nrf2/β-Catenin signaling pathway [97]. The compound gel of M. charantia polysaccharide (MP1) and Whey Protein Isolate (WPI) could improve the survival rate of Lactobacillus acidophilus after freeze-drying, which has the potential to treat metabolic syndrome and is an effective probiotic packaging agent [98].
Correlation of structure and biological activity
The biological activity of plant polysaccharides is closely related to their molecular weight, chemical structure and conformation [99, 100]. In particular, the structure of polysaccharides is closely related to their biological activity. Since there are few reports on the structure-biological activity of MCPs, it is difficult to relate their biological activity to their structure. However, some scientific inferences can be made from the published literature.
In general, the higher the molecular weight of polysaccharides is, the higher their biological activity. However, this statement is not entirely true, and polysaccharides with the same structure have the best activity only in the range of appropriate molecular weights [92]. Deng et al. [43] obtained two M. charantia polysaccharides, MCP1 and MCP2, by hot water extraction, with molecular weights of 85.5 kDa and 441 kDa, respectively. An in vitro study showed that MCP1 showed stronger immunomodulatory activity than MCP2, which may be related to the increase in the chance of low molecular weight binding to the immune complex of MCP1. In another study, four polysaccharides, MCP2s-1, MCP2s-2, MCP2s-3 and MCP2s-4, had molecular weights of 9.3 kDa, 8.1 kDa, 7.8 kDa and 7.2 kDa, respectively, among which MCP2s-4 had the highest inhibitory activity on HepG2 cells at the same concentration [41]. Yan et al. [27] isolated three polysaccharide fractions (BPS-I, BPS-F, and BPS-H) from M. charantia and found that BPS-I (406 kDa) displayed more potent bile acid-binding capacity and radical-scavenging ability than MCPs BPS-F (848 kDa) and BPS-H (235 kDa), which may be because BPS-I contains more aldehydes and neutral sugars. Uronic acid exists in the molecular chains of many kinds of polysaccharides, which can change the physicochemical properties and biological activity of polysaccharides [101]. A study also found that uronic acid in MCP shows significant antioxidant activity, indicating that uronic acid may affect the antioxidant activity of MCP [53].
Structural modification is a practical method to improve the biological activity of MCPs [99]. Various technologies, including carboxymethylation, sulfonation, acetylation, phosphorylation and selenylation [102, 103]. Carboxymethylated MCP showed higher antioxidant activity than acetylated polysaccharides, which may be due to the substitution of the –OH group chain by the carboxymethyl group, which increased the reactivity and solubility of MCPs in water, resulting in corresponding changes in physical and chemical properties, conformation and primary structure [66]. Similarly, MCP showed significant antioxidant capacity in vivo, mainly due to phosphorylation modification [64]. In a diabetic mouse model, selenized polysaccharide (Se-MCPIIa-1) showed a stronger hypoglycemic effect than MCPIIa-1, with a smoother and regular surface structure [50].
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the structure–activity relationship of MCPs is conducive to the better development and utilization of related food supplements and clinical drugs. However, the relationship between the structure and biological activity of MCPs has not been widely studied, and further studies are needed to confirm these hypotheses. Meanwhile, proper chemical modification is expected to show better biological effects.
Conclusion and future perspectives
MCP, as one of the main bioactive components of M. charantia, has aroused extensive interest from researchers in optimizing its extraction and purification methods, clarifying its structure and bioactivity based on its extensive biological activities. Studies have confirmed that MCP is a water-soluble heteropolysaccharide with a molecular weight between 4 and 900 kDa. Solution extraction is the main method for the extraction of MCP, among which water extraction is the most commonly used method. Acid and alkaline extractions are more likely to damage cell walls and are more efficient than water extraction. In addition, extraction methods such as ultrasonic extraction, enzymatic extraction and enzymatic ultrasonic-assisted extraction methods are more efficient. However, the MCPs obtained by the existing extraction method still contain magazines, such as proteins and pigments, and impurities need to be removed by ultrafiltration, dialysis, and deproteinization. MCPs obtained by different extraction and purification methods have different monosaccharide compositions, structural characteristics and biological activities. Therefore, the extraction and purification methods of MCPs need to be further studied.
The structural characteristics of polysaccharides determine their biological activity. Monosaccharide composition, molecular weight, molecular shape and configuration of glycosidic bonds are the main components of polysaccharide structure. However, the current research on the structural characteristics of MCPs is mainly limited to this. Different sources of M. charantia and different extraction and purification methods lead to different structures and biological activities of the obtained MCPs. The structure–activity relationship of MCPs has not been fully elucidated, which limits their application potential. Using new techniques such as three-dimensional and high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance to determine the structure of MCPs will help to clarify the relationship between the structure and activity of MCPs.
MCPs have a variety of biological activities, including antioxidation, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antidiabetes, lipid-lowering, neuroprotection, immune regulation, and gastrointestinal protection activities. Different biological activities are interrelated. For example, MCP plays a role in protecting the gastric mucosa through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. The antioxidant and pancreatic cell repair effects of MCP are closely related to its antidiabetic effect. To clarify the effects of MCPs on human health, further studies on the efficacy and safety of MCPs in humans are necessary.
This review could provide important reference value for the extraction, purification, structural characterization and biological activity of MCPs and provide a potential basis for the application of MCPs in food and medicine. With the deepening of human research on MCPs, it is believed that MCPs will be more widely used in food, pharmaceutical and medical fields.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Gao H, Wen JJ, Hu JL, Nie QX, Chen HH, Xiong T, Nie SP, Xie MY. Fermented Momordica charantia L. juice modulates hyperglycemia, lipid profile, and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic rats. Food Res Int. 2019;121:367–78.
Fang EF, Froetscher L, Scheibye-Knudsen M, Bohr VA, Wong JH, Ng TB. Emerging antitumor activities of the bitter melon (Momordica charantia). Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(3):296–301.
Fan M, Kim EK, Choi YJ, Tang Y, Moon SH. The role of Momordica charantia in resisting obesity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(18):3251.
Bortolotti M, Mercatelli D, Polito L. Momordica charantia, a nutraceutical approach for inflammatory related diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:486.
Cortez-Navarrete M, Martínez-Abundis E, Pérez-Rubio KG, González-Ortiz M, Méndez-Del VM. Momordica charantia administration improves insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Food. 2018;21(7):672–7.
Pattarachotanant N, Prasansuklab A, Tencomnao T. Momordica charantia L. extract protects hippocampal neuronal cells against PAHs-induced neurotoxicity: possible active constituents include stigmasterol and vitamin E. Nutrients. 2021;13(7):2368.
Kim SK, Jung J, Jung JH, Yoon N, Kang SS, Roh GS, Hahm JR. Hypoglycemic efficacy and safety of Momordica charantia (bitter melon) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Complement Ther Med. 2020;52: 102524.
Jia S, Shen M, Zhang F, Xie J. Recent advances in Momordica charantia: functional components and biological activities. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(12):2555.
Grover JK, Yadav SP. Pharmacological actions and potential uses of Momordica charantia: a review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;93(1):123–32.
Mahamat O, Flora H, Tume C, Kamanyi A. Immunomodulatory activity of Momordica charantia L. (Cucurbitaceae) leaf diethyl ether and methanol extracts on salmonella typhi-infected mice and LPS-induced phagocytic activities of macrophages and neutrophils. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:5248346.
Li F, Zhao J, Wei Y, Jiao X, Li Q. Holistic review of polysaccharides isolated from pumpkin: preparation methods, structures and bioactivities. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;193(Pt A):541–52.
Luo L, Liu Y, Cai X, Wang Y, Xue J, Zhang J, Yang F. Bletilla striata polysaccharides ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in intestinal epithelial cells. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(5):302–8.
Tian X, Liang T, Liu Y, Ding G, Zhang F, Ma Z. Extraction, structural characterization, and biological functions of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides: a review. Biomolecules. 2019;9(9):389.
Kubola J, Siriamornpun S. Phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) leaf, stem and fruit fraction extracts in vitro. Food Chem. 2008;110(4):881–90.
Hou CY, Yin MS, Lan P, Wang HR, Nie H, Ji XL. Recent progress in the research of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels polysaccharides: extraction, purification, structure and bioactivities. Chem Biol Technol Agric. 2021;8(1):13.
Bora AFM, Kouame KJE, Li X, Liu L, Pan Y. New insights into the bioactive polysaccharides, proteins, and triterpenoids isolated from bitter melon (Momordica charantia) and their relevance for nutraceutical and food application: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;231: 123173.
Duan ZZ, Zhou XL, Li YH, Zhang F, Li FY, Su-Hua Q. Protection of Momordica charantia polysaccharide against intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury through JNK3 signaling pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015;35(6):523–9.
Shafie MH, Samsudin D, Yusof R, Gan CY. Characterization of bio-based plastic made from a mixture of Momordica charantia bioactive polysaccharide and choline chloride/glycerol based deep eutectic solvent. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118(Pt A):1183–92.
Ji XL, Hou CY, Shi MM, Yan YZ, Liu YQ. An insight into the research concerning Panax ginseng C. A Meyer polysaccharides: a review. Food Rev Int. 2022;38(6):1149–65.
Zhang J, Wen C, Zhang H, Duan Y. Review of isolation, structural properties, chain conformation, and bioactivities of psyllium polysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;139:409–20.
Sun X, Jin X, Pan W, Wang J. Syntheses of new rare earth complexes with carboxymethylated polysaccharides and evaluation of their in vitro antifungal activities. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;113:194–9.
Perveen H, Dey A, Nilavar NM, Chandra GK, Islam SS, Chattopadhyay S. Dietary CCPS from bitter gourd attenuates sodium arsenite induced female reproductive ailments cum infertility in wistar rats: anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic role. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019;131: 110545.
Chen F, Huang G, Yang Z, Hou Y. Antioxidant activity of Momordica charantia polysaccharide and its derivatives. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;138:673–80.
Tan HF, Gan CY. Polysaccharide with antioxidant, α-amylase inhibitory and ACE inhibitory activities from Momordica charantia. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;85:487–96.
Zhou S, Huang G. Extraction, derivatization, and antioxidant activity of Morinda citrifolia polysaccharide. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022;99(4):603–8.
Nie XR, Fu Y, Wu DT, Huang TT, Jiang Q, Zhao L, Zhang Q, Lin DR, Chen H, Qin W. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction, structural characterization, chain conformation, and biological activities of a pectic-polysaccharide from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Molecules. 2020;25(5):1155.
Yan JK, Wu LX, Qiao ZR, Cai WD, Ma H. Effect of different drying methods on the product quality and bioactive polysaccharides of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) slices. Food Chem. 2019;271:588–96.
Wang Q, Wu X, Shi F, Liu Y. Comparison of antidiabetic effects of saponins and polysaccharides from Momordica charantia L. in STZ-induced type 2 diabetic mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:744–50.
Zheng S, Zhang G, Wang H, Long Z, Wei T, Li Q. Progress in ultrasound-assisted extraction of the value-added products from microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021;37(4):71.
Qin Y, Yuan Q, Zhang Y, Li J, Zhu X, Zhao L, Wen J, Liu J, Zhao L, Zhao J. Enzyme-assisted extraction optimization, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from sea cucumber Phyllophorus proteus. Molecules. 2018;23(3):590.
Zhu Y, Li Q, Mao G, Zou Y, Feng W, Zheng D, Wang W, Zhou L, Zhang T, Yang J, Yang L, Wu X. Optimization of enzyme-assisted extraction and characterization of polysaccharides from Hericium erinaceus. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;101:606–13.
Fan T, Hu J, Fu L, Zhang L. Optimization of enzymolysis-ultrasonic assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Momordica charabtia L. by response surface methodology. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;115:701–6.
Yan JK, Wang YY, Qiu WY, Ma H, Wang ZB, Wu JY. Three-phase partitioning as an elegant and versatile platform applied to nonchromatographic bioseparation processes. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018;58(14):2416–31.
Patil SS, Bhasarkar S, Rathod VK. Extraction of curcuminoids from Curcuma longa: comparative study between batch extraction and novel three phase partitioning. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;49(4):407–18.
Yan JK, Yu YB, Wang C, Cai WD, Wu LX, Yang Y, Zhang HN. Production, physicochemical characteristics, and in vitro biological activities of polysaccharides obtained from fresh bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) via room temperature extraction techniques. Food Chem. 2021;337: 127798.
Ren Y, Bai Y, Zhang Z, Cai W, Del Rio FA. The preparation and structure analysis methods of natural polysaccharides of plants and fungi: a review of recent development. Molecules. 2019;24(17):3122.
Chen Y, Yao F, Ming K, Wang D, Hu Y, Liu J. Polysaccharides from traditional Chinese medicines: extraction, purification, modification, and biological activity. Molecules. 2016;21(12):1705.
Liu M, Liu Y, Cao MJ, Liu GM, Chen Q, Sun L, Chen H. Antibacterial activity and mechanisms of depolymerized fucoidans isolated from Laminaria japonica. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;172:294–305.
Xu X, Shan B, Liao CH, Xie JH, Wen PW, Shi JY. Anti-diabetic properties of Momordica charantia L. polysaccharide in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;81:538–43.
Liu X, Chen T, Hu Y, Li K, Yan L. Catalytic synthesis and antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide from Momordica charantia L. Biopolymers. 2014;101(3):210–5.
Guan L. Synthesis and anti-tumour activities of sulphated polysaccharide obtained from Momordica charantia. Nat Prod Res. 2012;26(14):1303–9.
Zhang C, Chen H, Bai W. Characterization of Momordica charantia L. polysaccharide and its protective effect on pancreatic cells injury in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:45–52.
Deng YY, Yi Y, Zhang LF, Zhang RF, Zhang Y, Wei ZC, Tang XJ, Zhang MW. Immunomodulatory activity and partial characterisation of polysaccharides from Momordica charantia. Molecules. 2014;19(9):13432–47.
Chen WH, Wu JJ, Li XF, Lu JM, Wu W, Sun YQ, Zhu B, Qin LP. Isolation, structural properties, bioactivities of polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale Kimura et. Migo: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;184:1000–13.
Zhang F, Lin L, Xie J. A mini-review of chemical and biological properties of polysaccharides from Momordica charantia. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;92:246–53.
Zhang X, Luo Y, Wei G, Li Y, Huang Y, Huang J, Liu C, Huang R, Liu G, Wei Z, Du S. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of the degradations of polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale and their suitable molecular weight range on inducing HeLa cell apoptosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:4127360.
Nai J, Zhang C, Shao H, Li B, Li H, Gao L, Dai M, Zhu L, Sheng H. Extraction, structure, pharmacological activities and drug carrier applications of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;183:2337–53.
Ma P, Sun C, Li W, Deng W, Adu-Frimpong M, Yu J, Xu X. Extraction and structural analysis of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide with low molecular weight and its lipid-lowering effect on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Sci Nutr. 2020;8(7):3212–24.
Cai W, Xu H, Xie L, Sun J, Sun T, Wu X, Fu Q. Purification, characterization and in vitro anticoagulant activity of polysaccharides from Gentiana scabra Bunge roots. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;140:308–13.
Ru Y, Liu K, Kong X, Li X, Shi X, Chen H. Synthesis of selenylated polysaccharides from Momordica charantia L. and its hypoglycemic activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;152:295–304.
Zhang S, Liu B, Yan G, Wu H, Han Y, Cui H. Chemical properties and anti-fatigue effect of polysaccharide from Pholiota nameko. J Food Biochem. 2022;46(1): e14015.
He M, Yang Y, Shao Z, Zhang J, Feng C, Wang L, Mao W. Chemical structure and anticoagulant property of a novel sulfated polysaccharide from the green alga Cladophora oligoclada. Mar Drugs. 2021;19(10):554.
Panda BC, Mondal S, Devi KS, Maiti TK, Khatua S, Acharya K, Islam SS. Pectic polysaccharide from the green fruits of Momordica charantia (Karela): structural characterization and study of immunoenhancing and antioxidant properties. Carbohydr Res. 2015;401:24–31.
Beaussart A, Péchoux C, Trieu-Cuot P, Hols P, Mistou MY, Dufrêne YF. Molecular mapping of the cell wall polysaccharides of the human pathogen Streptococcus agalactiae. Nanoscale. 2014;6(24):14820–7.
Fan Y, Yu Q, Wang G, Tan J, Liu S, Pu S, Chen W, Xie P, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Liao Y, Luo A. Effects of non-thermal plasma treatment on the polysaccharide from Dendrobium nobile Lindl. and its immune activities in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;153:942–50.
Gong R, Cao W, Huang H, Yu B, Chen H, Tao W, Luorong Q, Luo J, Zhang D. Antitumor potential and structure characterization of polysaccharides from Lagotis brevituba Maxim in the Tibetan plateau. Front Nutr. 2022;9: 921892.
Tan N, Gwee KA, Tack J, Zhang M, Li Y, Chen M, Xiao Y. Herbal medicine in the treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;35(4):544–56.
Wang XY, Zhang DD, Yin JY, Nie SP, Xie MY. Recent developments in Hericium erinaceus polysaccharides: extraction, purification, structural characteristics and biological activities. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S96–115.
Ji X, Hou C, Gao Y, Xue Y, Yan Y, Guo X. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota modulatory effects of jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) polysaccharides in a colorectal cancer mouse model. Food Funct. 2020;11(1):163–73.
Raish M, Ahmad A, Ansari MA, Alkharfy KM, Aljenoobi FI, Jan BL, Al-Mohizea AM, Khan A, Ali N. Momordica charantia polysaccharides ameliorate oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in ethanol-induced gastritis in mucosa through NF-kB signaling pathway inhibition. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;111:193–9.
Ji S, Zhang Q. Momordica charantia polysaccharides alleviate diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome by regulating intestinal inflammation and barrier via NF-κB pathway. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2022;50(3):62–70.
Forman HJ, Zhang H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(9):689–709.
Kopa PN, Pawliczak R. IQOS—a heat-not-burn (HnB) tobacco product—chemical composition and possible impact on oxidative stress and inflammatory response. A systematic review. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2020;30(2):81–7.
Chen F, Huang G, Huang H. Preparation, analysis, antioxidant activities in vivo of phosphorylated polysaccharide from Momordica charantia. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;252: 117179.
Huang H, Chen F, Long R, Huang G. The antioxidant activities in vivo of bitter gourd polysaccharide. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;145:141–4.
Chen F, Huang G. Extraction, derivatization and antioxidant activity of bitter gourd polysaccharide. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;141:14–20.
Mayer A, Zhang Y, Perelson AS, Wingreen NS. Regulation of T cell expansion by antigen presentation dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116(13):5914–9.
Yu J, Cong L, Wang C, Li H, Zhang C, Guan X, Liu P, Xie Y, Chen J, Sun J. Immunomodulatory effect of Schisandra polysaccharides in cyclophosphamide-induced immunocompromised mice. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6):4755–62.
Roszczyk A, Turło J, Zagożdżon R, Kaleta B. Immunomodulatory properties of polysaccharides from lentinula edodes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(16):8980.
Zhang W, Ma W, Zhang J, Song X, Sun W, Fan Y. The immunoregulatory activities of astragalus polysaccharide liposome on macrophages and dendritic cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;105(Pt 1):852–61.
Wang M, Jiang C, Ma L, Zhang Z, Cao L, Liu J, Zeng X. Preparation, preliminary characterization and immunostimulatory activity of polysaccharide fractions from the peduncles of Hovenia dulcis. Food Chem. 2013;138(1):41–7.
Gong J, Sun F, Li Y, Zhou X, Duan Z, Duan F, Zhao L, Chen H, Qi S, Shen J. Momordica charantia polysaccharides could protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting oxidative stress mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology. 2015;91:123–34.
Ma J, Fan H, Cai H, Hu Z, Zhou X, Li F, Chen H, Shen J, Qi S. Promotion of Momordica charantia polysaccharides on neural stem cell proliferation by increasing SIRT1 activity after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Brain Res Bull. 2021;170:254–63.
Hu Z, Li F, Zhou X, Zhang F, Huang L, Gu B, Shen J, Qi S. Momordica charantia polysaccharides modulate the differentiation of neural stem cells via SIRT1/Β-catenin axis in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):485.
Lopresti AL, Hood SD, Drummond PD. Multiple antidepressant potential modes of action of curcumin: a review of its anti-inflammatory, monoaminergic, antioxidant, immune-modulating and neuroprotective effects. J Psychopharmacol. 2012;26(12):1512–24.
Zhang J, Lin W, Tang M, Zhao Y, Zhang K, Wang X, Li Y. Inhibition of JNK ameliorates depressive-like behaviors and reduces the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the phosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptors at serine 246 induced by neuroinflammation. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020;113: 104580.
Deng Z, Yuan C, Yang J, Peng Y, Wang W, Wang Y, Gao W. Behavioral defects induced by chronic social defeat stress are protected by Momordica charantia polysaccharides via attenuation of JNK3/PI3K/AKT neuroinflammatory pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(1):6.
Boparai JK, Sharma PK. Mini review on antimicrobial peptides, sources, mechanism and recent applications. Protein Pept Lett. 2020;27(1):4–16.
Maisetta G, Batoni G, Caboni P, Esin S, Rinaldi AC, Zucca P. Tannin profile, antioxidant properties, and antimicrobial activity of extracts from two Mediterranean species of parasitic plant Cytinus. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):82.
Jun JY, Jung MJ, Jeong IH, Yamazaki K, Kawai Y, Kim BM. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae against dental plaque bacteria. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(9):301.
Hammami N, Gara AB, Bargougui K, Ayedi H, Abdalleh FB, Belghith K. Improved in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial capacities of polysaccharides isolated from Salicornia arabica. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120(Pt B):2123–30.
Zhang PP, Liu JF, Wang CL, Ye YT, Xie JH. Study on the antimicrobial activities of the extracts from Momordica charantia L. Nat Prod Res Dev. 2008;20(4):721–4.
Qin Y, Xiong L, Li M, Liu J, Wu H, Qiu H, Mu H, Xu X, Sun Q. Preparation of bioactive polysaccharide nanoparticles with enhanced radical scavenging activity and antimicrobial activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66(17):4373–83.
Ji XL, Guo JH, Cao TZ, Zhang TT, Liu YQ, Yan YZ. Review on mechanisms and structure-activity relationship of hypoglycemic effects of polysaccharides from natural resources. Food Sci Hum Well. 2023;12(6):1969–80.
Wang PC, Zhao S, Yang BY, Wang QH, Kuang HX. Anti-diabetic polysaccharides from natural sources: a review. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;148:86–97.
Dandawate PR, Subramaniam D, Padhye SB, Anant S. Bitter melon: a panacea for inflammation and cancer. Chin J Nat Med. 2016;14(2):81–100.
Bai W, Zhang C, Chen H. Transcriptomic analysis of Momordica charantia polysaccharide on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Gene. 2018;675:208–16.
Peng M, Yang X. Controlling diabetes by chromium complexes: the role of the ligands. J Inorg Biochem. 2015;146:97–103.
Zhang C, Huang M, Hong R, Chen H. Preparation of a Momordica charantia L. polysaccharide-chromium (III) complex and its anti-hyperglycemic activity in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;122:619–27.
Gao H, Wen JJ, Hu JL, Nie QX, Chen HH, Xiong T, Nie SP, Xie MY. Polysaccharide from fermented Momordica charantia L. with Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 ameliorates type 2 diabetes in rats. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;201:624–33.
Hou C, Chen L, Yang L, Ji X. An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of natural polysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;153:248–55.
Raish M. Momordica charantia polysaccharides ameliorate oxidative stress, hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and apoptosis during myocardial infarction by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;97:544–51.
Sajadimajd S, Mohammadi B, Bahrami G, Madani SH, Hatami R, Miraghaee SS. Modulation of Notch signaling and angiogenesis via an isolated polysaccharide from Momordica charantia in diabetic rats. J Food Biochem. 2022;46(2): e14033.
Wen JJ, Gao H, Hu JL, Nie QX, Chen HH, Xiong T, Nie SP, Xie MY. Polysaccharides from fermented Momordica charantia ameliorate obesity in high-fat induced obese rats. Food Funct. 2019;10(1):448–57.
Raish M, Ahmad A, Jan BL, Alkharfy KM, Ansari MA, Mohsin K, Jenoobi FA, Al-Mohizea A. Momordica charantia polysaccharides mitigate the progression of STZ induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;91:394–9.
Liu K, Zhao Y, Zhang L, He M, Lin W, Sun H, Liu Z, Hu J, Wang L. Biocompatible platinum nanoclusters prepared using bitter gourd polysaccharide for colorimetric detection of ascorbic acid. Biomolecules. 2021;11(5):647.
Yue J, Guo P, Jin Y, Li M, Hu X, Wang W, Wei X, Qi S. Momordica charantia polysaccharide ameliorates d-galactose-induced aging through the Nrf2/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Metab Brain Dis. 2023;38(3):1067–77.
Bora AFM, Kouame KJE, Li X, Liu L, Sun Y, Ma Q, Liu Y. Development, characterization and probiotic encapsulating ability of novel Momordica charantia bioactive polysaccharides/whey protein isolate composite gels. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;225:454–66.
Ji XL, Peng BX, Ding HH, Cui BB, Nie H, Yan YZ. Purification, structure and biological activity of pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) polysaccharides: a review. Food Rev Int. 2023;39(1):307–19.
Zhang Y, Wang C, Liu C, Wang X, Chen B, Yao L, Qiao Y, Zheng H. Recent developments in stigma maydis polysaccharides: isolation, structural characteristics, biological activities and industrial application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;150:246–52.
Liu B, Liu H, Ai C, Zhu Z, Wen C, Song S, Zhu B. Distribution of uronic acid-containing polysaccharides in 5 species of shellfishes. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;164:195–9.
Yang M, Ren W, Li G, Yang P, Chen R, He H. The effect of structure and preparation method on the bioactivity of polysaccharides from plants and fungi. Food Funct. 2022;13(24):12541–60.
Yu W, Ren Z, Zhang X, Xing S, Tao S, Liu C, Wei G, Yuan Y, Lei Z. Structural characterization of polysaccharides from dendrobium officinale and their effects on apoptosis of HeLa cell line. Molecules. 2018;23(10):2484.
Acknowledgements
Kai Zhan, Lei Luo and Xiaolong Ji would like to acknowledge the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (Grant No. 212300410297) and Star Maker Space Project of Zhengzhou University of Light Industry (2021ZCKJ205) for supporting this study.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (Grant No. 212300410297) and the Star Maker Space Project of Zhengzhou University of Light Industry (2021ZCKJ205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KZ, writing and editing. LL, writing—reviewing and editing. XJ, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, K., Ji, X. & Luo, L. Recent progress in research on Momordica charantia polysaccharides: extraction, purification, structural characteristics and bioactivities. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 10, 58 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-023-00433-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-023-00433-4